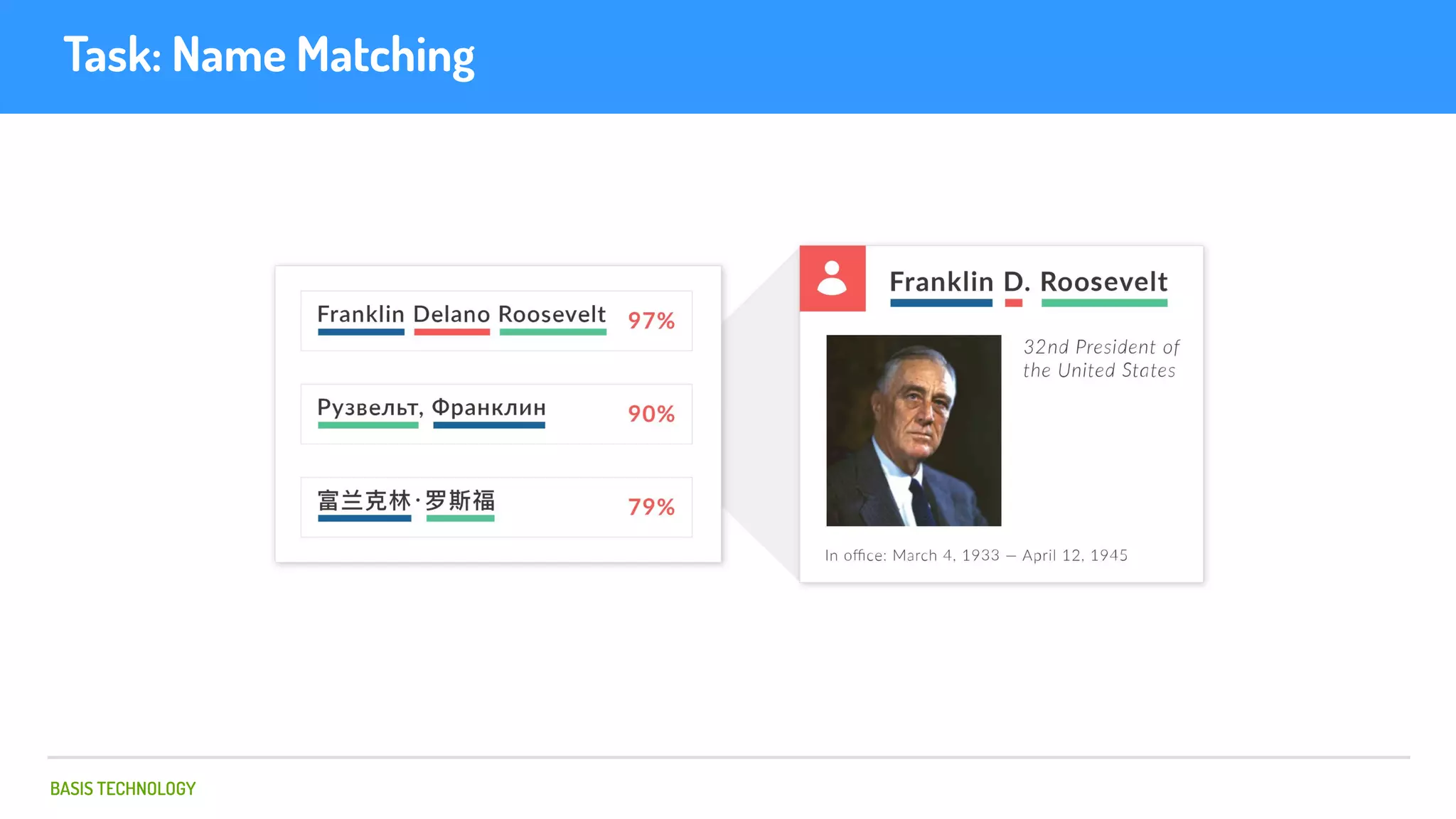
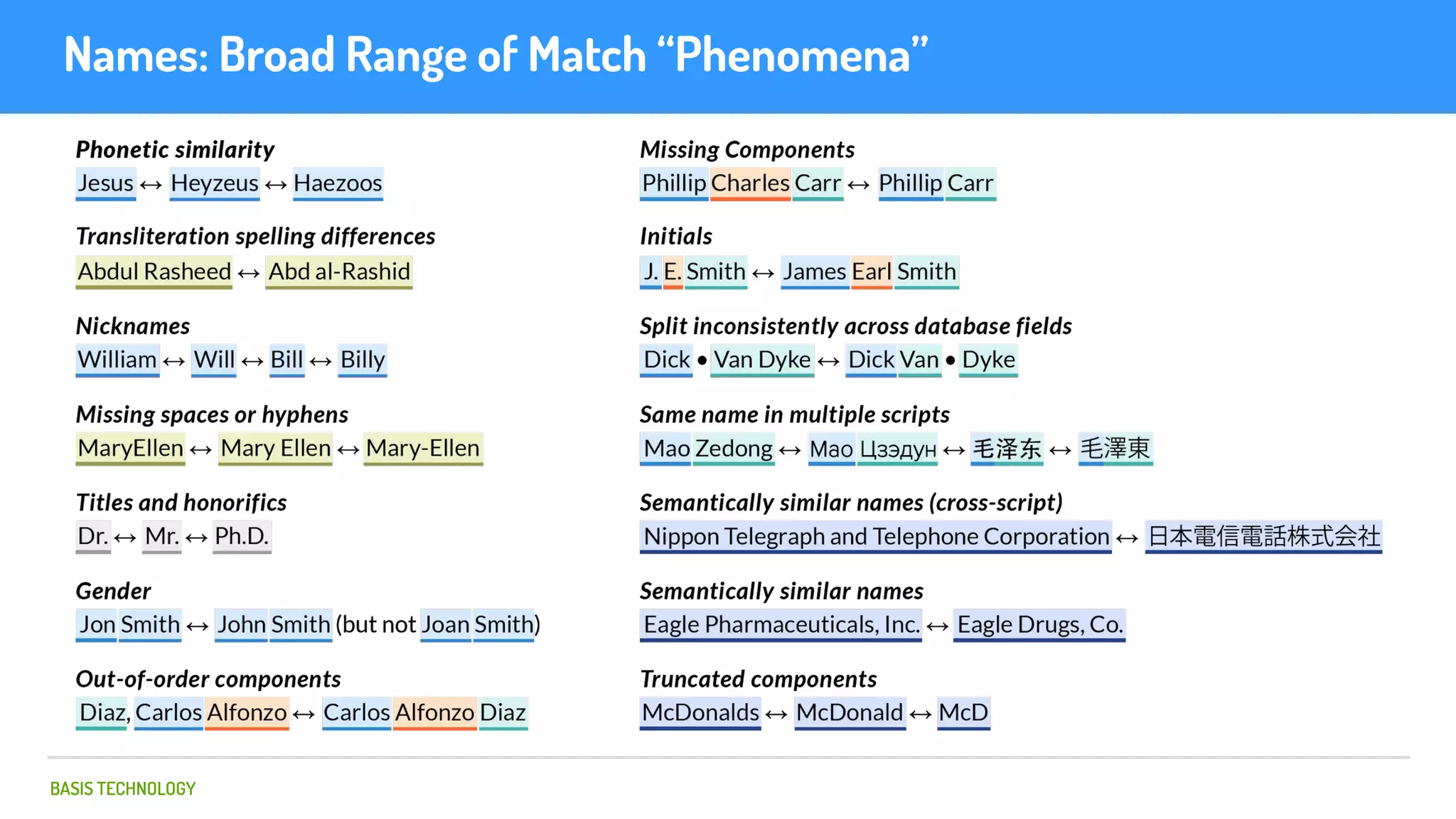
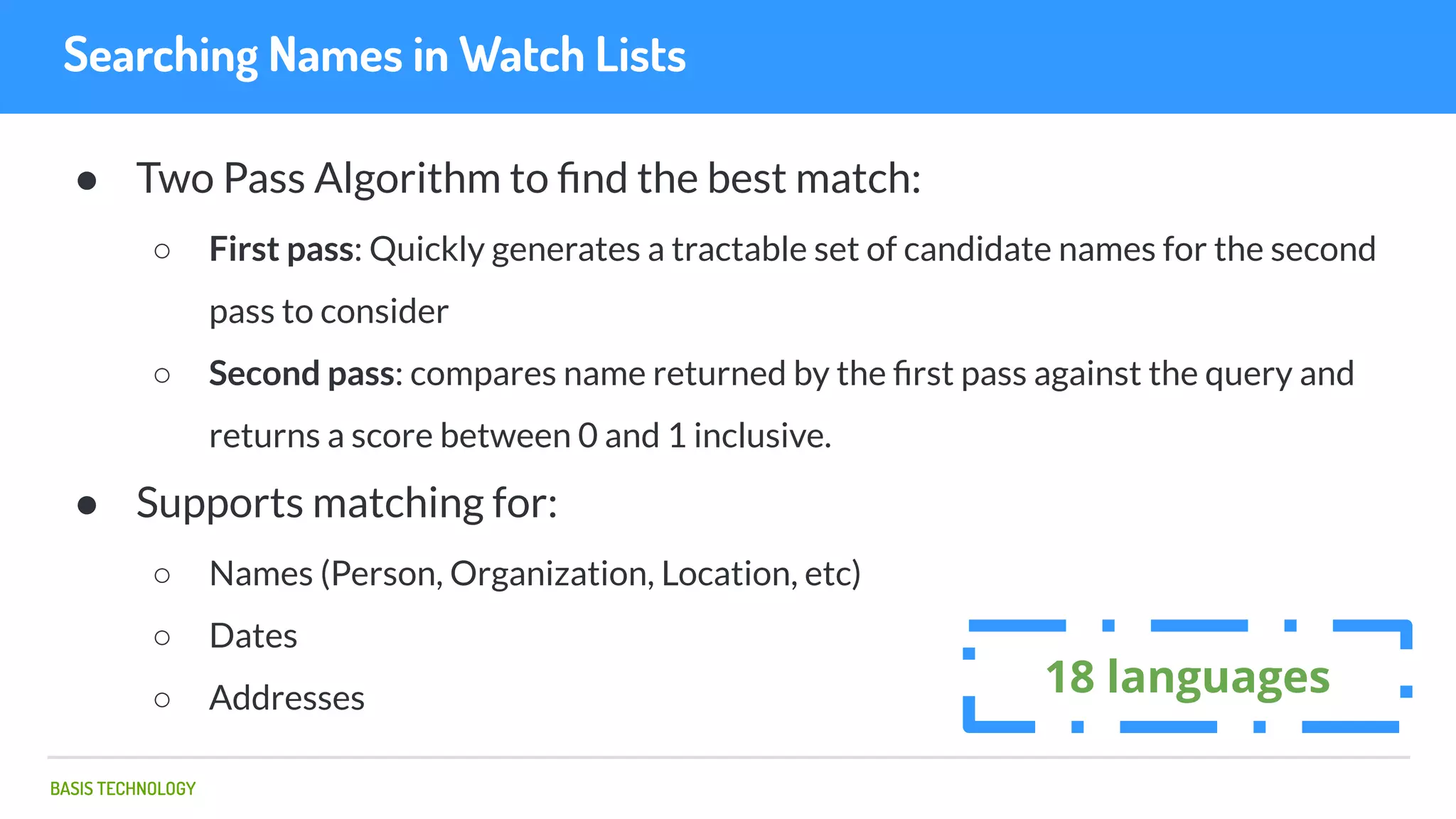
