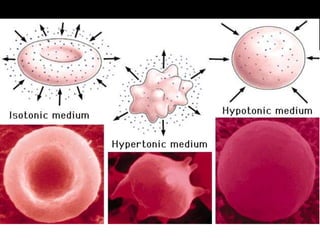
Cells control what enters and leaves through the cell membrane. Diffusion occurs when molecules move from areas of higher concentration to lower concentration until concentrations are equalized. Osmosis is the diffusion of water through the semipermeable cell membrane. In hypertonic solutions, cells shrink as water diffuses out. In hypotonic solutions, cells swell as water diffuses in. In isotonic solutions, there is no net water movement as concentrations are balanced.