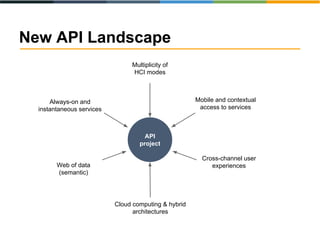
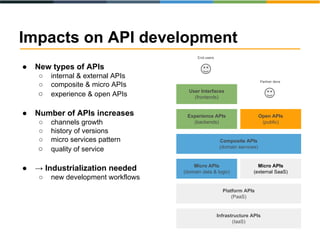
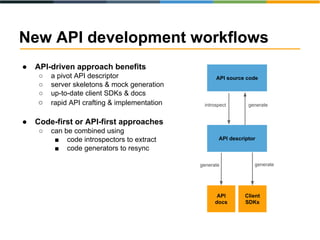
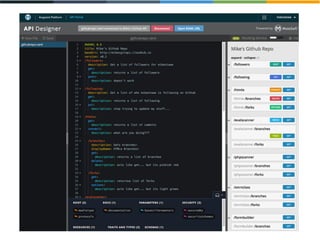
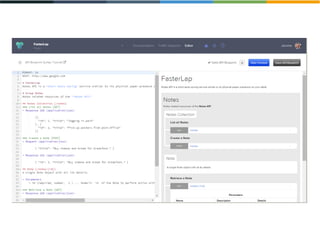
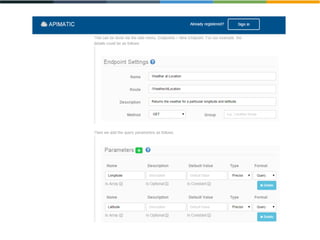
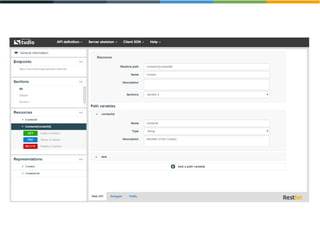
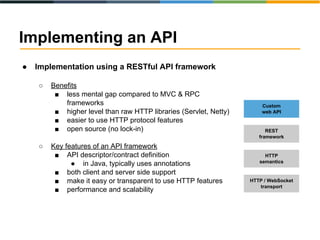
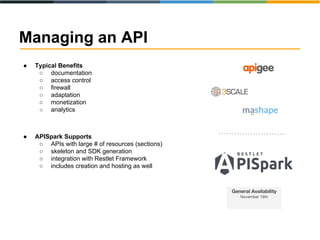
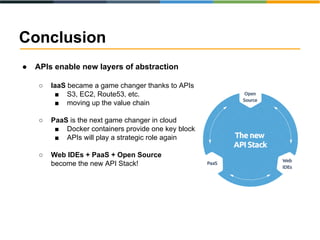
The document discusses the evolving landscape of APIs, highlighting the emergence of various types such as micro and experience APIs, and the increasing number and complexity of interfaces driven by cloud computing and hybrid architectures. It emphasizes the need for industrialized workflows in API development to facilitate faster and more efficient crafting and implementation. Additionally, it outlines the benefits of using RESTful API frameworks and PaaS solutions for deployment, management, and scalability, ultimately positioning APIs as crucial tools for enabling higher-level abstraction in technology.