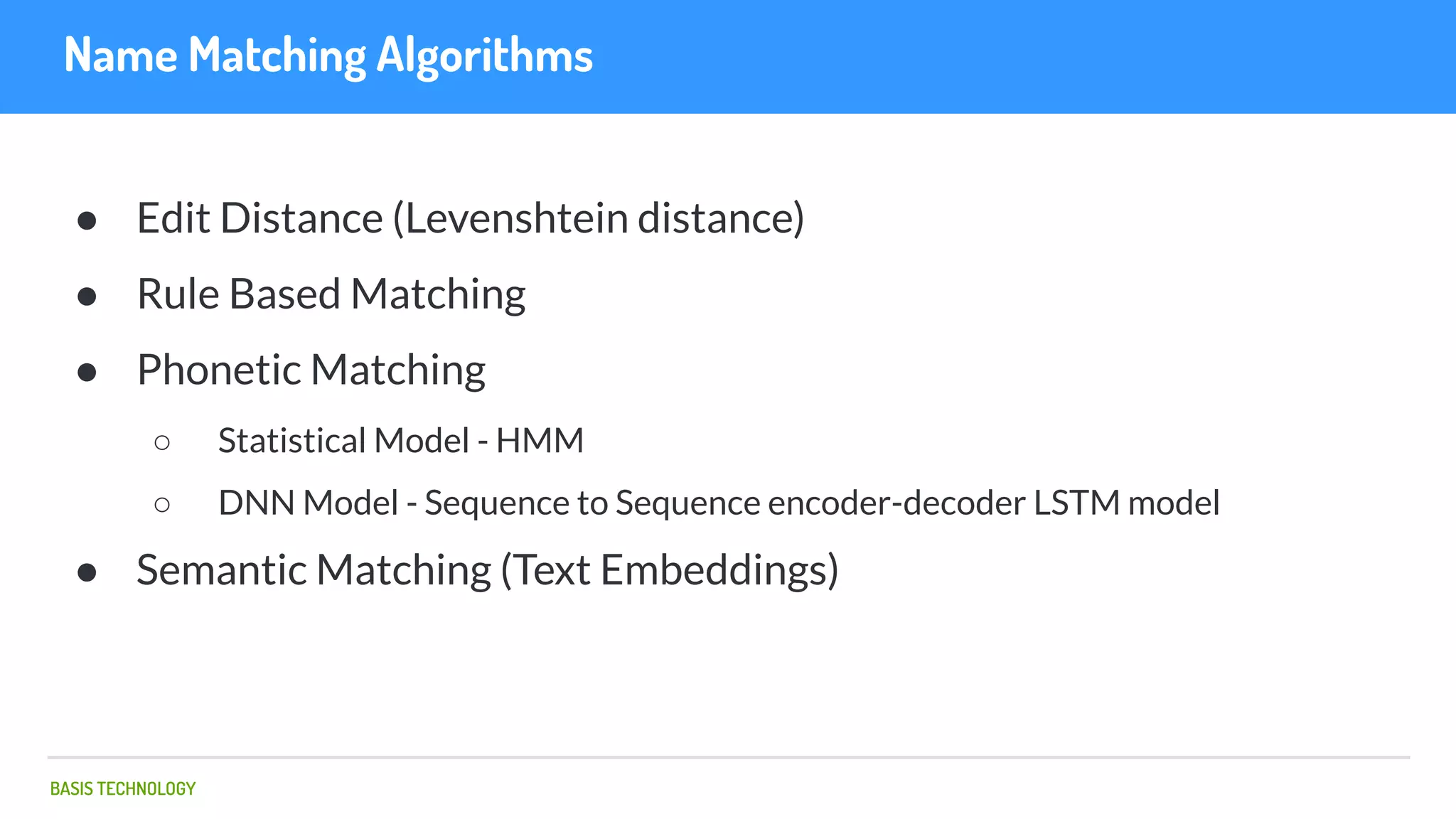
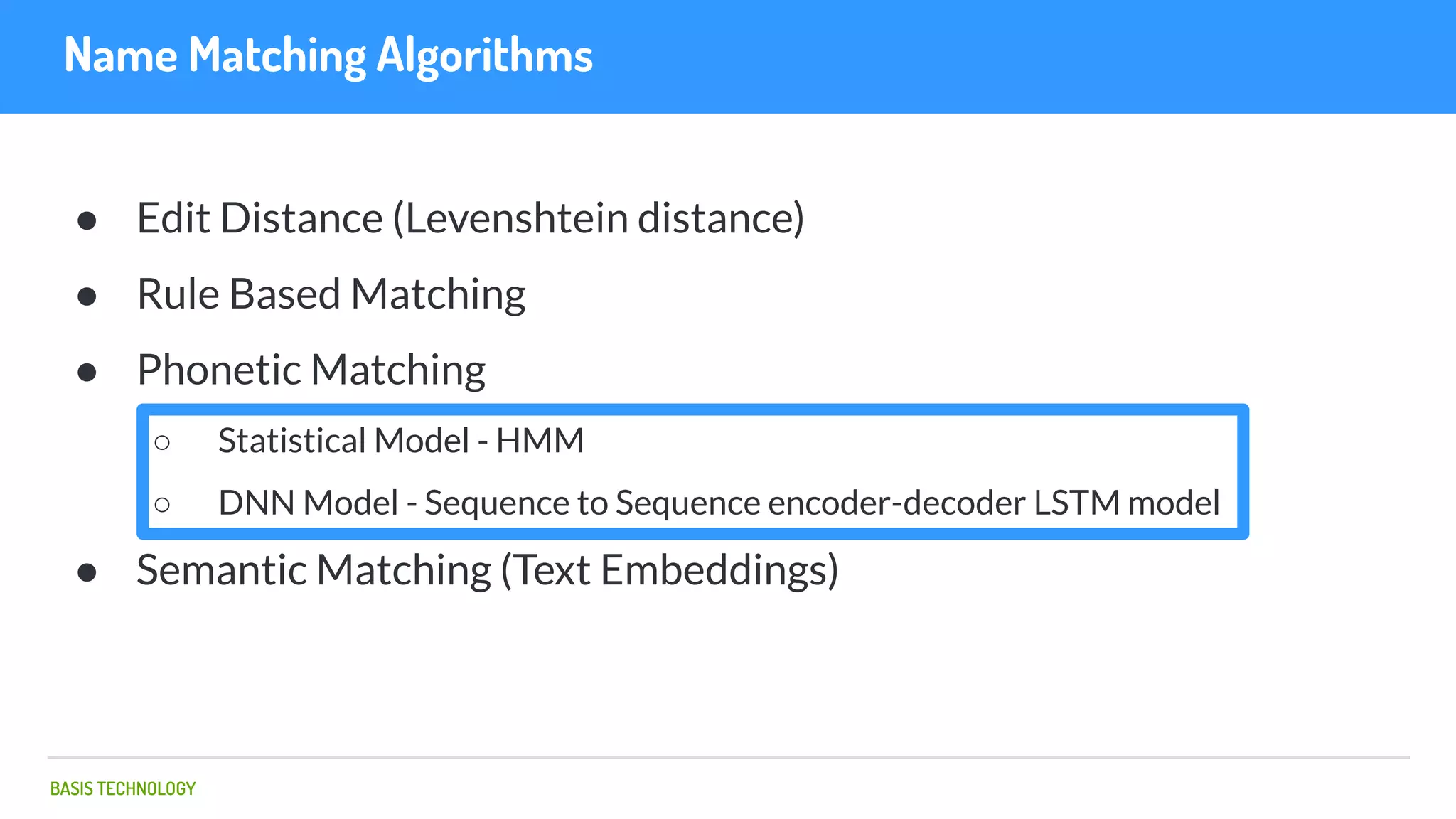
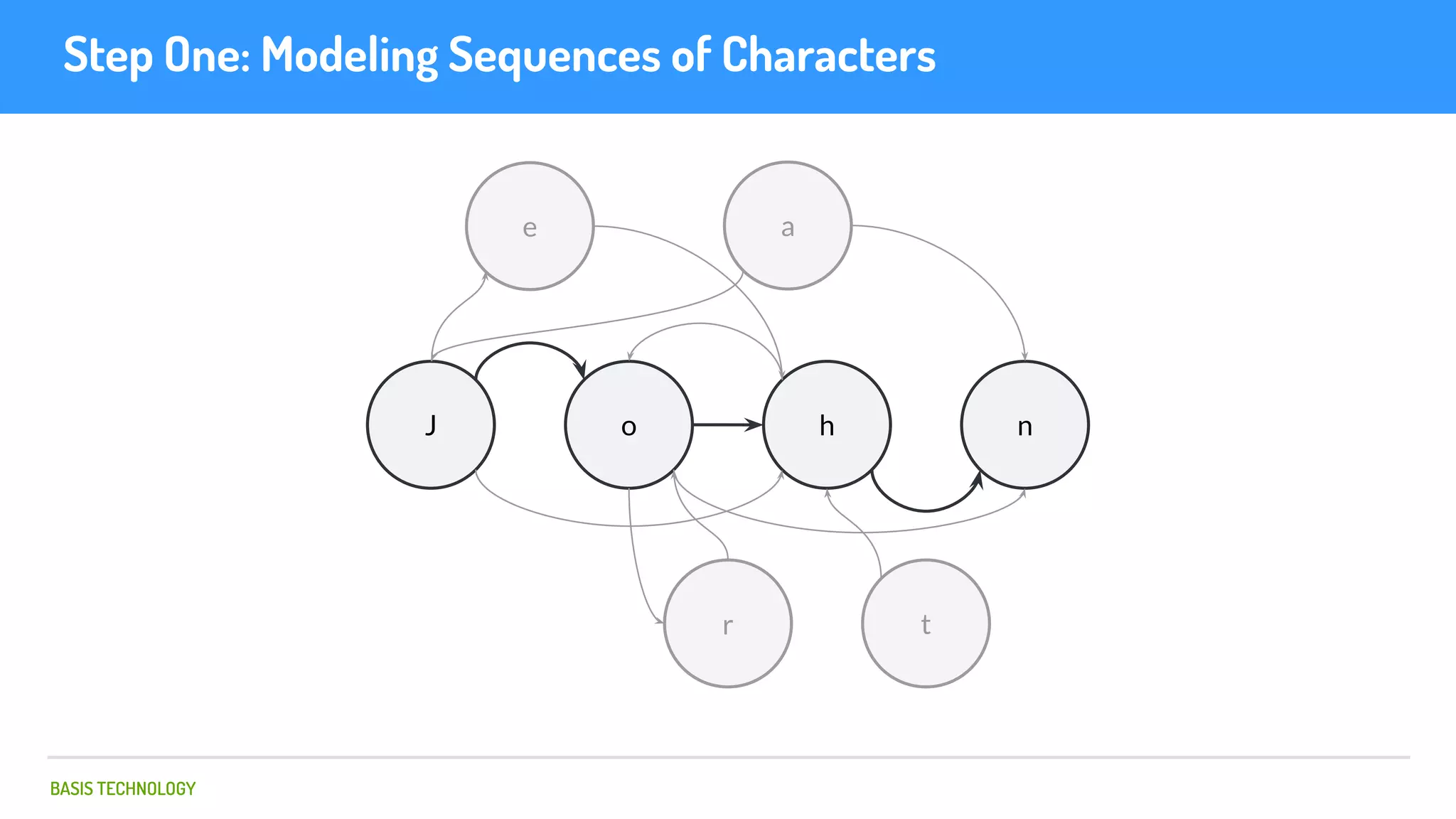
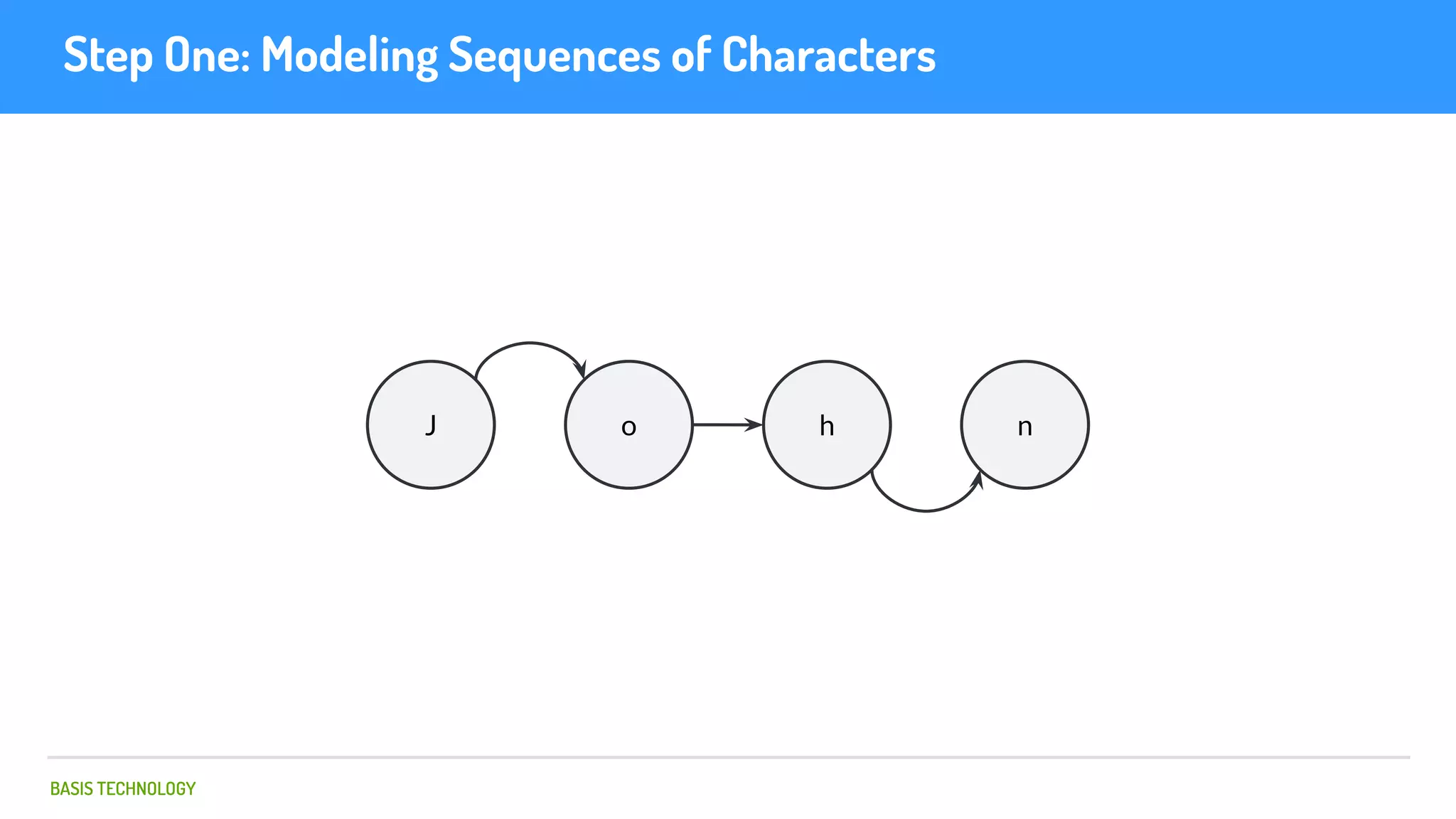
