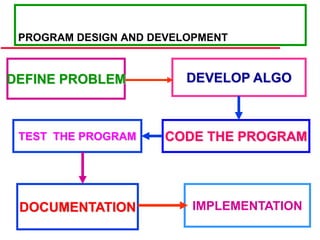
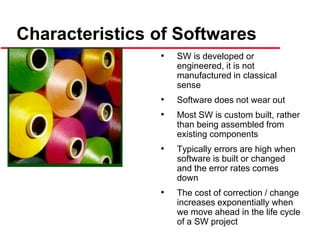
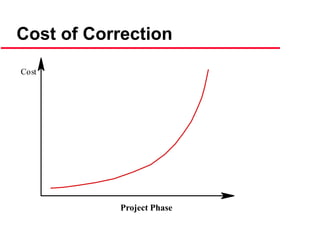
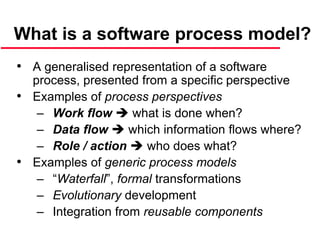
This document provides an introduction to software engineering. It outlines the objectives of software engineering as introducing the field, explaining its importance, and addressing ethical issues. It then discusses key concepts like the software development lifecycle, characteristics of well-engineered software, software costs which often exceed hardware costs, and challenges facing software engineering like coping with legacy systems and demands for faster delivery. Common software problems are also outlined such as high costs, late or failed projects, poor performance, and software being difficult to use or maintain.