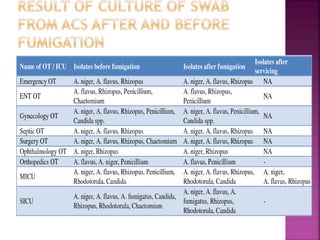
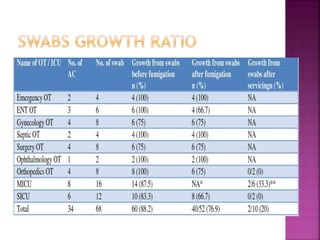
Fumigation is a process used to sterilize operating theaters and other hospital areas using formaldehyde gas. It involves cleaning the area, sealing it, and heating a formaldehyde solution to generate gaseous formaldehyde. The gas kills microbes but is toxic, so protective equipment must be worn. After 12-24 hours, ammonia is released to neutralize the formaldehyde. A record of all fumigation details must be maintained. Several other toxic gases can also be used for fumigation but require special precautions due to their strong potency. Exposure to fumigation gases usually causes immediate side effects that are treated by inducing vomiting and giving medications to reduce the chemical concentration in the body.