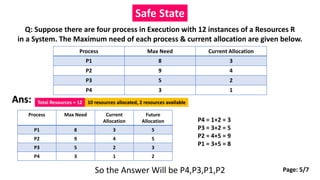
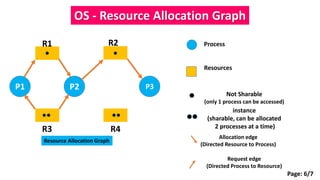
This document summarizes key concepts related to deadlock avoidance in operating systems. It discusses the four conditions for deadlock, describes the concept of a safe state for resource allocation, and provides an example of modeling resource allocation using a resource allocation graph. The document is presented as part of a course on operating systems, covering topics such as deadlock avoidance, safe state determination, and modeling resource allocation through graphs.