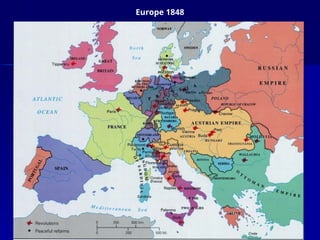
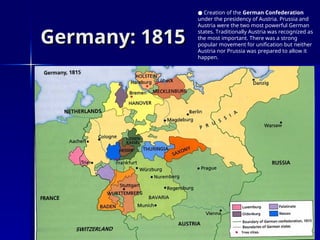
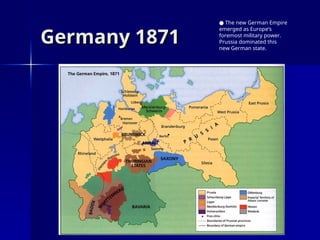
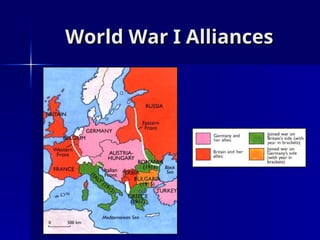
The document discusses the unification of Germany in the 19th century, detailing the rise of Otto von Bismarck and his realpolitik strategies which led to three wars for unification: the Austro-Prussian War, the Franco-Prussian War, and the establishment of the German Empire in 1871. It outlines the political structure of the newly formed empire, dominated by Prussia, and Bismarck's subsequent campaigns against the Catholic Church and socialist movements to maintain order. The document concludes with Bismarck's foreign alliances and the eventual dismissal by Kaiser William II, leading to shifting alliances that contributed to the outbreak of World War I.