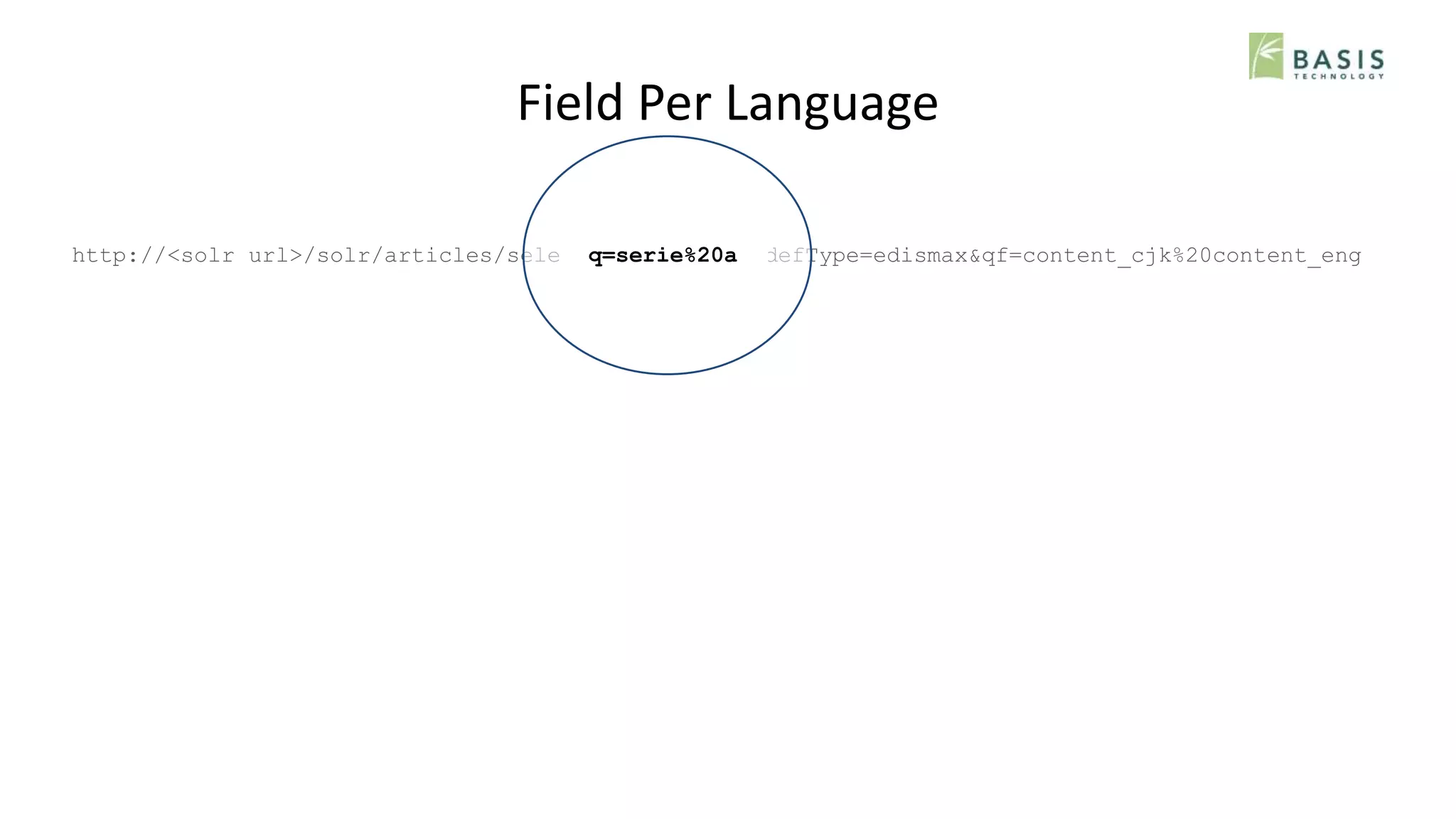
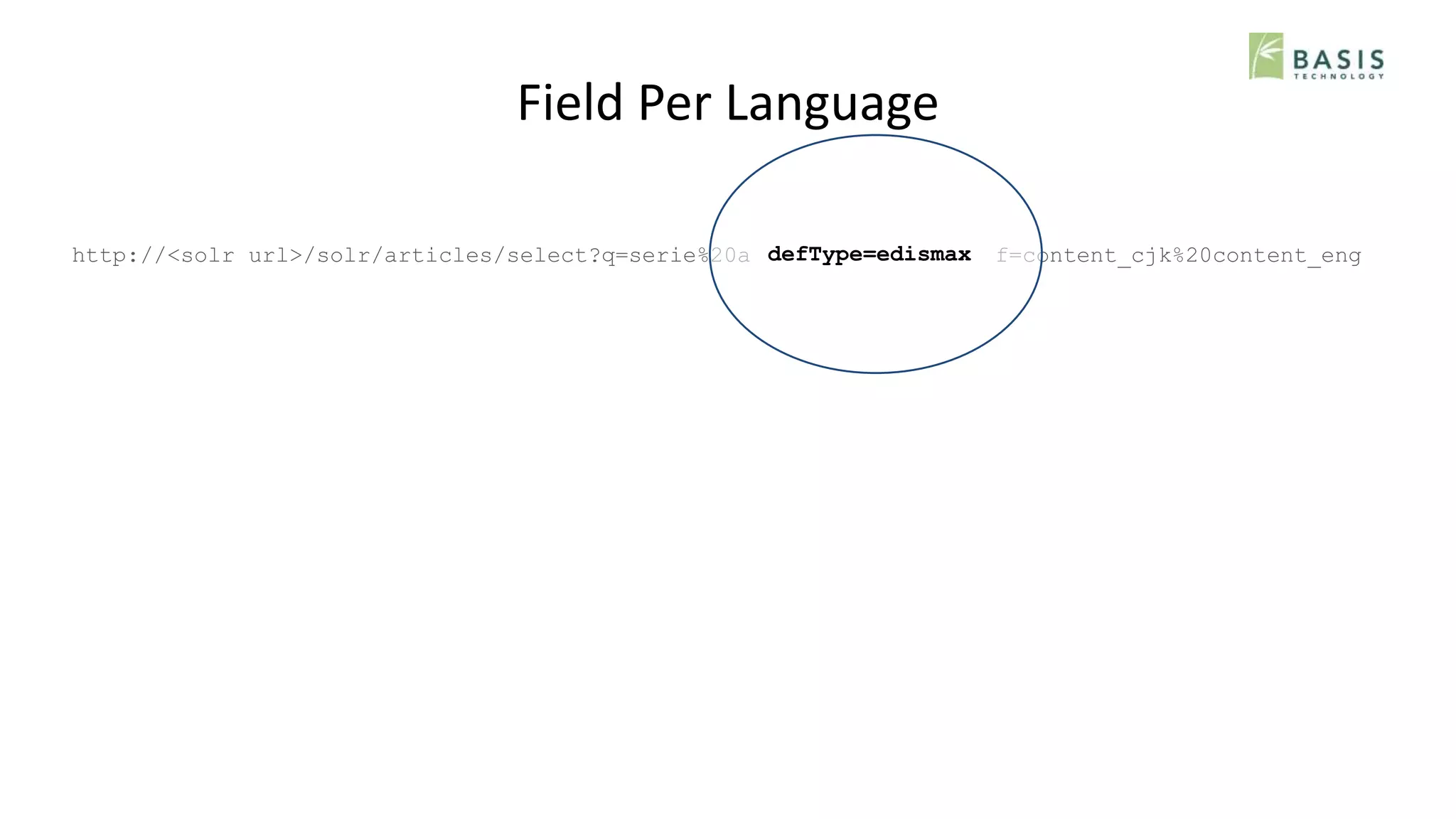
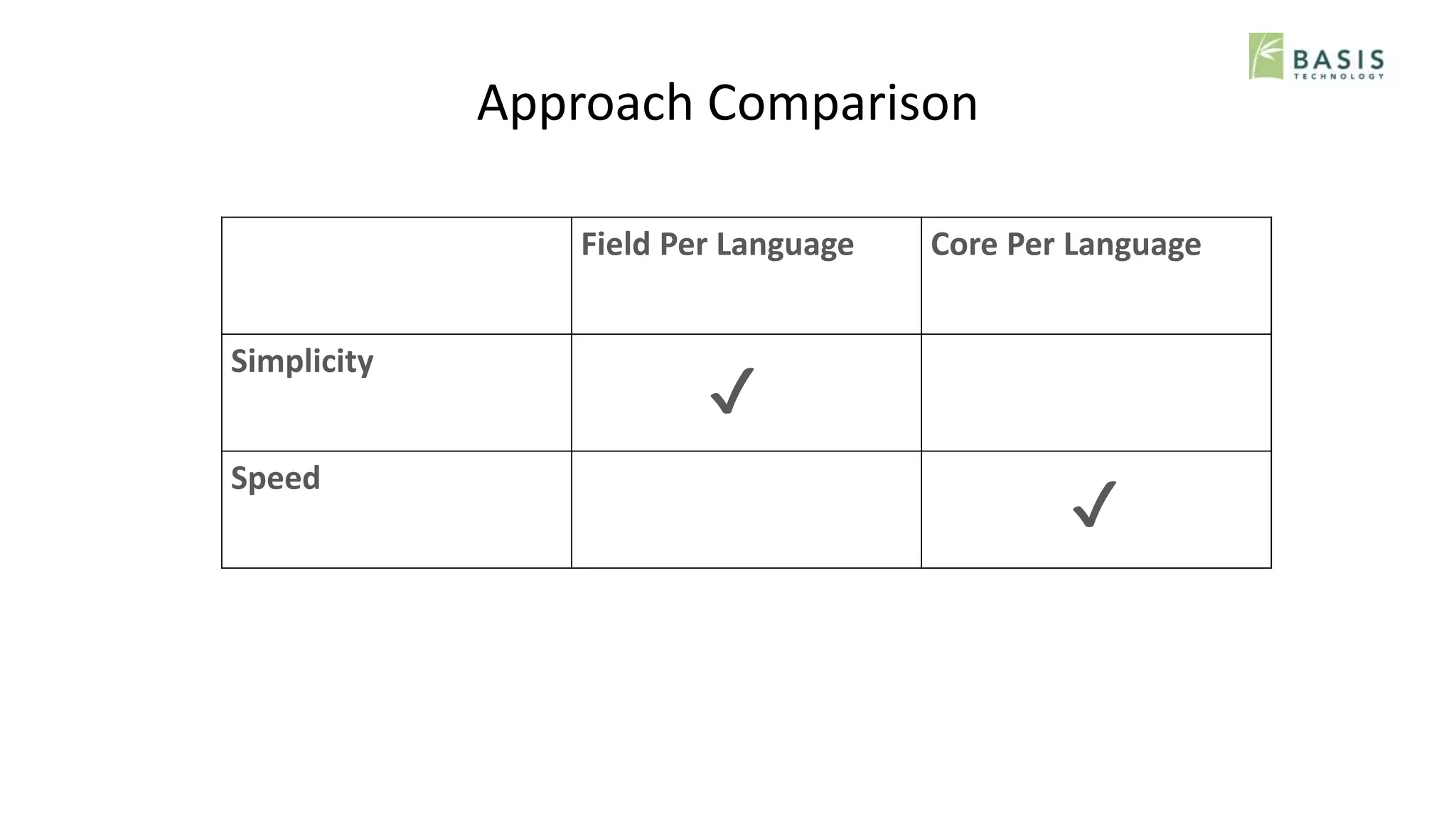
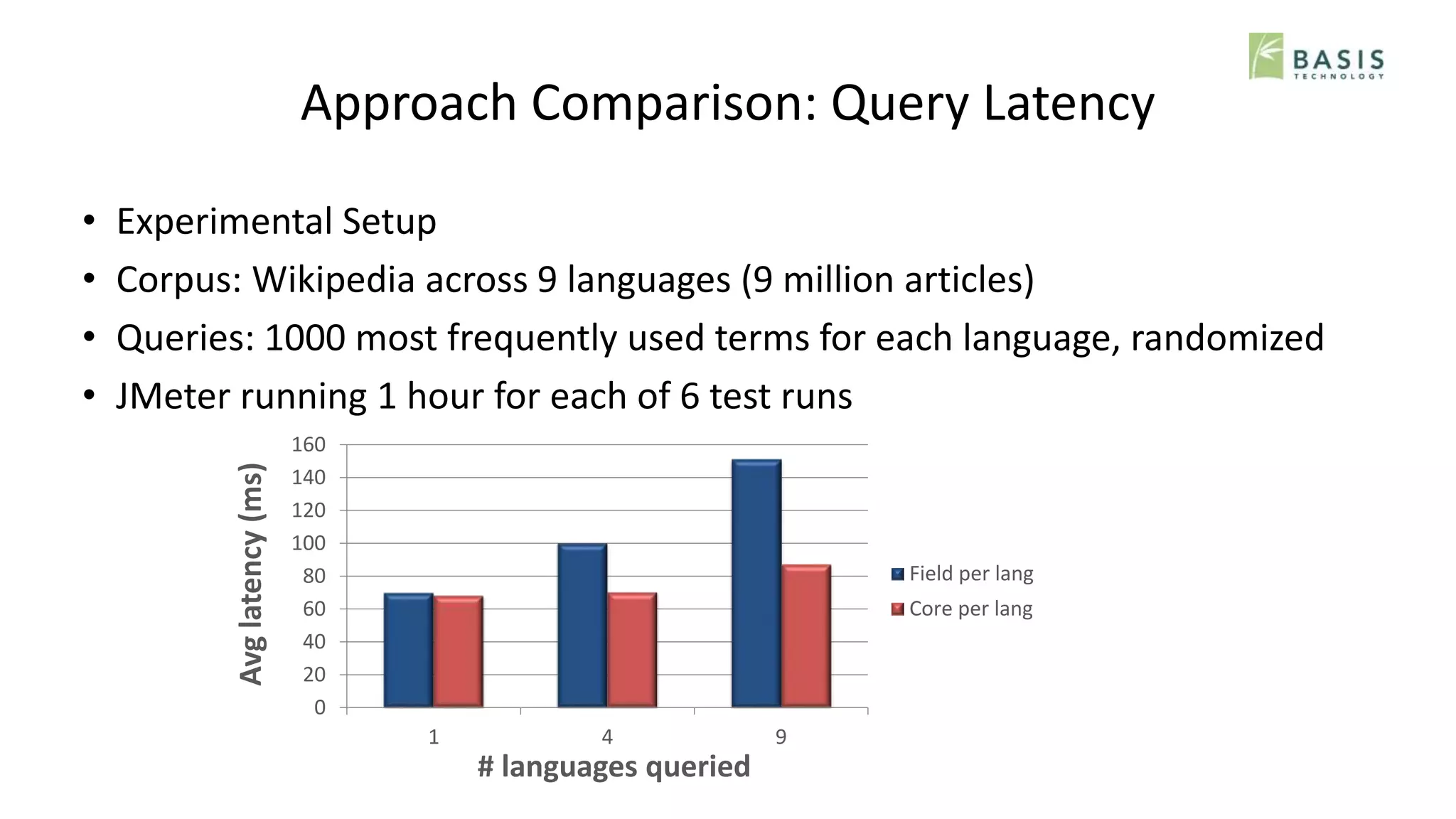
The document outlines strategies for optimizing multilingual search using natural language processing (NLP) within the Solr search engine. It discusses various NLP techniques including language detection, tokenization, decompounding, and normalization, and presents approaches such as field-based and core-based indexing per language. The overall goal is to enhance search capabilities across mixed-language documents while addressing challenges in precision and recall for different languages.
















