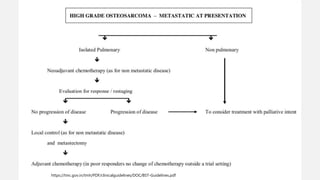
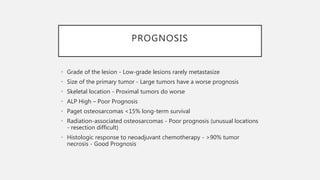
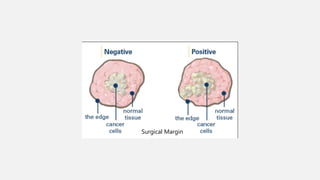
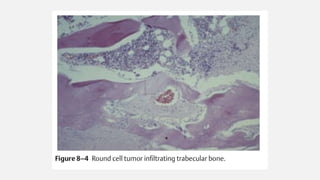
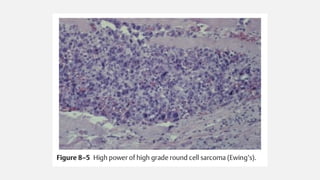
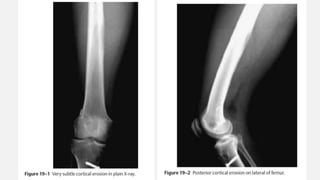
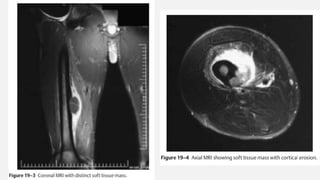
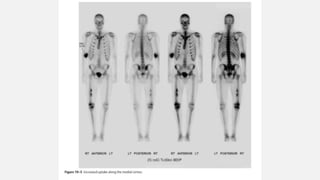
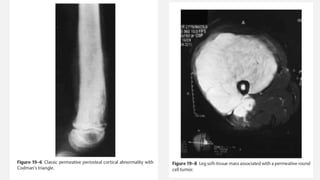
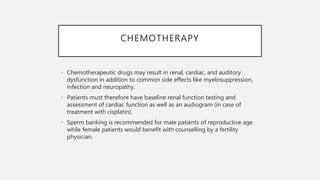
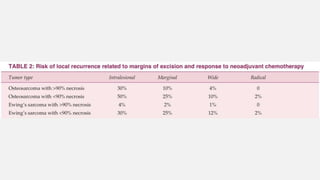
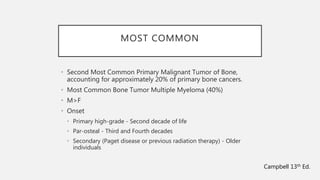
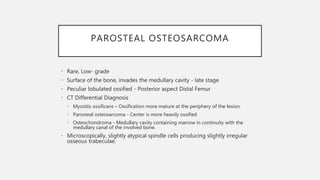
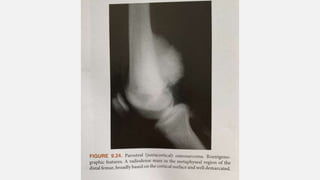
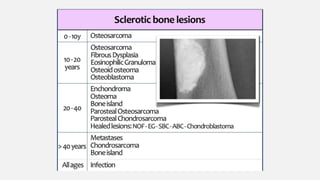
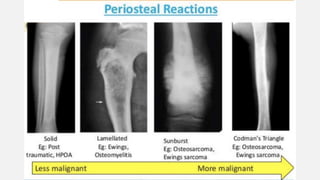
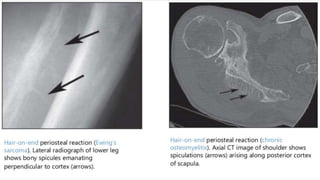
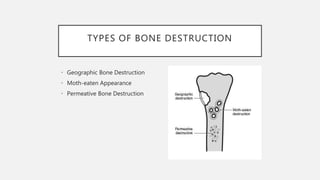
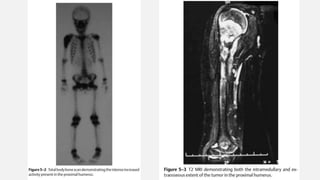
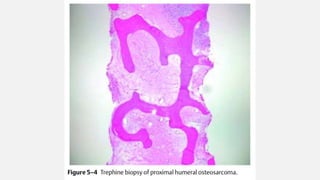
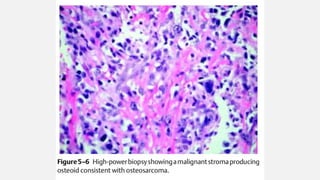
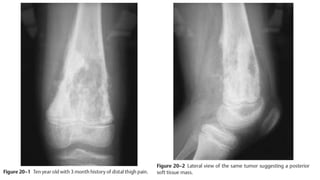
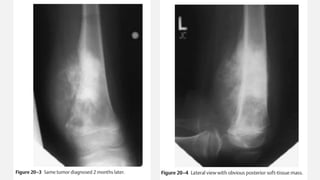
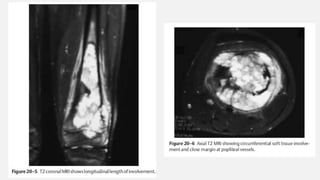
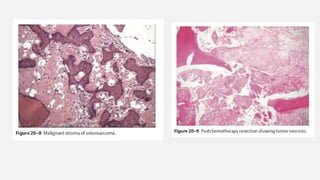
This document provides an overview of osteosarcoma and Ewing's sarcoma, including their genetic basis, clinical presentation, radiological findings, biopsy, management, and prognosis. Osteosarcoma is the second most common primary bone cancer and most commonly affects the metaphysis of long bones in adolescents and young adults. Presentation includes pain, swelling, and sometimes pathological fractures. Diagnosis involves imaging such as X-ray, CT, MRI and biopsy. Treatment typically involves neoadjuvant chemotherapy, surgical resection with wide margins, and additional chemotherapy. Prognosis depends on stage and response to treatment, with 5-year survival rates ranging from 60-80% for localized disease.


















![NCCN AND ESMO-PAEDCAN-EURACAN
CLINICAL PRACTICE GUIDELINES FOR
TREATMENT OF OSTEOSARCOMA
• Guidelines for the treatment of osteosarcoma have been published by
the following organizations:
• National Comprehensive Cancer Network (NCCN) [30]
• European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO), European Reference
Network for Paediatric Cancers (PaedCan), and European Network for
Rare Adult Solid Cancer (EURACAN) [31]
