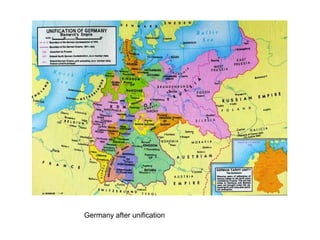
Otto von Bismarck was a Prussian statesman who served as Chancellor of Germany from 1871 to 1890. He came from a noble Prussian family and studied law. Through a series of wars in the 1860s, Bismarck helped Prussia defeat Denmark, Austria, and France to unite Germany under Prussian leadership. He orchestrated the unification of Germany in 1871 and served as its first Chancellor. Bismarck introduced Germany's social welfare state in the 1880s to counter socialists. He retired in 1890 and spent his final years in Friedrichsruh, where he died in 1898.