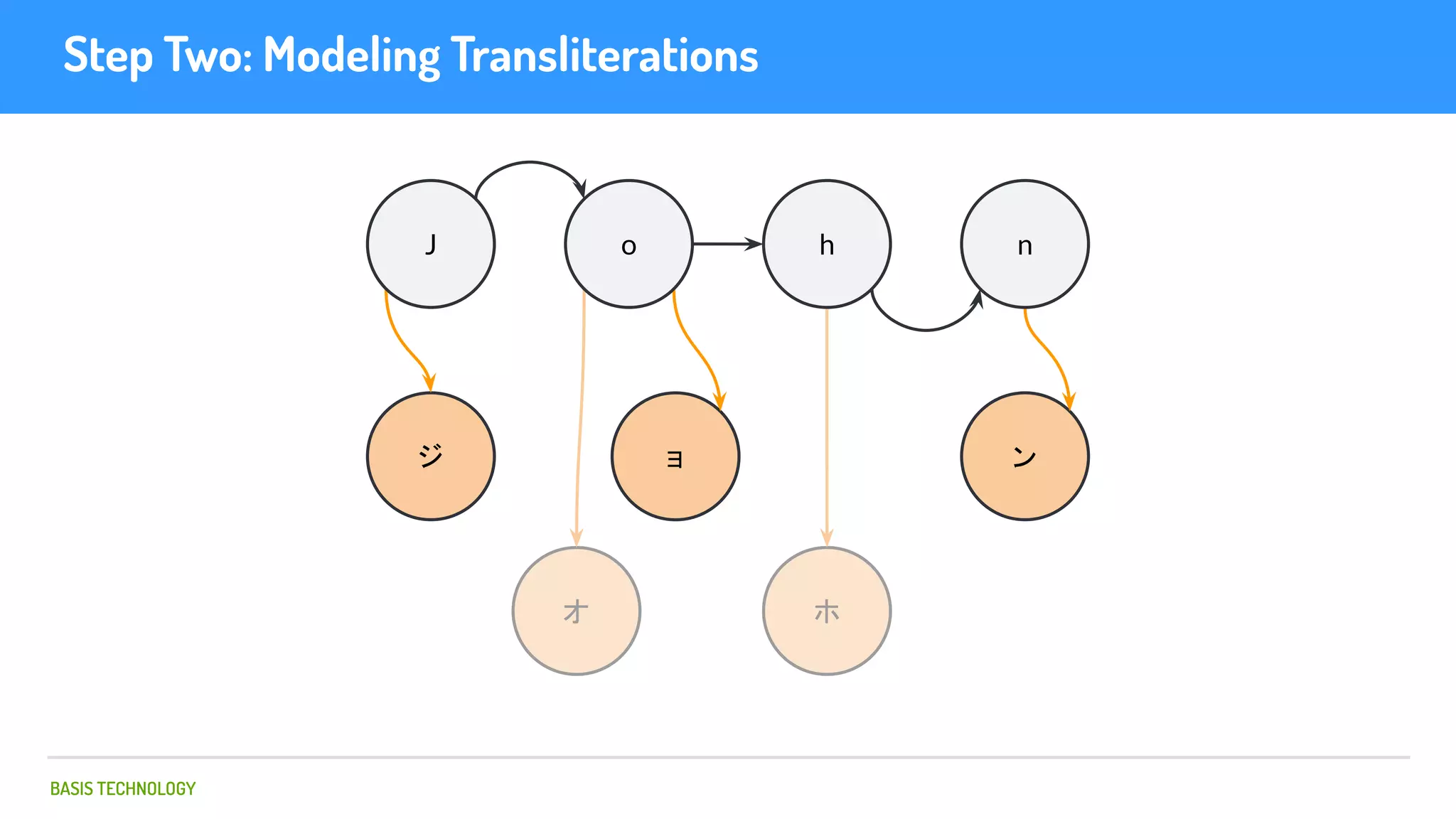
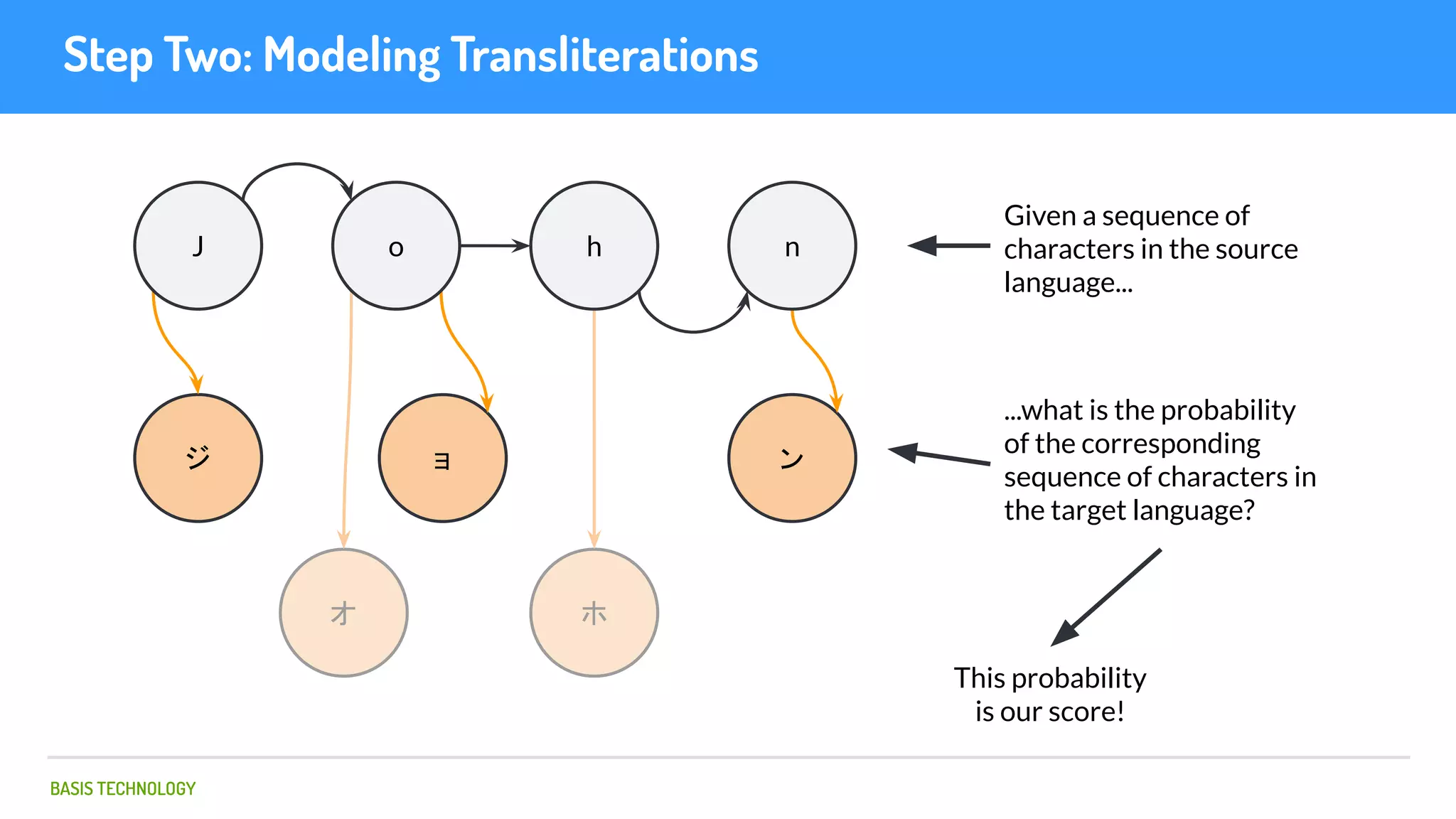
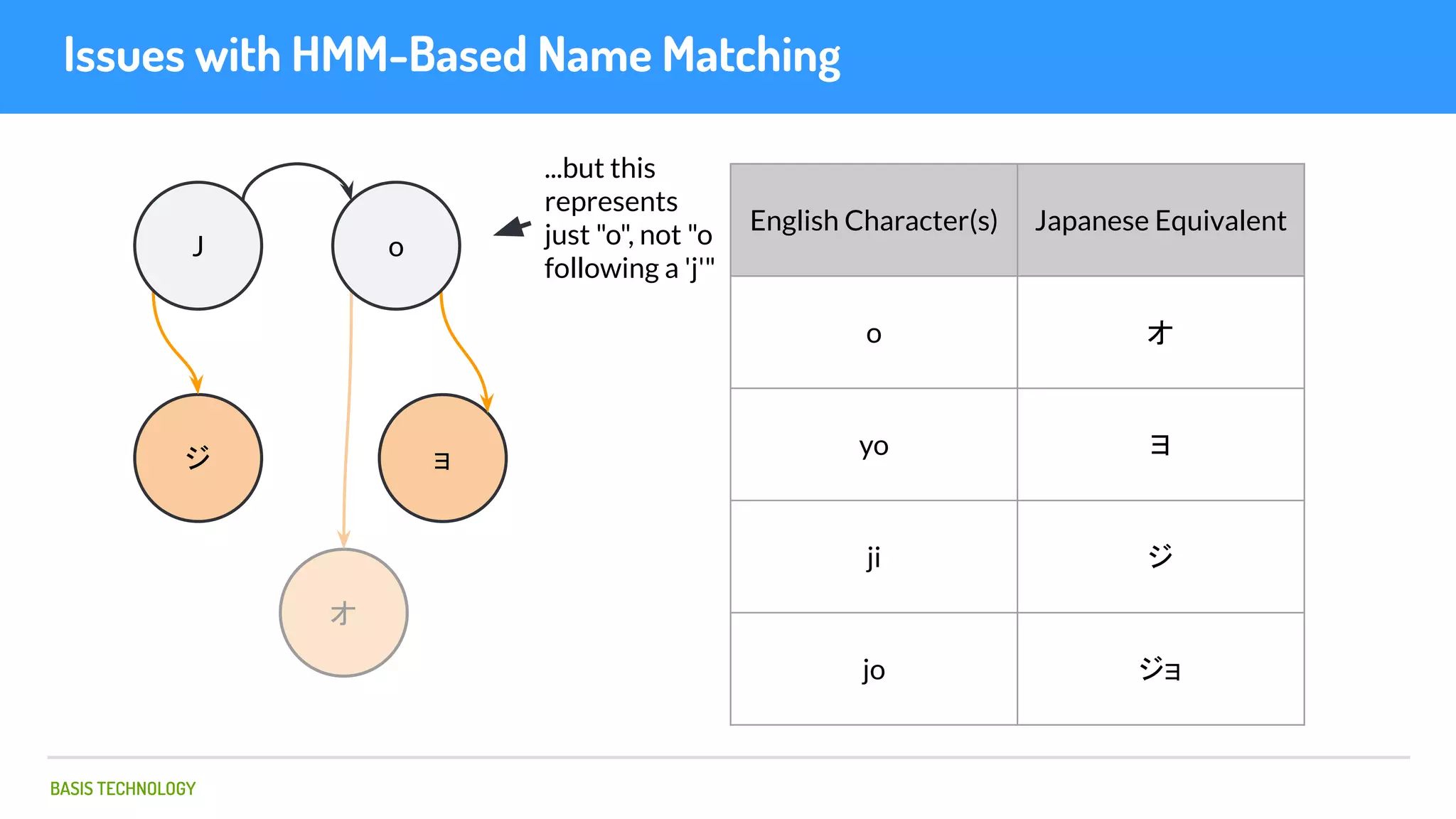