![An Alternative Approach
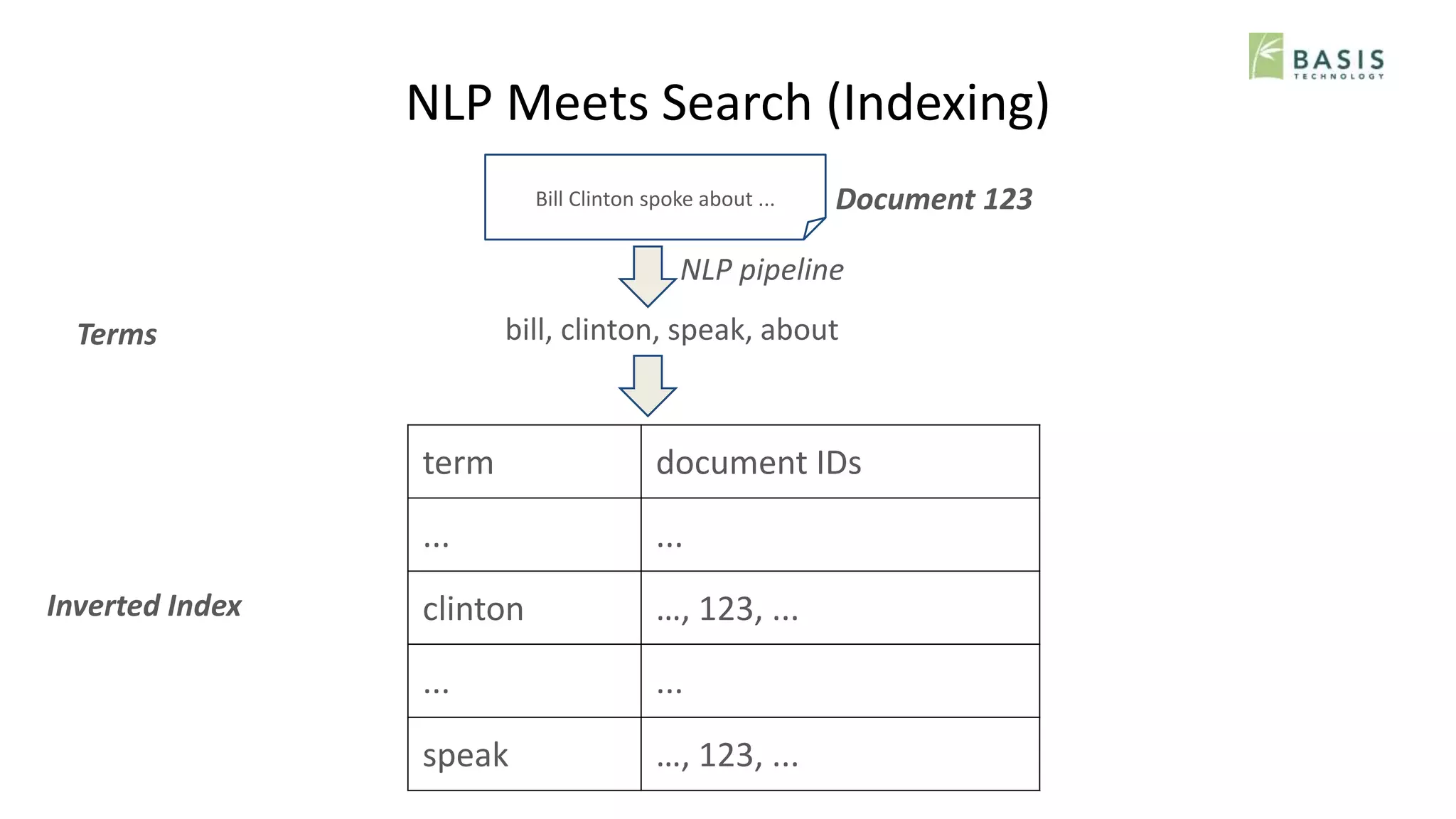
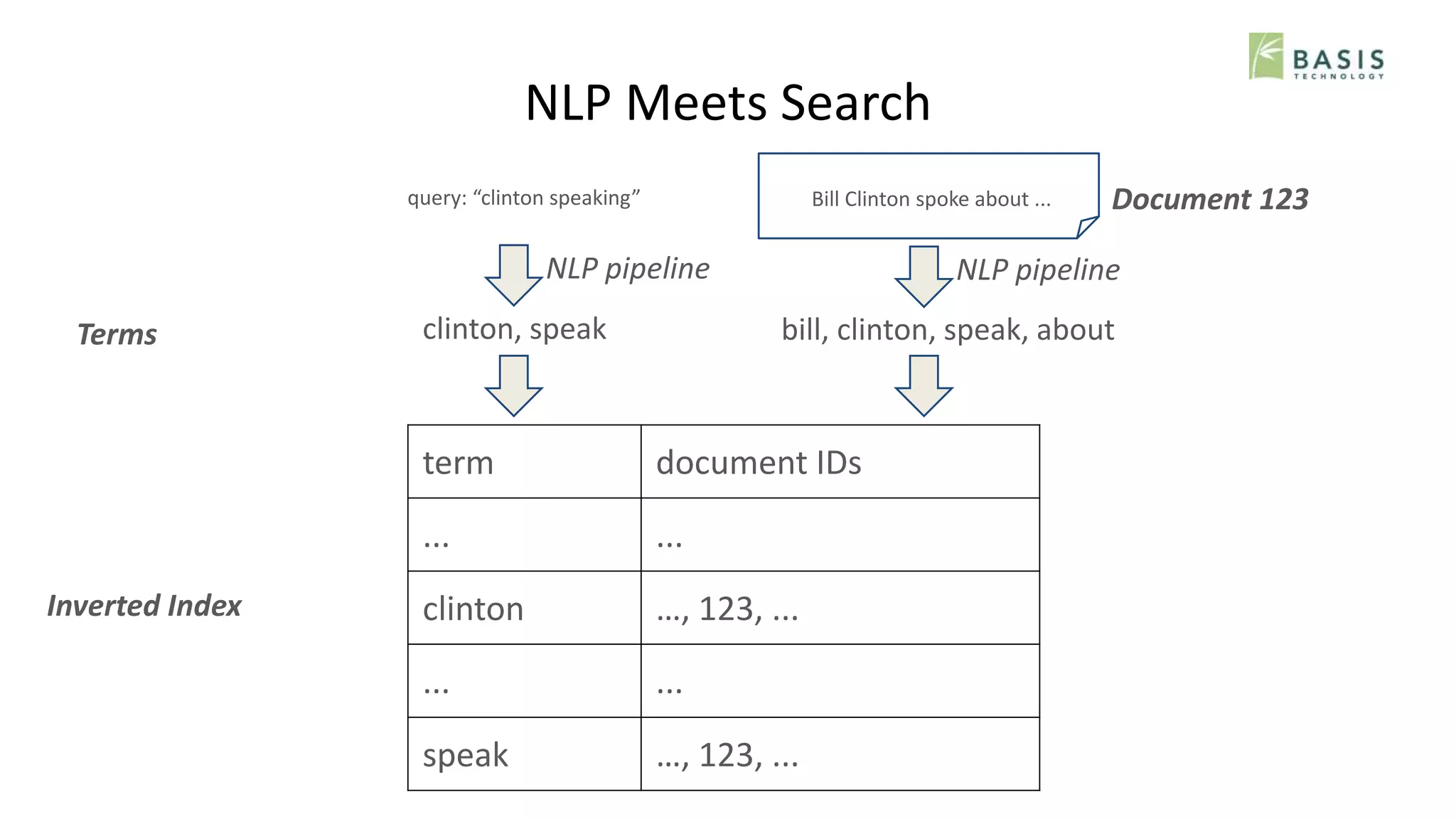
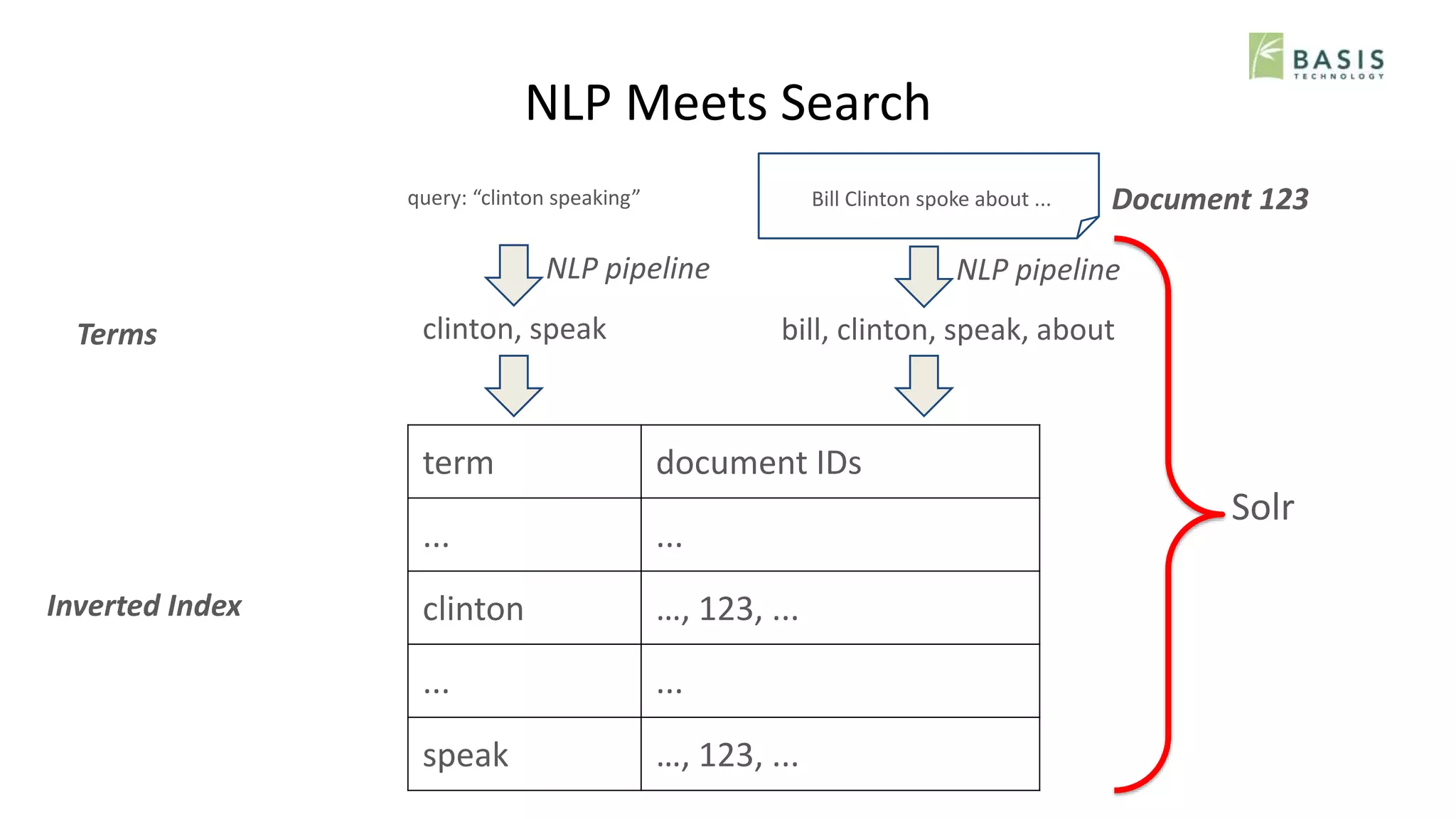
Terms
Inverted Index
term document IDs
... ...
clinton …, 123, ...
... ...
speak …, 123, ...
query: “[en, es]clinton speaking”
Inspect [en, es], apply English and Spanish field
types to “clinton speaking”, merge results
clinton, speak](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/optimizingmultilingualsearch-davidtroiano-2-141231121514-conversion-gate02/75/Optimizing-multilingual-search-in-SOLR-27-2048.jpg)





