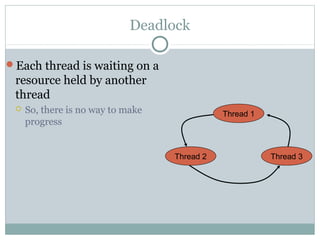
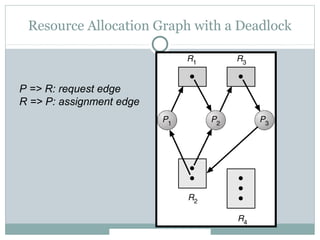
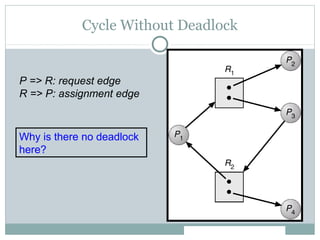
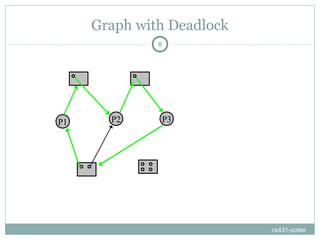
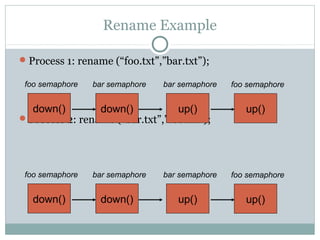
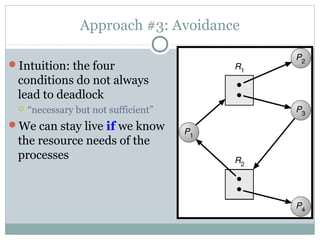
Deadlock occurs when threads are waiting on resources held by other threads, creating a circular dependency where no progress can be made. There are four necessary conditions for deadlock: mutual exclusion, hold and wait, no preemption, and circular wait. Approaches to dealing with deadlock include avoidance, prevention, and detection/recovery. Prevention methods aim to break one of the four conditions, such as enforcing a fixed locking order to prevent circular waits. Avoidance uses algorithms like the bankers algorithm to ensure the resource graph remains reducible. Detection finds cycles in the resource graph to identify deadlocks.