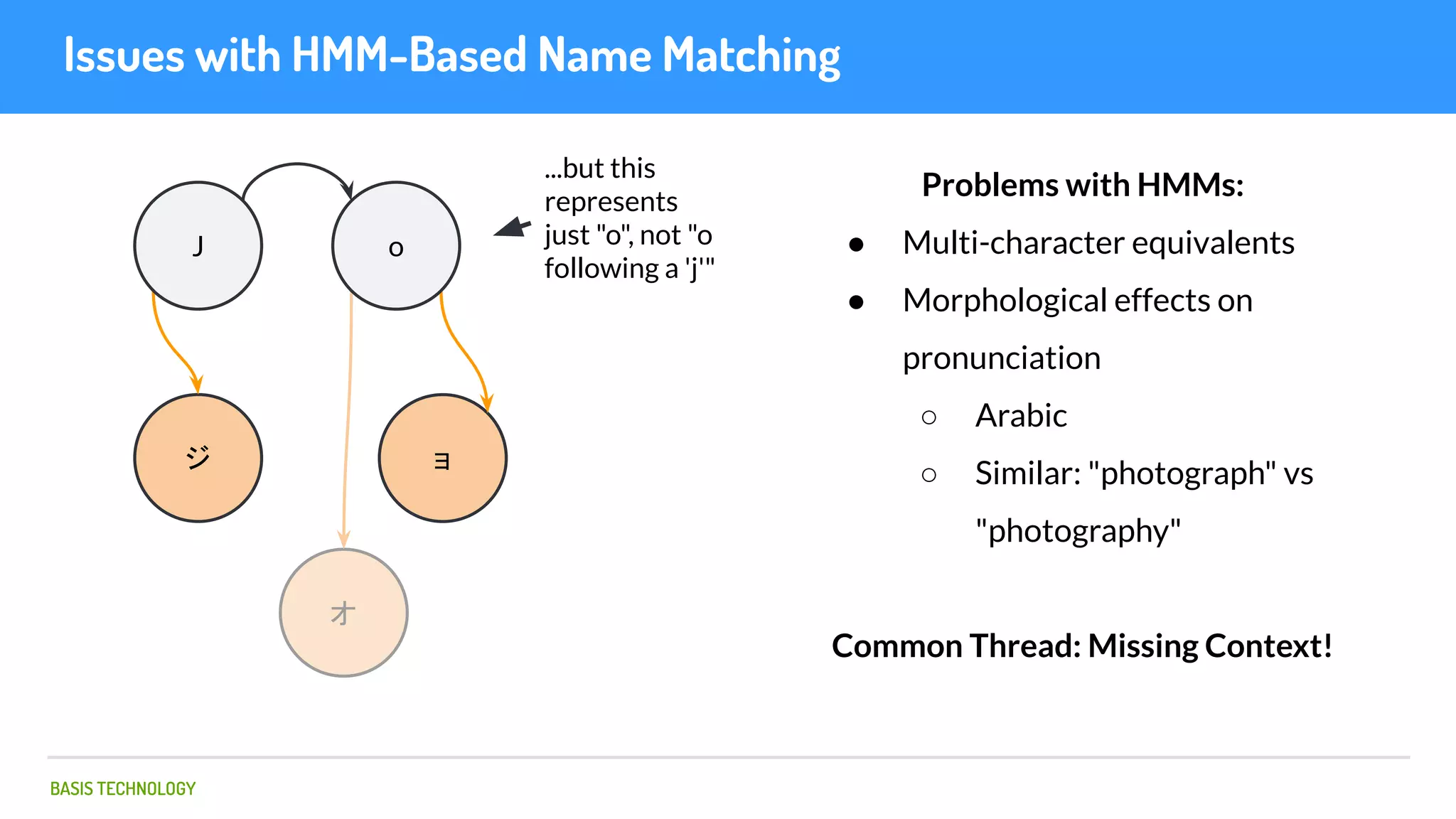
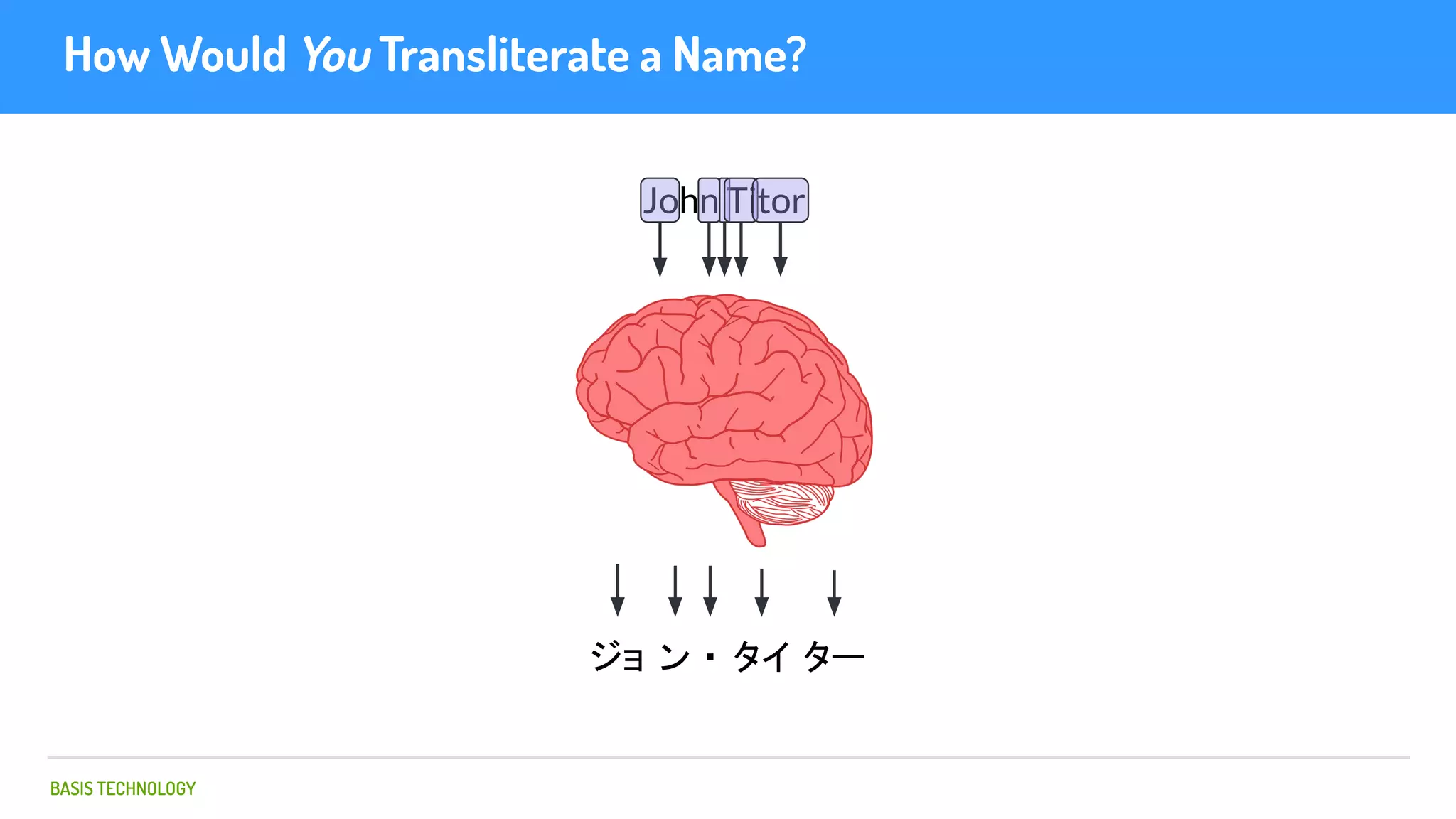
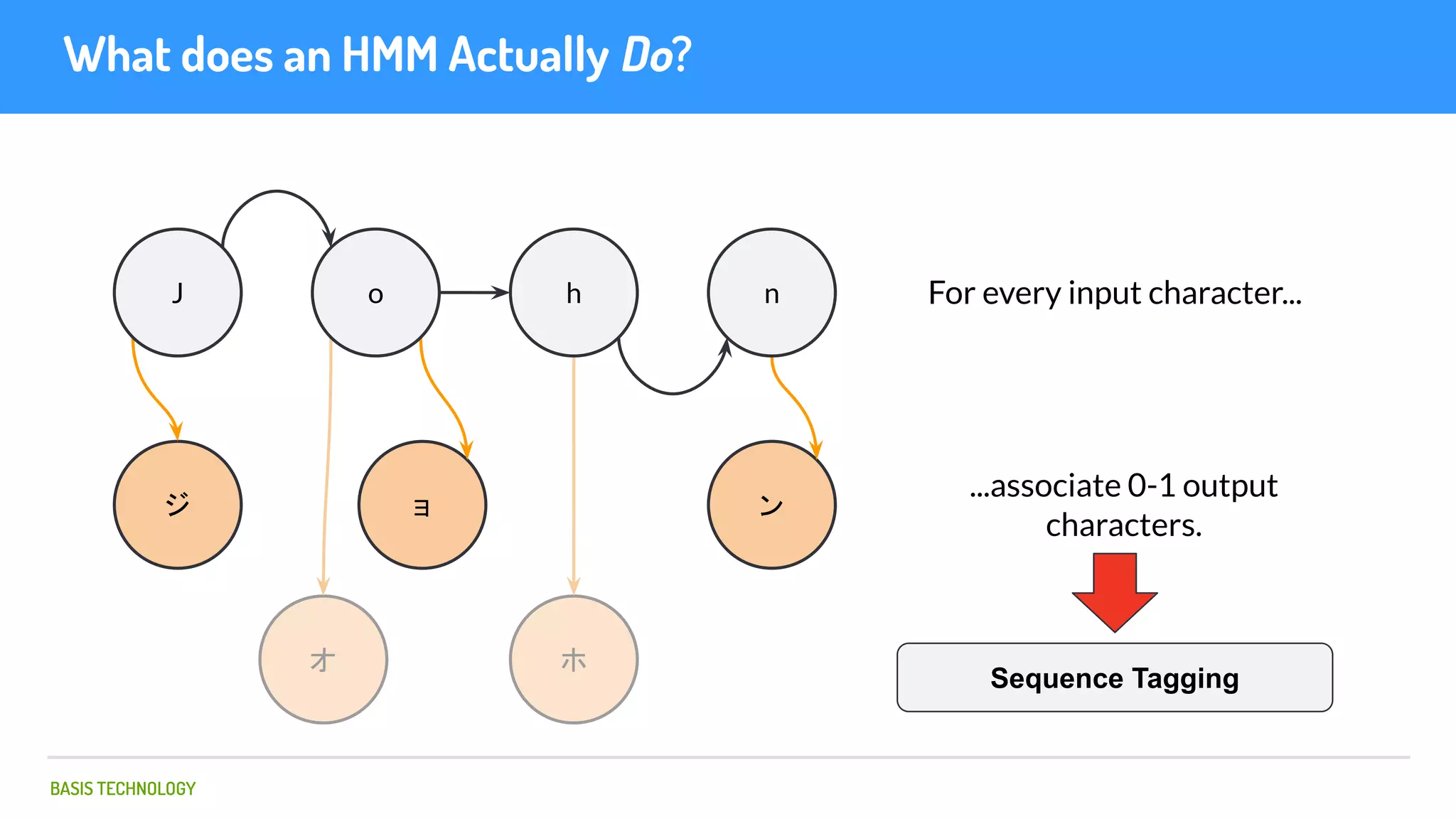
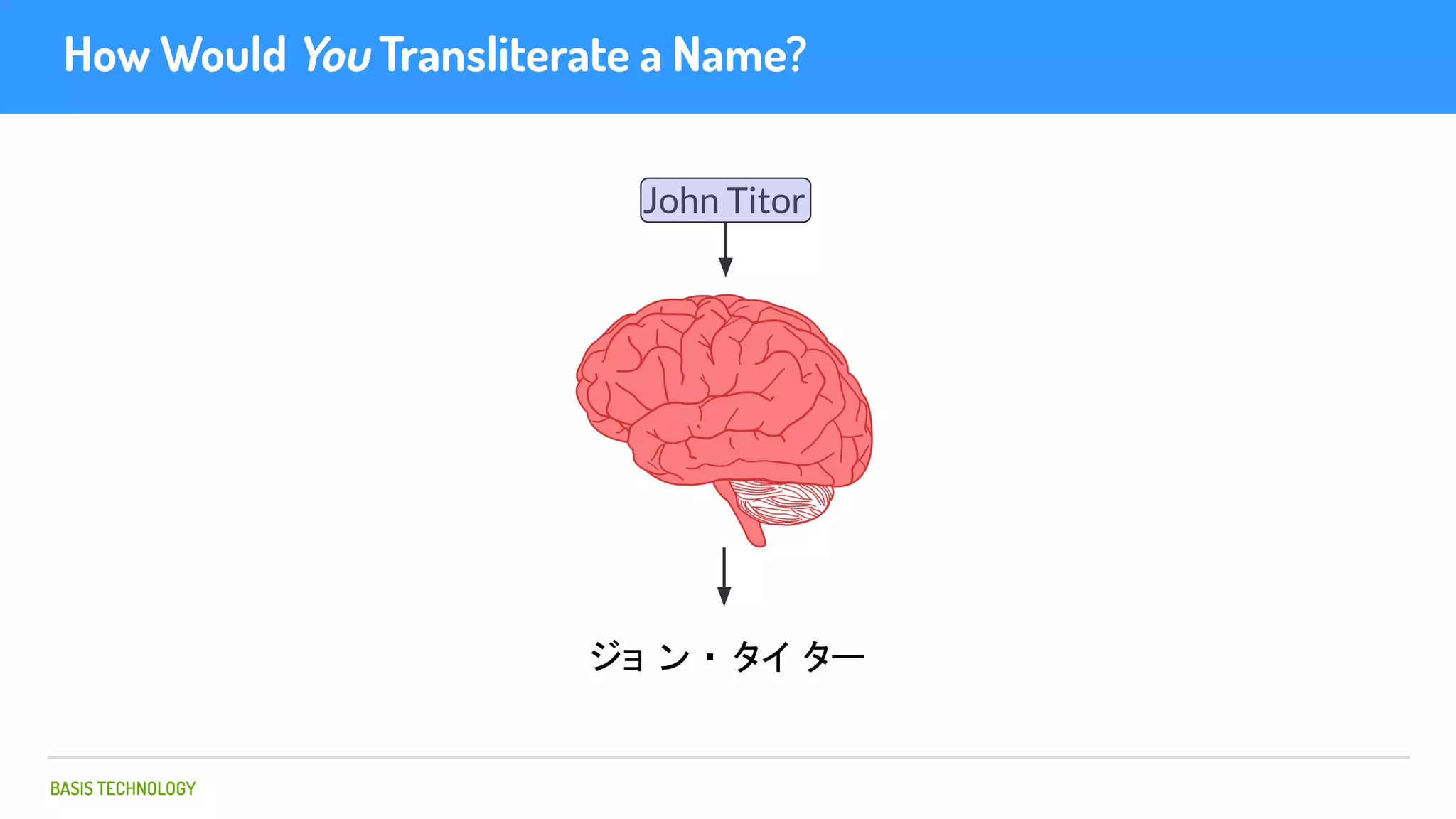
