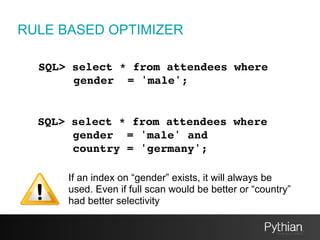
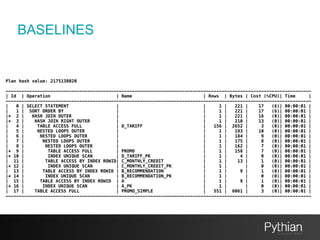
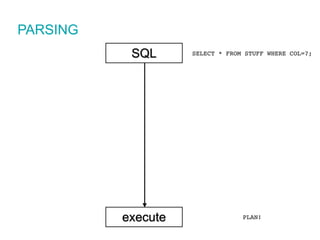
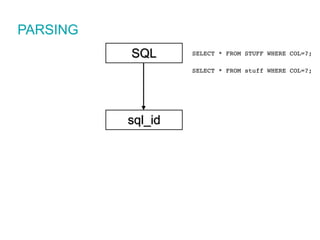
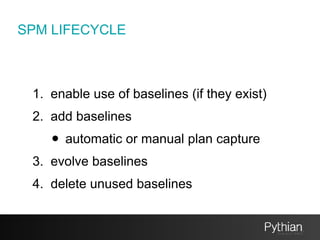
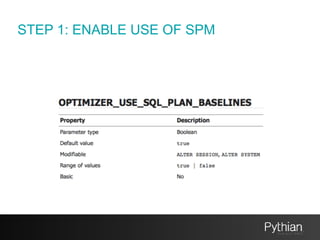
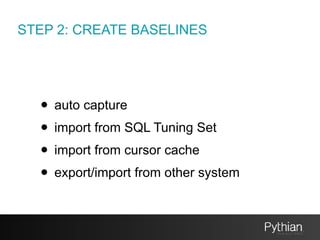
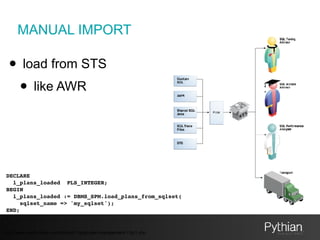
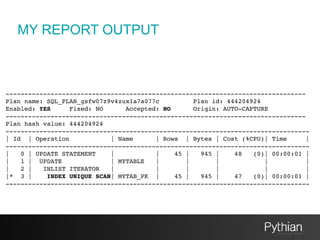
The document discusses SQL tuning with SQL Plan Management (SPM), focusing on improving execution plan stability in Oracle databases. It outlines the evolution from a Rule-Based Optimizer (RBO) to a Cost-Based Optimizer (CBO), emphasizing the challenges of unpredictable execution plans under CBO and how SPM can mitigate these issues. The presentation also details the goals, implementation processes, and lifecycle management of SPM to enhance SQL performance in operational contexts.




















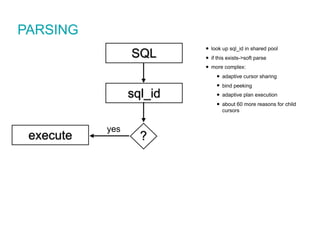
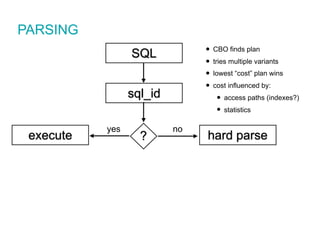
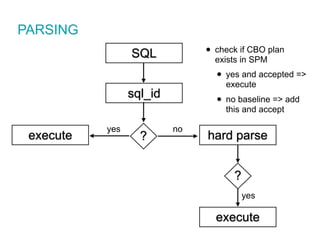
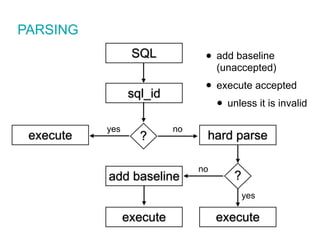

















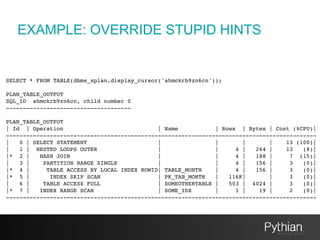
![CREATE OR REPLACE VIEW "SOME"."VIEW" ("COL1","COL2","COL3")
AS SELECT /*+ use_hash(c, tc) */
[...]
FROM SOME.TAB1_monat c
JOIN SOME.TAB2 tc
ON
tc.col42 = c.col23
LEFT JOIN SOME.TAB3 vp
ON
vp.col1 = c.col2
EXAMPLE: OVERRIDE STUPID HINTS](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/spm-161031054419/85/Oracle-SQL-tuning-with-SQL-Plan-Management-59-320.jpg)