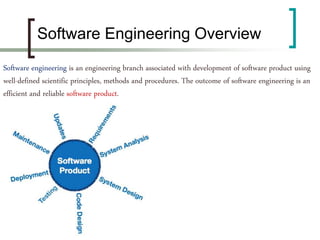
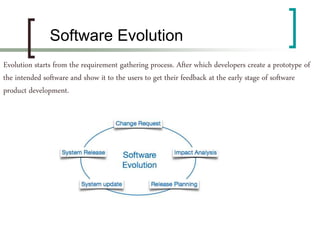
This document provides an overview of software engineering. It begins by defining software engineering as the application of engineering principles and methods to the development of software. It then discusses some key aspects of software engineering like the software development life cycle, software project management, and paradigms. Finally, it outlines some important characteristics of good software like usability, efficiency, correctness, portability and maintainability.