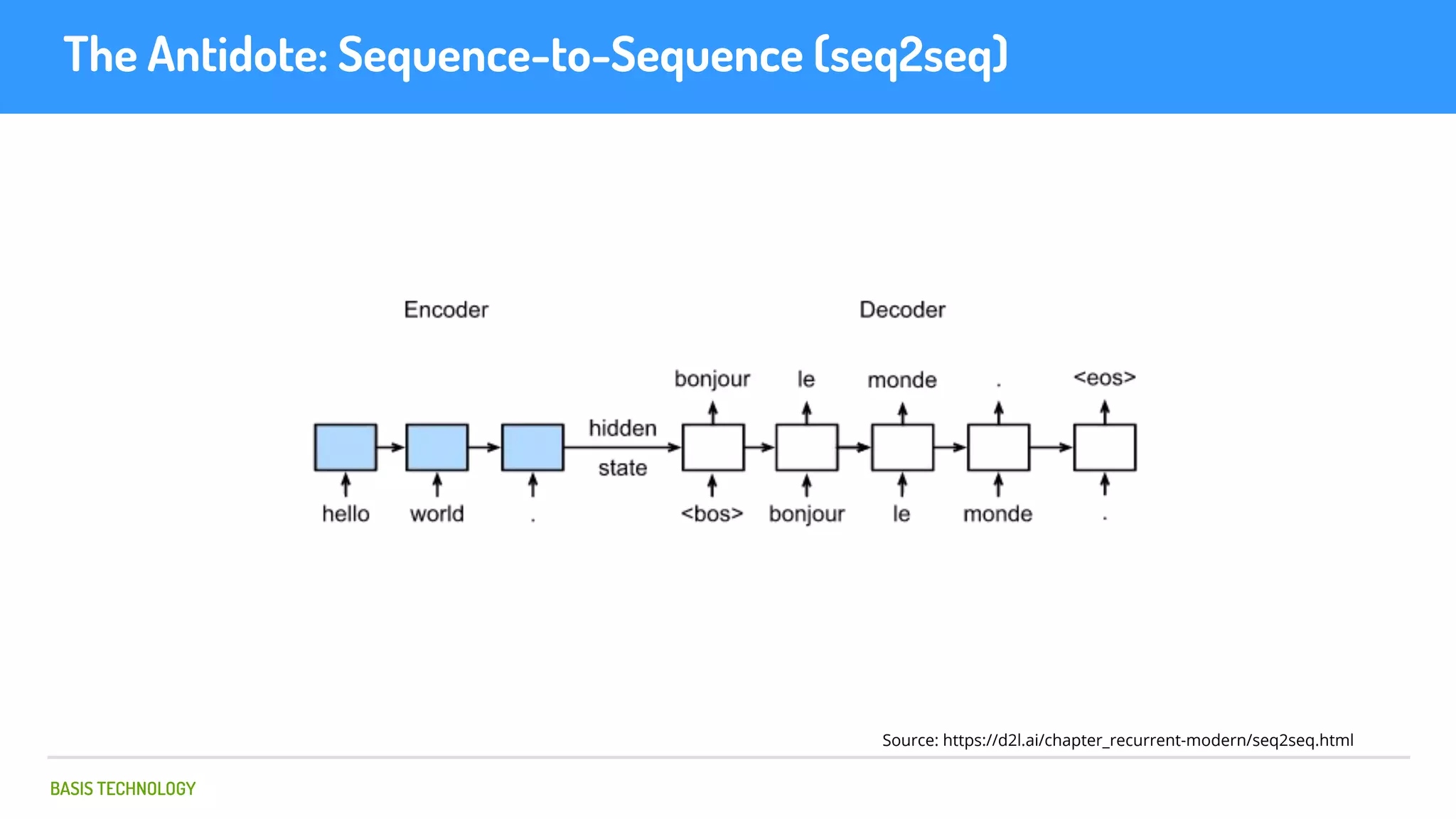
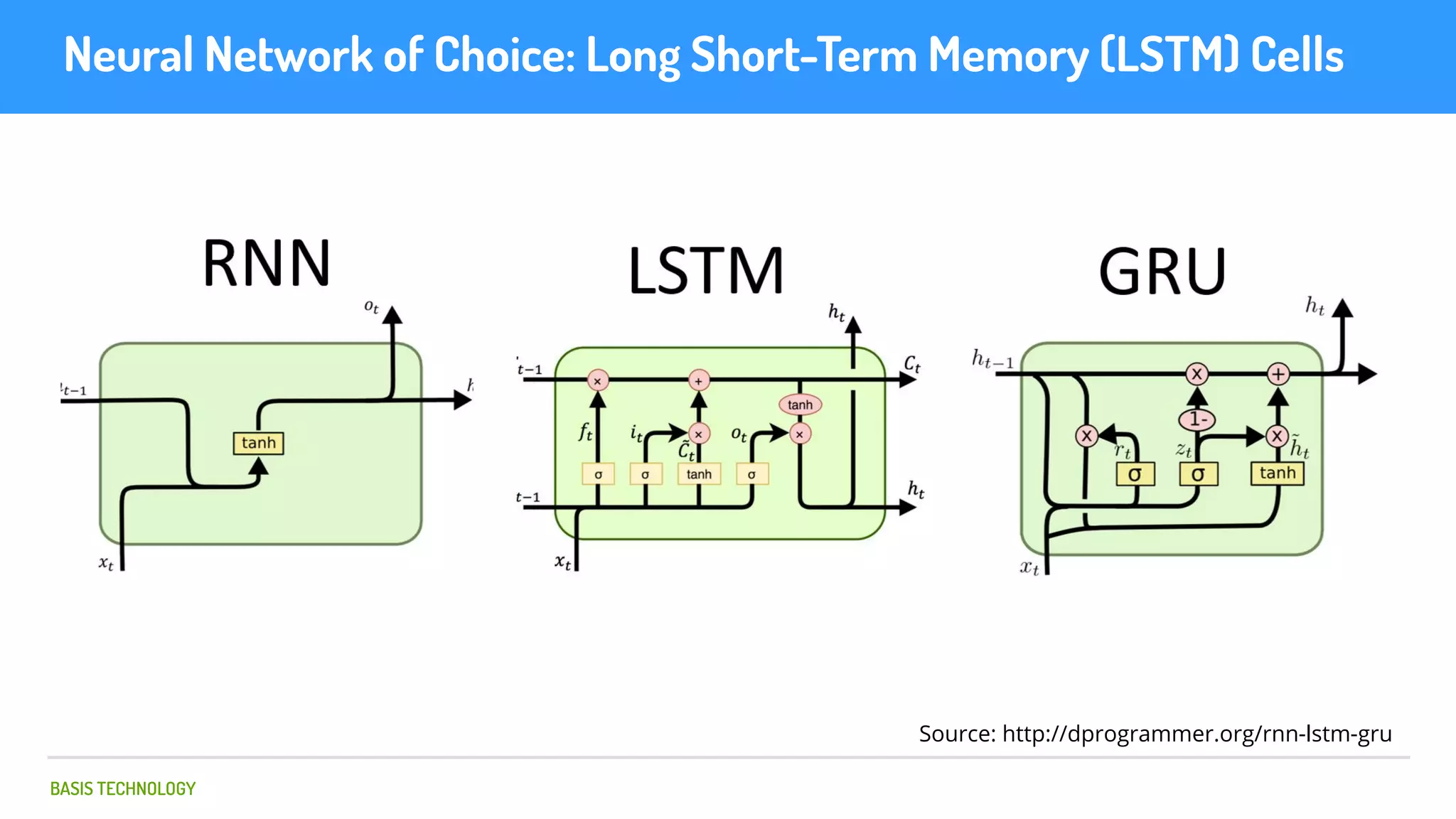
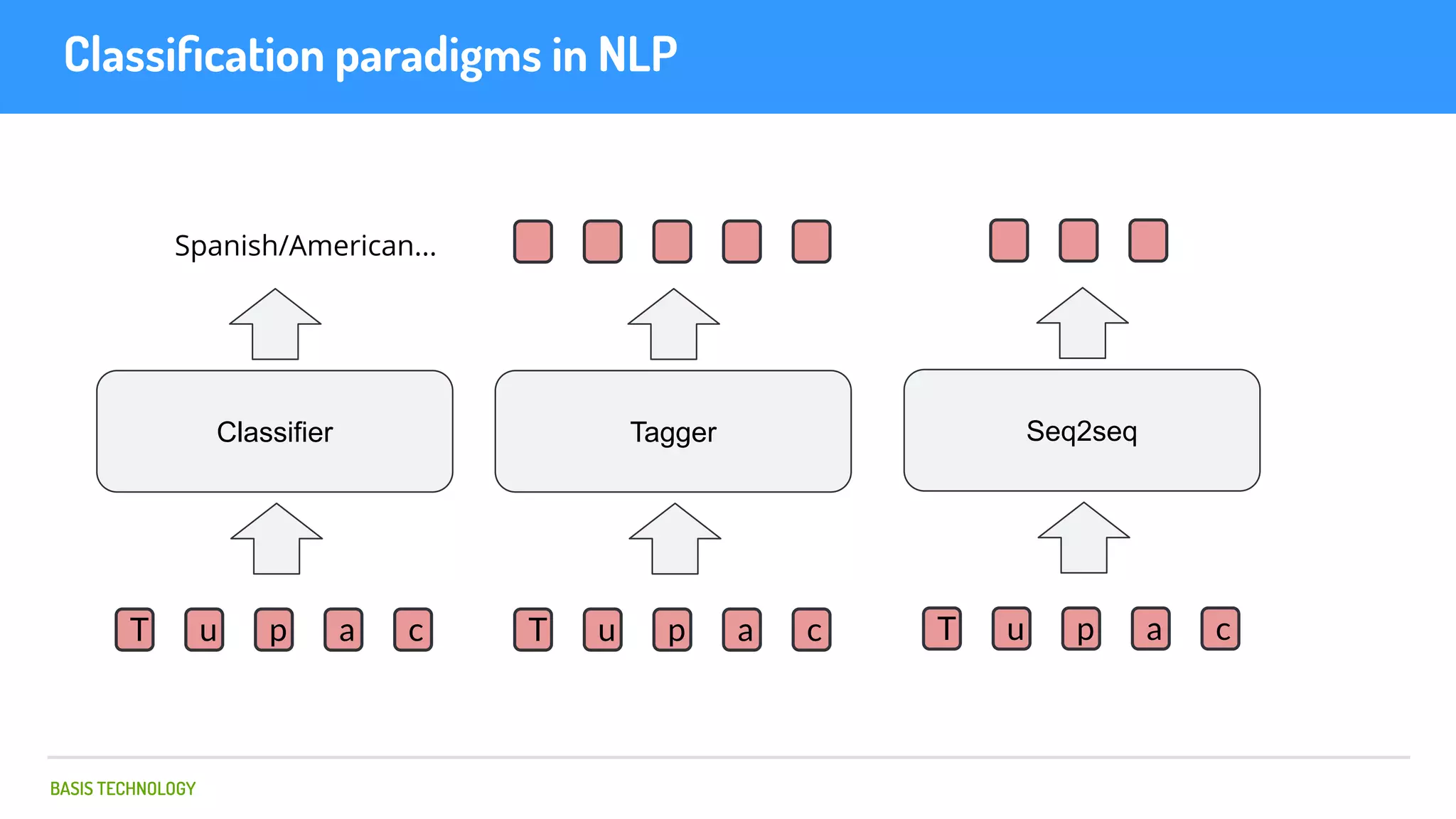
