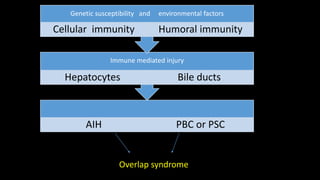
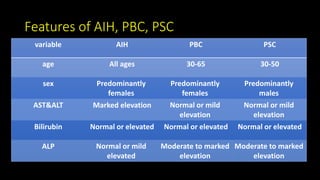
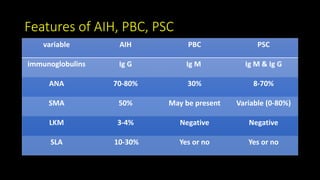
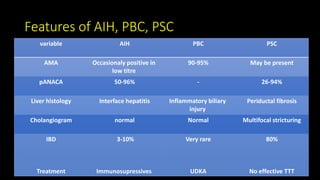
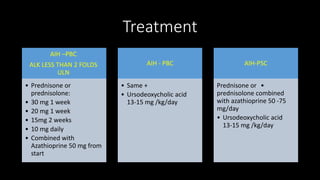
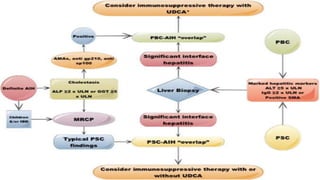
This document discusses overlap syndromes, specifically hepatic overlap syndromes where a patient presents with features of both autoimmune hepatitis (AIH) and primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) or primary sclerosing cholangitis (PSC). It provides details on the proposed explanations for overlap syndromes, features that distinguish AIH, PBC and PSC, criteria for diagnosing AIH-PBC and AIH-PSC overlap syndromes, treatment recommendations, and practical points regarding implications for prognosis and management depending on the underlying conditions.