• Guideline recommendations on treatment of osteosarcoma vary by
disease stage.](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/osteosarcomaewings-200228154417/85/Osteosarcoma-Ewings-53-320.jpg)
![STAGES IA-IB (LOW GRADE)
OSTEOSARCOMAS
• Localized, low-grade osteosarcomas – The NCCN recommends wide excision
alone; chemotherapy prior to excision is not typically recommended but
could be considered for periosteal lesions
• Low-grade intramedullary and surface osteosarcoma and periosteal
sarcomas with pathological findings of high-grade disease – The NCCN
recommends postoperative chemotherapy [30] ; ESMO-PaedCan-EURACAN
recommends surgery alone for low-grade parosteal osteosarcomas, and
finds no benefit for chemotherapy for periosteal lesions
• Unresectable or incompletely resected osteosarcoma – The NCCN and
ESMO-PaedCan-EURACAN guidelines concur that combined photon/proton
or proton beam radiotherapy for local control is an option](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/osteosarcomaewings-200228154417/85/Osteosarcoma-Ewings-54-320.jpg)



![CHEMOTHERAPY REGIMENS
• For first-line osteosarcoma therapy (primary/neoadjuvant/adjuvant
therapy or for metastatic disease), NCCN recommendations are as
follows [30] :
• Cisplatin and doxorubicin (category 1)
• MAP (high-dose methotrexate, cisplatin, and doxorubicin) (category 1)
• Doxorubicin, cisplatin, ifosfamide, and high-dose methotrexate
• Ifosfamide, cisplatin, and epirubicin](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/osteosarcomaewings-200228154417/85/Osteosarcoma-Ewings-58-320.jpg)
![CHEMOTHERAPY REGIMENS
• For second-line therapy
(relapsed/refractory or metastatic
disease), NCCN recommendations are
as follows [30] :
• Docetaxel and gemcitabine
• Cyclophosphamide and etoposide
• Cyclophosphamide and topotecan
• Gemcitabine
• Ifosfamide (high dose) ± etoposide
• Ifosfamide, carboplatin, and
etoposide
• High-dose methotrexate, etoposide,
and ifosfamide
• Samarium-153 ethylene diamine
tetramethylene phosphonate (SM-
EDTMP) for relapsed or refractory
disease beyond second-line therapy
• Radium-223
• Sorafenib](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/osteosarcomaewings-200228154417/85/Osteosarcoma-Ewings-59-320.jpg)