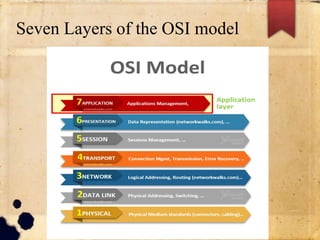
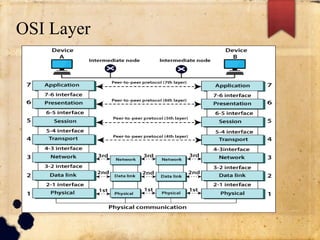
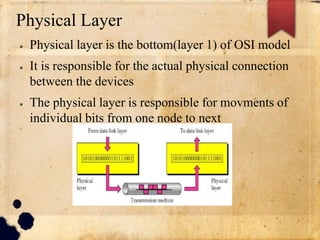
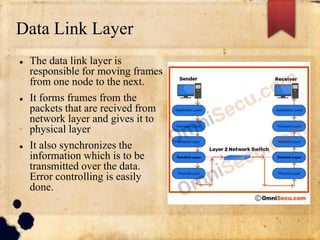
The document discusses the OSI and TCP/IP models for networking. It describes the seven layers of the OSI model and the functions of each layer, with a focus on the physical and data link layers. The physical layer is responsible for the actual connection and transmission of bits between devices, while the data link layer forms frames from packets and handles error control and synchronization of data being transmitted. The overall purpose is to break down the communication process into layers to reduce complexity and allow different systems to communicate.