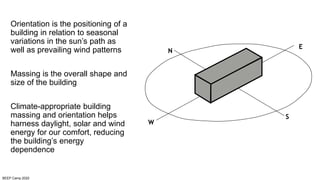
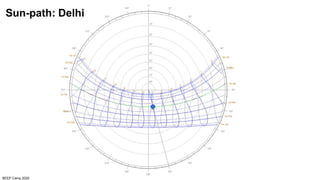
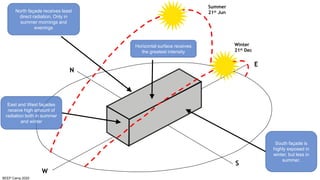
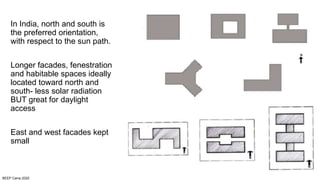
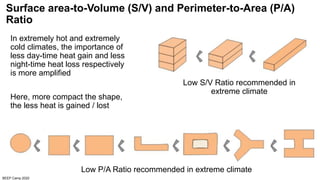
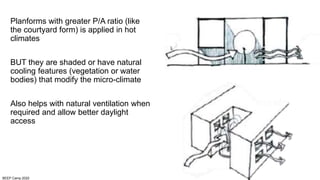
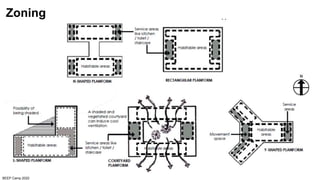
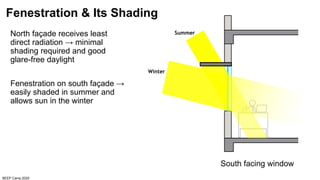
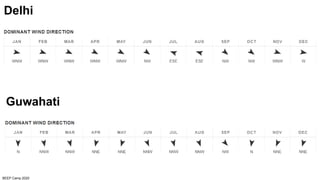
The document discusses the importance of proper building orientation and massing for energy efficiency. It explains that orientation should consider the sun path to minimize solar gains in summer and maximize gains in winter, while massing should reduce surface area to volume ratio to minimize heat transfer. Specific guidelines are provided for orientation in India, with longer facades facing north and south for daylight access while limiting east and west exposures. Massing and fenestration design must also account for solar angles and shading needs to harness daylight while avoiding overheating. Balancing orientation for sun and wind access may require angled positioning rather than strict cardinal directions.