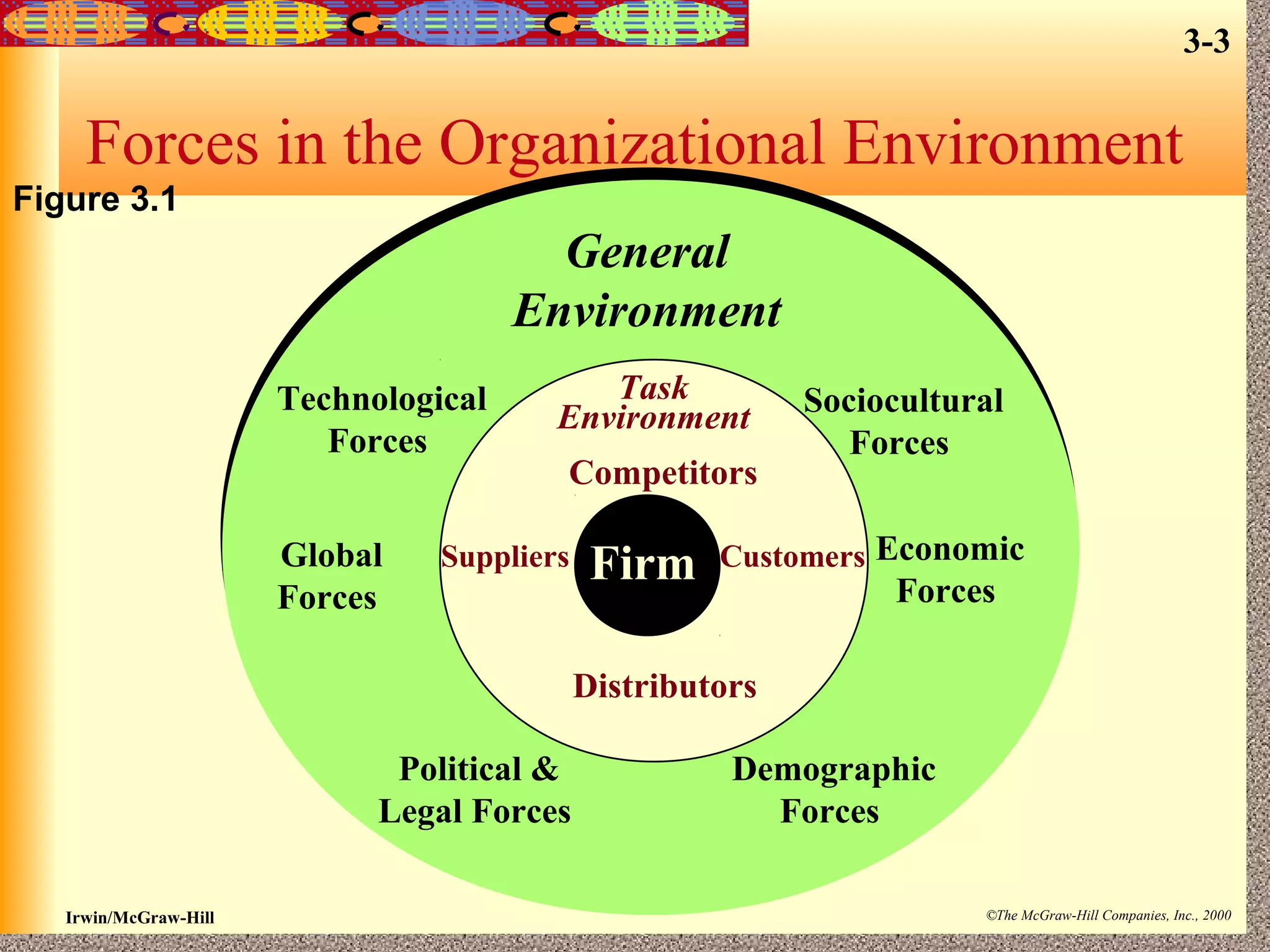
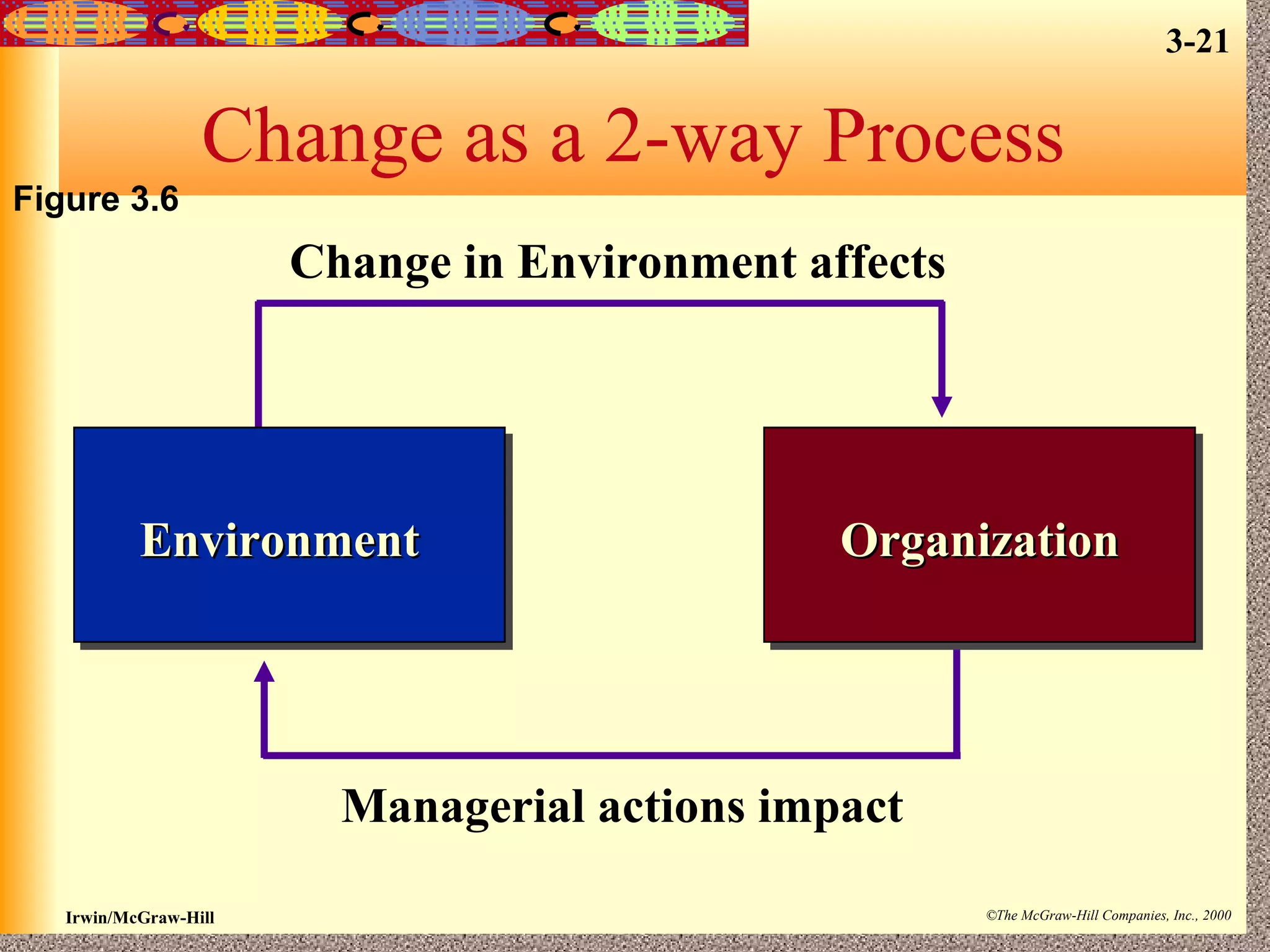
The document discusses an organization's environmental forces and how managers can address them. An organization's environment consists of task environment forces from suppliers, distributors, customers and competitors as well as general forces like economic, technological and demographic trends. Managers must assess the complexity of these forces and rate of change to understand threats and opportunities. They can implement strategies like boundary spanning, scanning the environment, and creating structures to adapt to different conditions in the organizational environment.