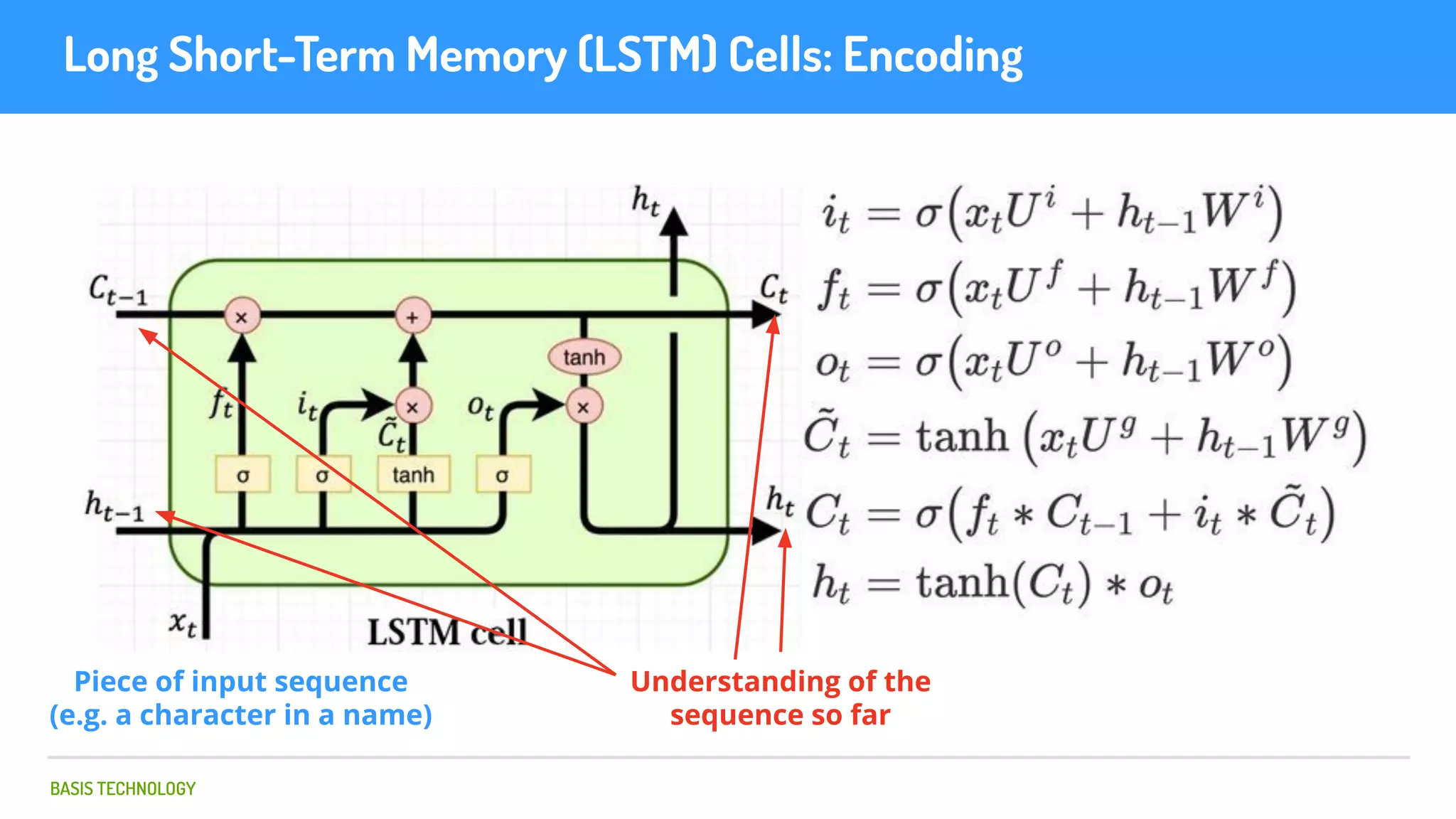
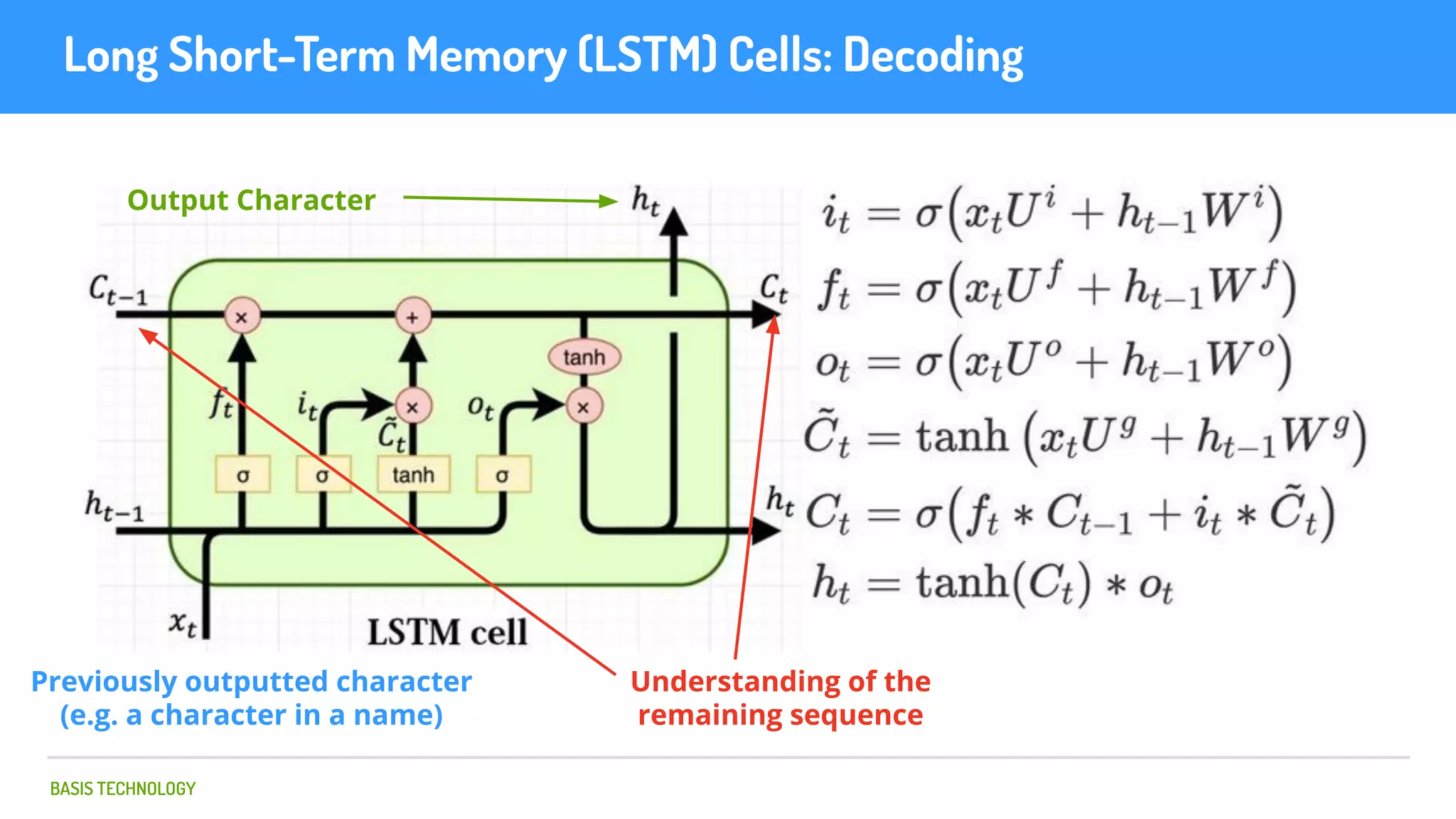
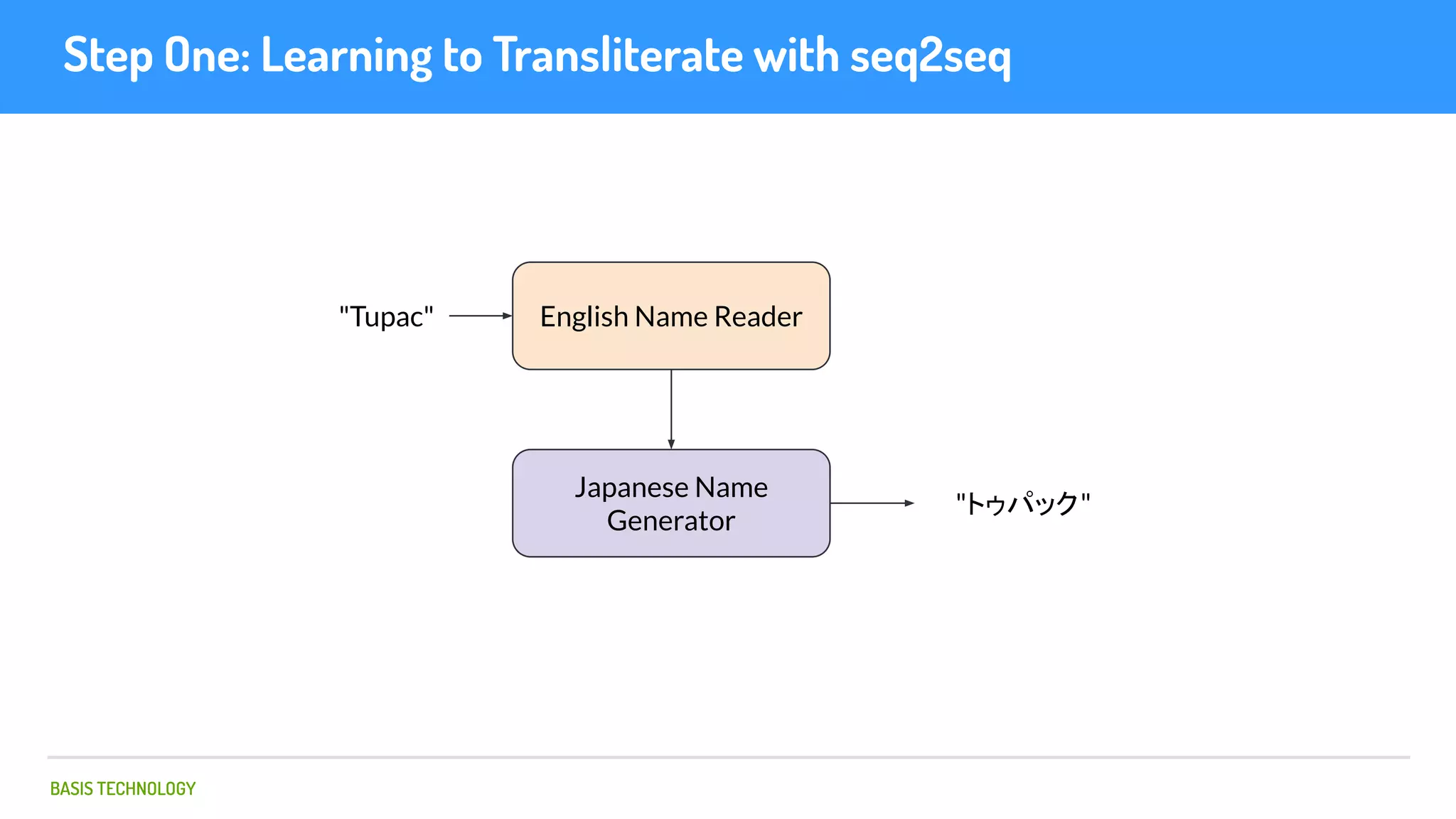
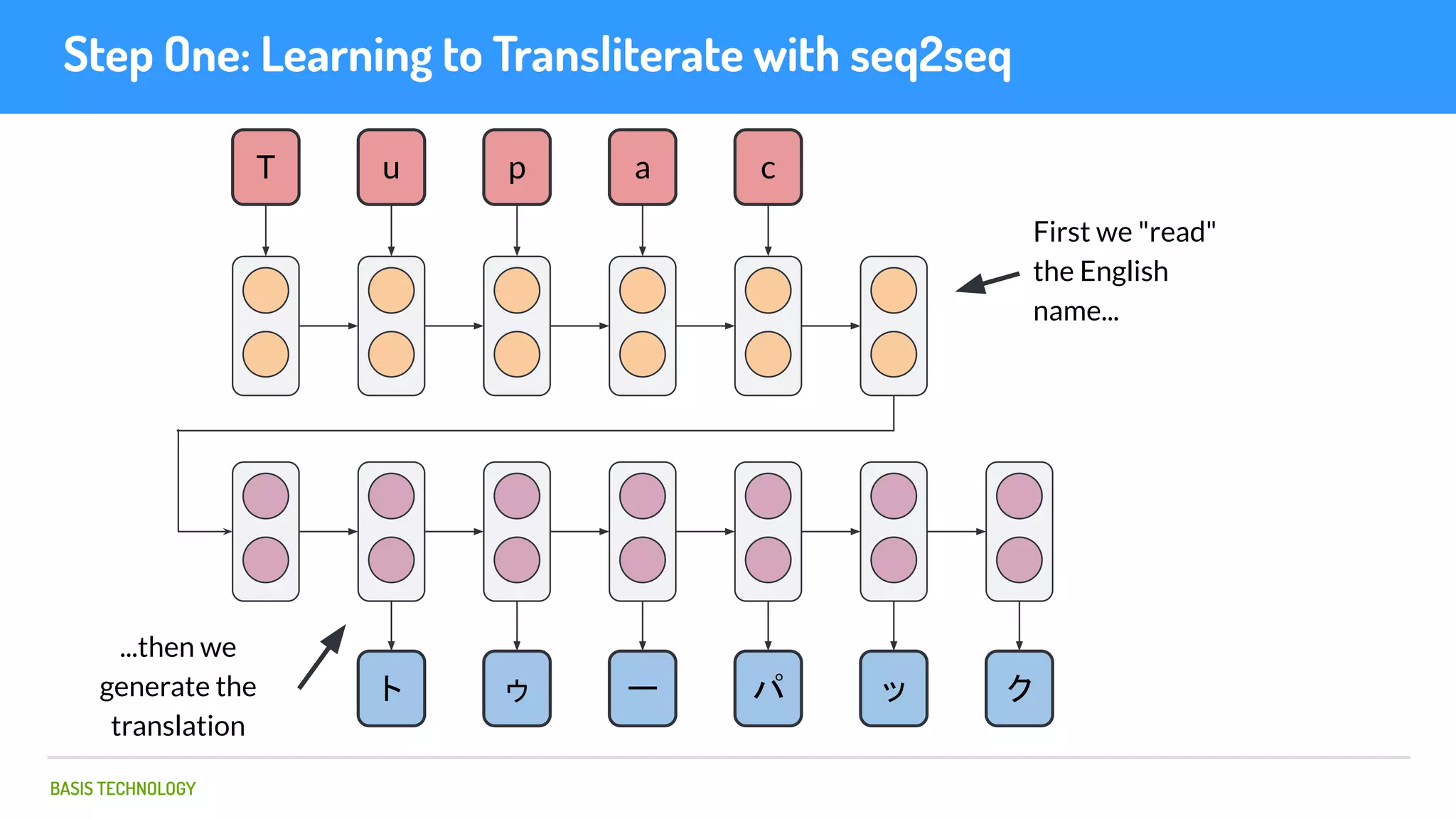
