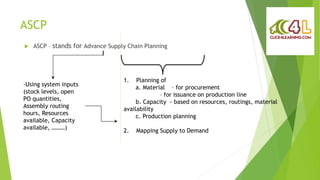
This document provides an overview of an ASCP training session on Oracle's Advanced Supply Chain Planning solution. It discusses:
1) The basics of ASCP, including planning materials, capacity, and production to map supply to demand.
2) Key terms used in ASCP like purchase orders, work orders, routings, and resources.
3) An implementation of ASCP for a machining center to improve scheduling and capacity planning across 21 machines and over 150 SKUs.
4) The steps required to properly set up the planning environment in ASCP, including cleaning up old data, maintaining accurate item masters, and entering material and resource constraints.





![Planning Cycle
Planning Cycle: Planners perform end-to-end planning flow during the
course of planning cycle. The flow demonstrates the key features of
Oracle ASCP that a typical planner would use in the course of their
work.
STEP 1: Various sources of demand are as below:
STEP 2: Run collections to bring planning data from the source instance to
the planning server, where the data will be accessible to Oracle ASCP.
STEP 3: After an MDS has been defined, a Production, Manufacturing, or
Distribution plan/schedule can be created.
STEP 4: After you have created your MRP, MPS, or MPP plan/schedule and
saved it, choose the plan from [Production, Manufacturing, or Distribution
Plan] > Names and select Launch Plan.
STEP 5: Review Key Performance Indicators (KPIs)](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/ascptraining-sarita-171121132539/85/Oracle-ASCP-Training-7-320.jpg)






