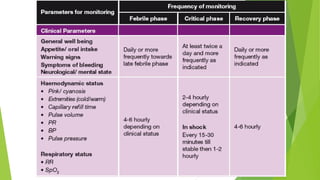
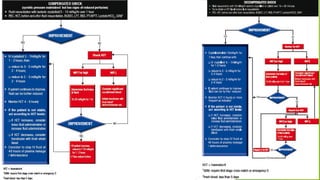
The document provides information on Dengue Fever, including that it is caused by a mosquito-borne flavivirus transmitted by Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes. It has four serotypes that provide varying levels of immunity. Symptoms include fever, headache, rash and bleeding. Diagnosis involves antibody and viral testing. Severe dengue is classified as dengue hemorrhagic fever or dengue shock syndrome, characterized by bleeding, low platelets and plasma leakage. Monitoring of patients involves serial complete blood counts and hematocrit levels to detect signs of plasma leakage. Proper fluid management and monitoring for bleeding and organ dysfunction is important throughout the illness.







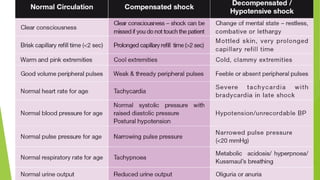
![WHO (1999) CASE DEFINITION FOR DENGUE
SHOCK SYNDROME
All of the above four criteria for DHF must be present, plus
evidence of circulatory failure manifested by :
Rapid and weak pulse, and
Narrow pulse pressure [<20mmHg (2.7 kPa)]
OR manifested by :
Hypotension for age, and
Cold, clammy skin and restlessness.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/dengue-140316063751-phpapp02/85/Dengue-CPG-Summary-8-320.jpg)