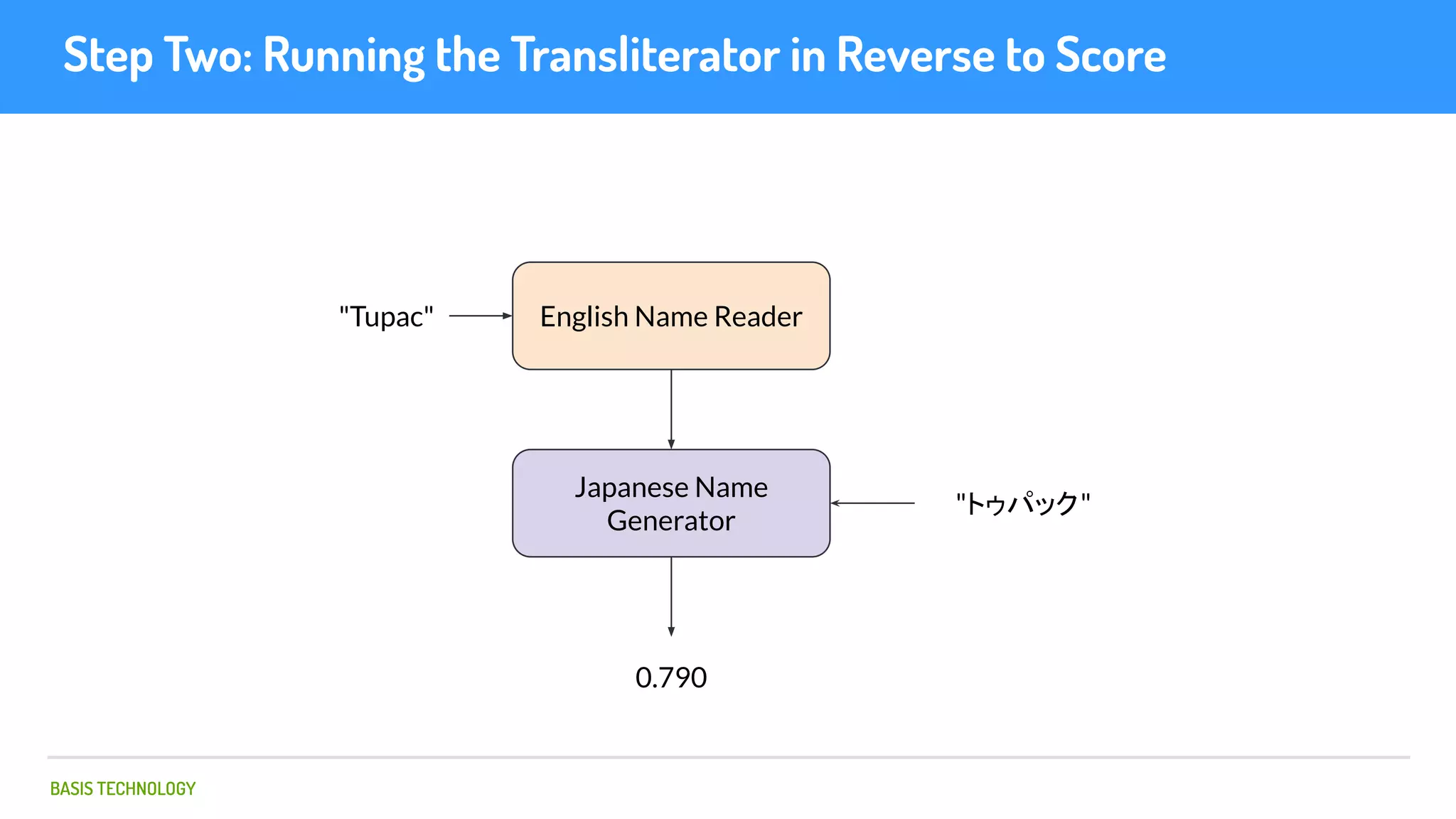
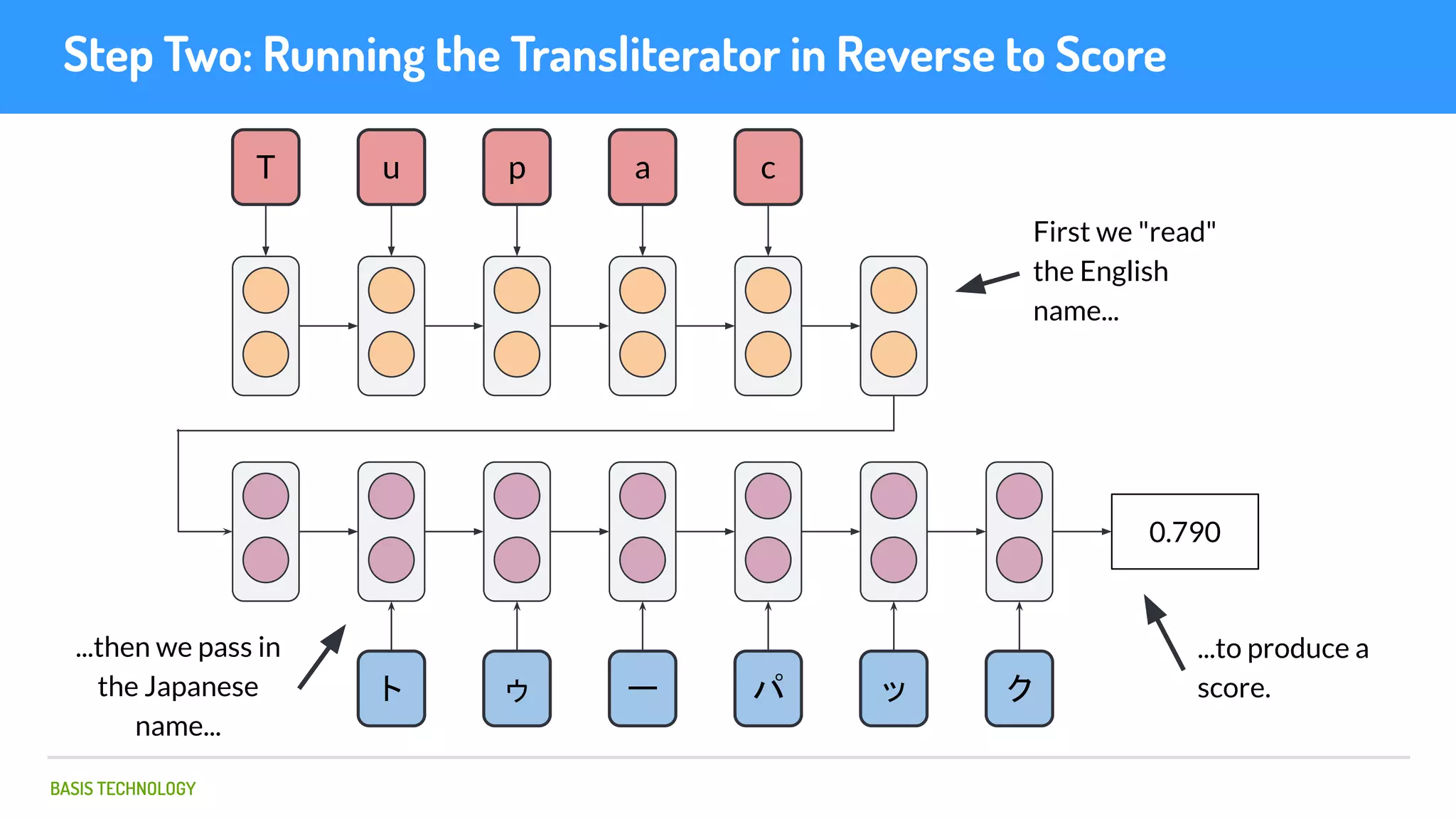
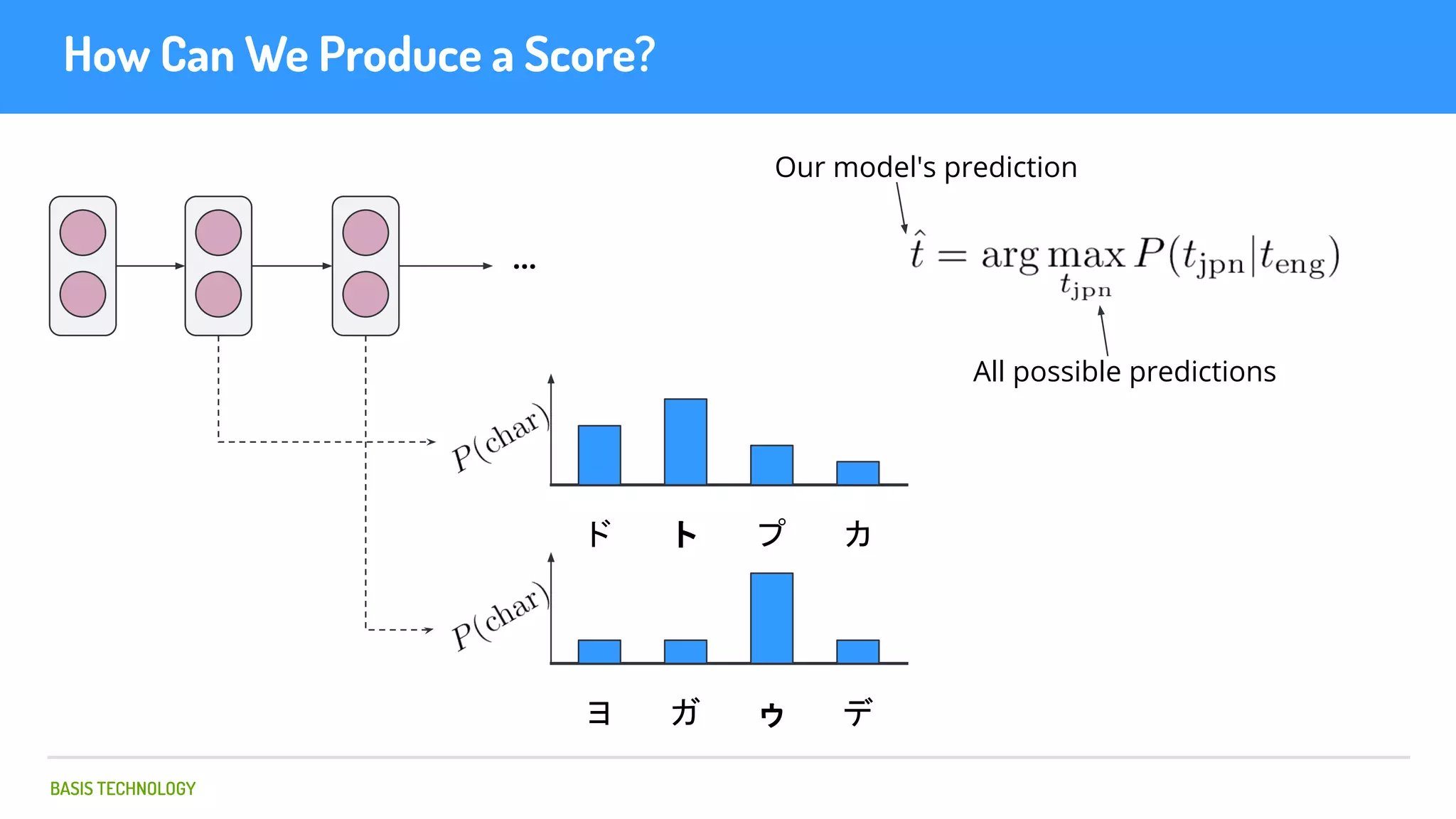
