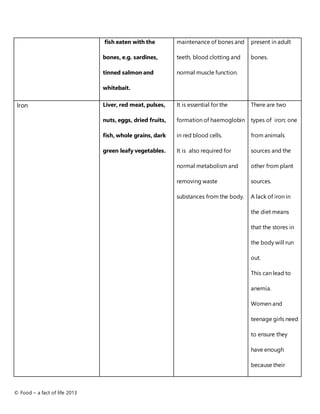
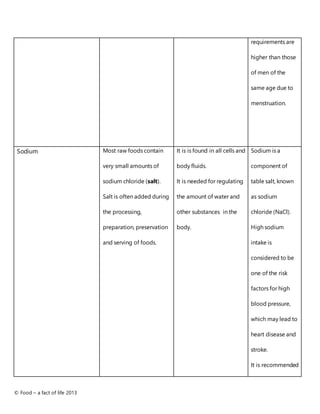
This document provides information about important nutrients including macronutrients like carbohydrates, protein, and fat as well as micronutrients like vitamins and minerals. It lists common food sources of each nutrient and their main functions in the body. For example, it states that carbohydrates from foods like fruits, vegetables and grains provide an important source of energy, while proteins from animal and plant foods are essential for growth and repair. The document also notes vitamins and minerals needed for bone health, immune function, energy production and more.