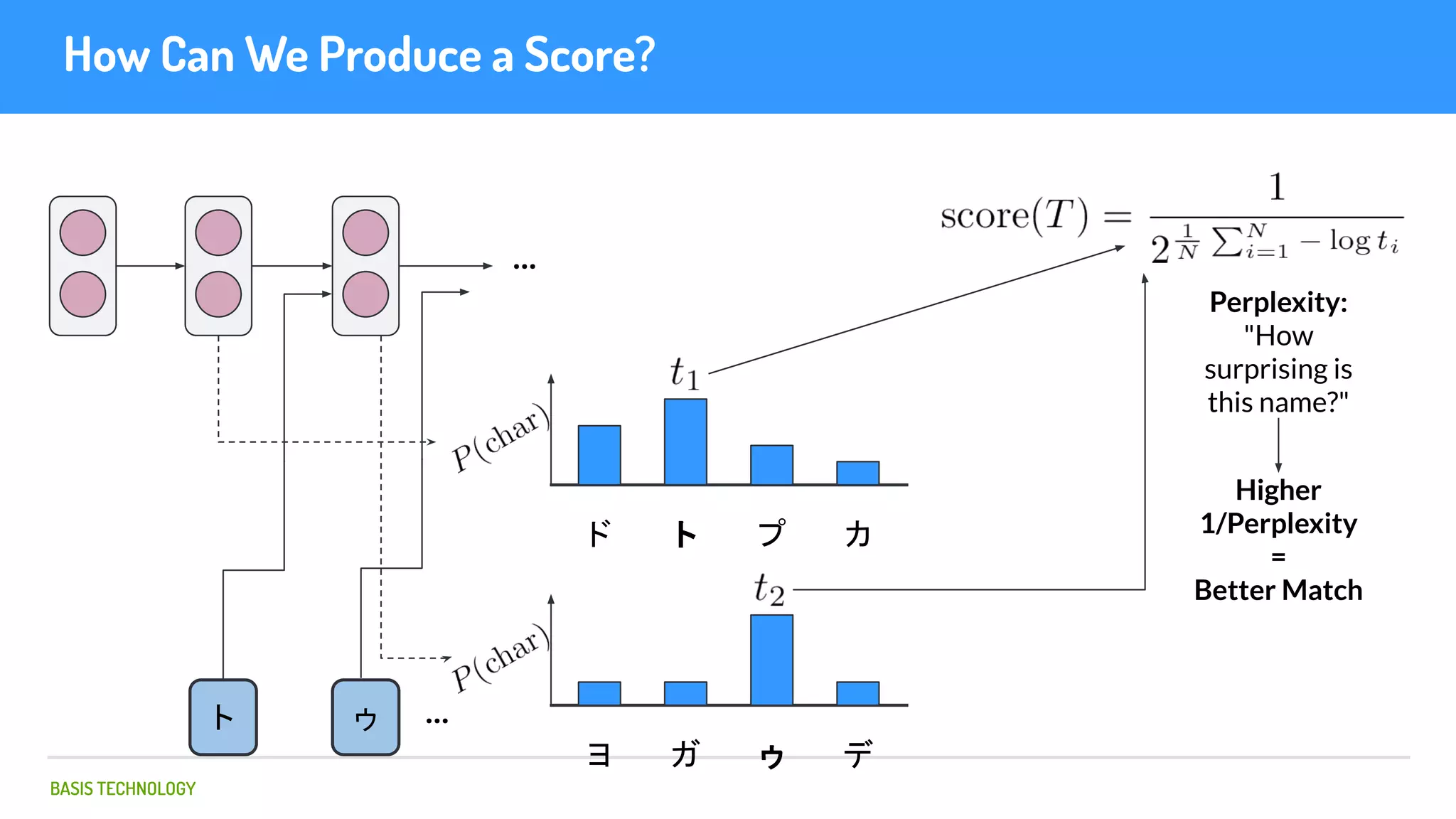
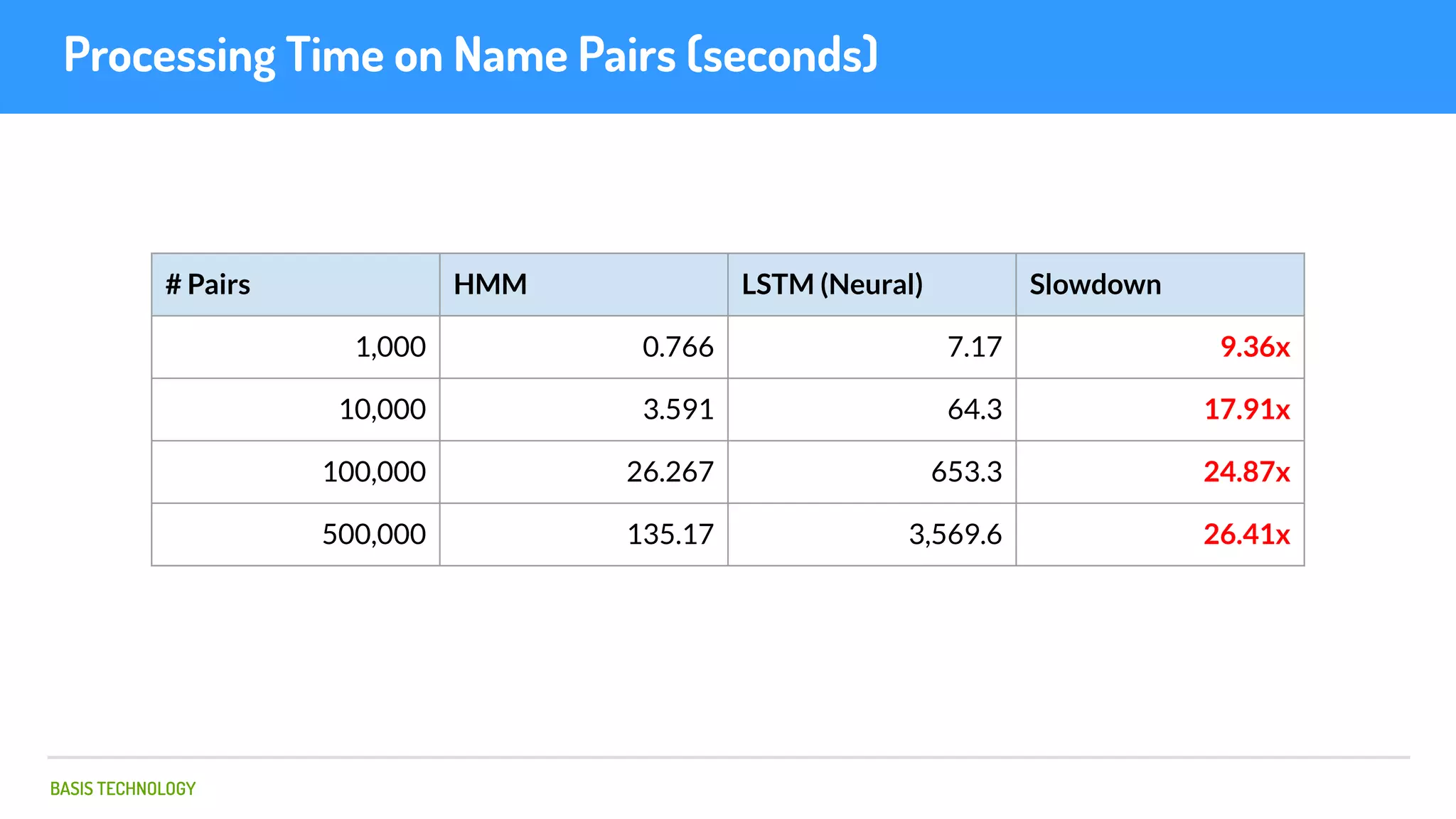
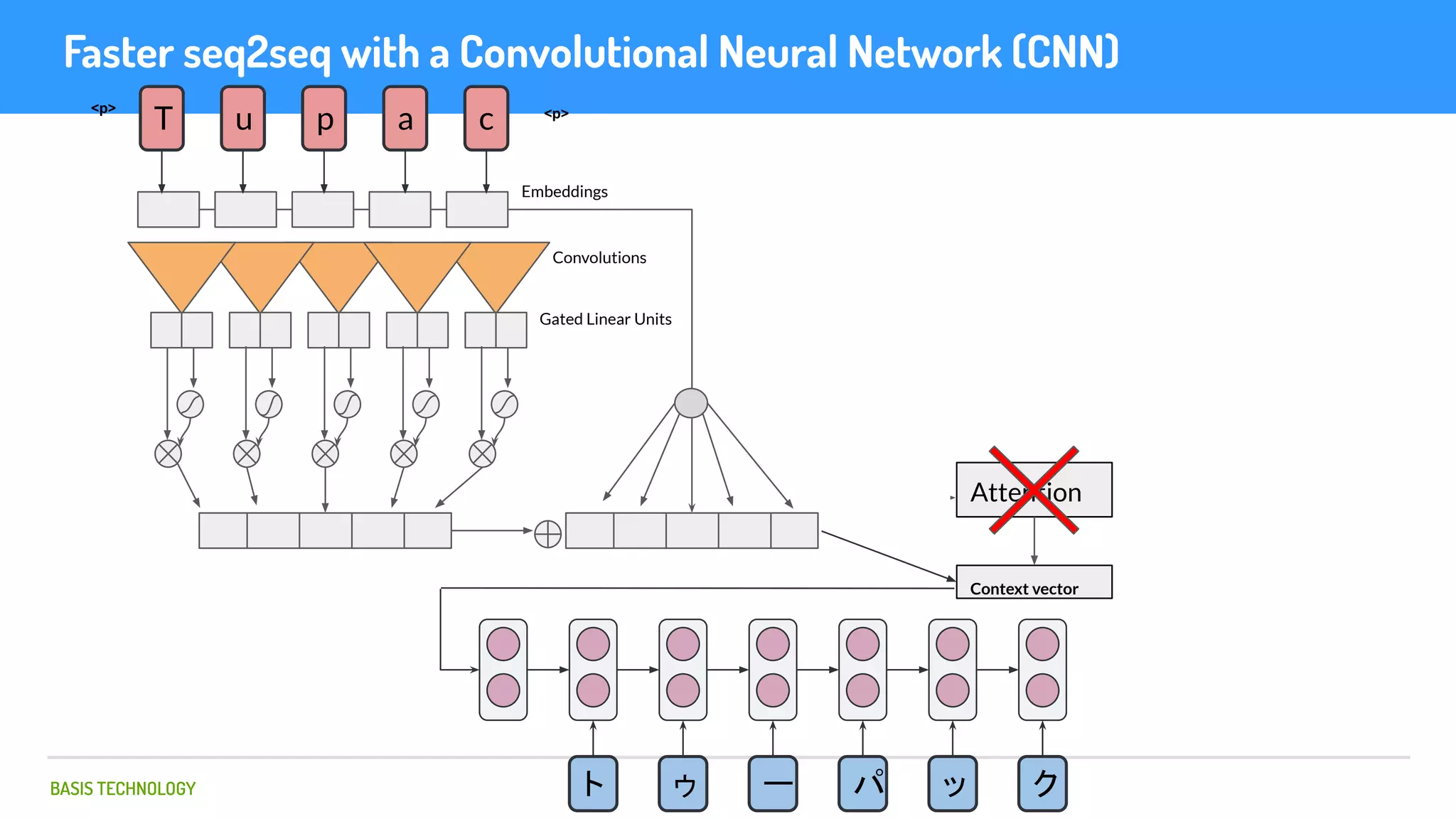
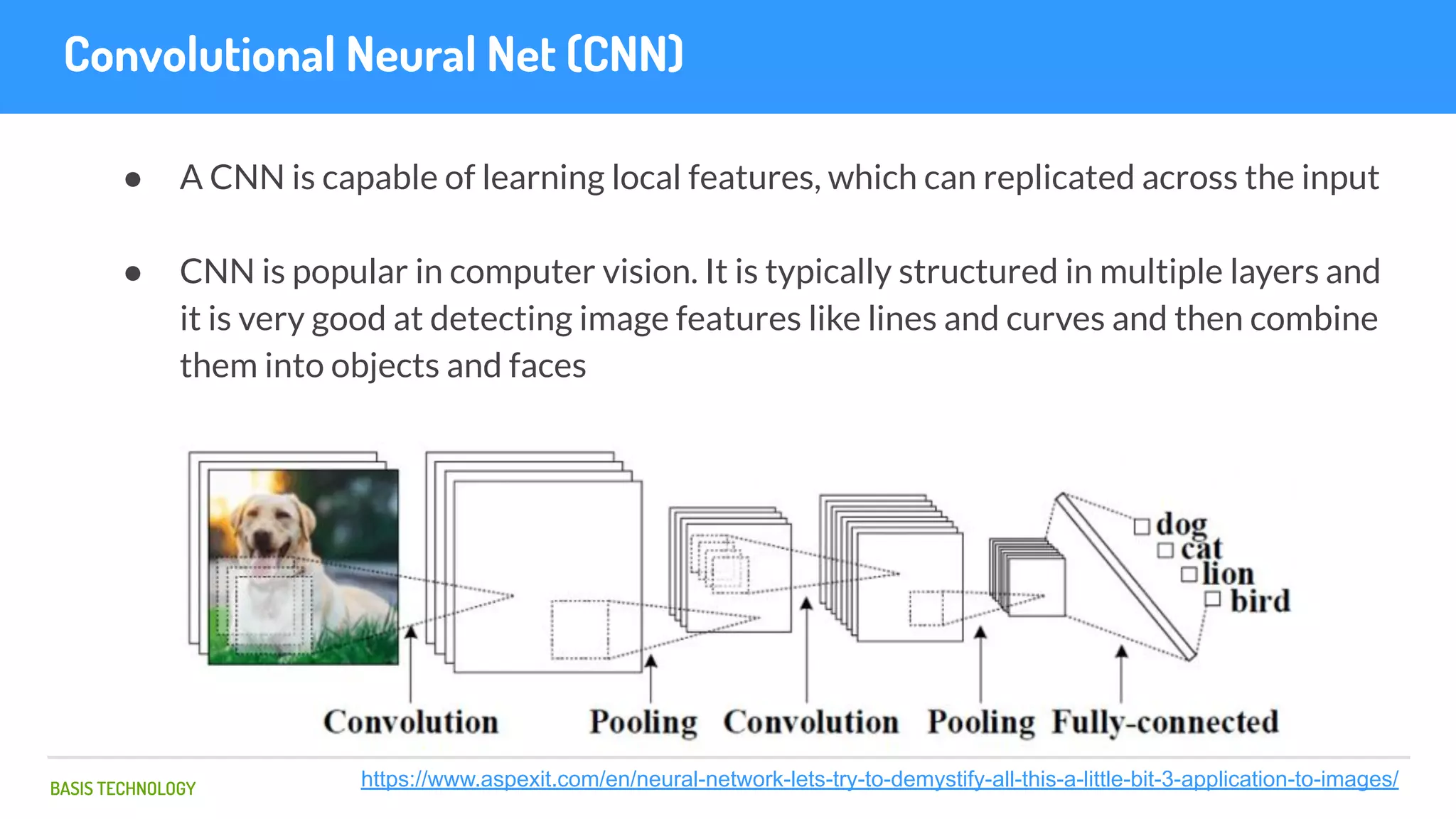
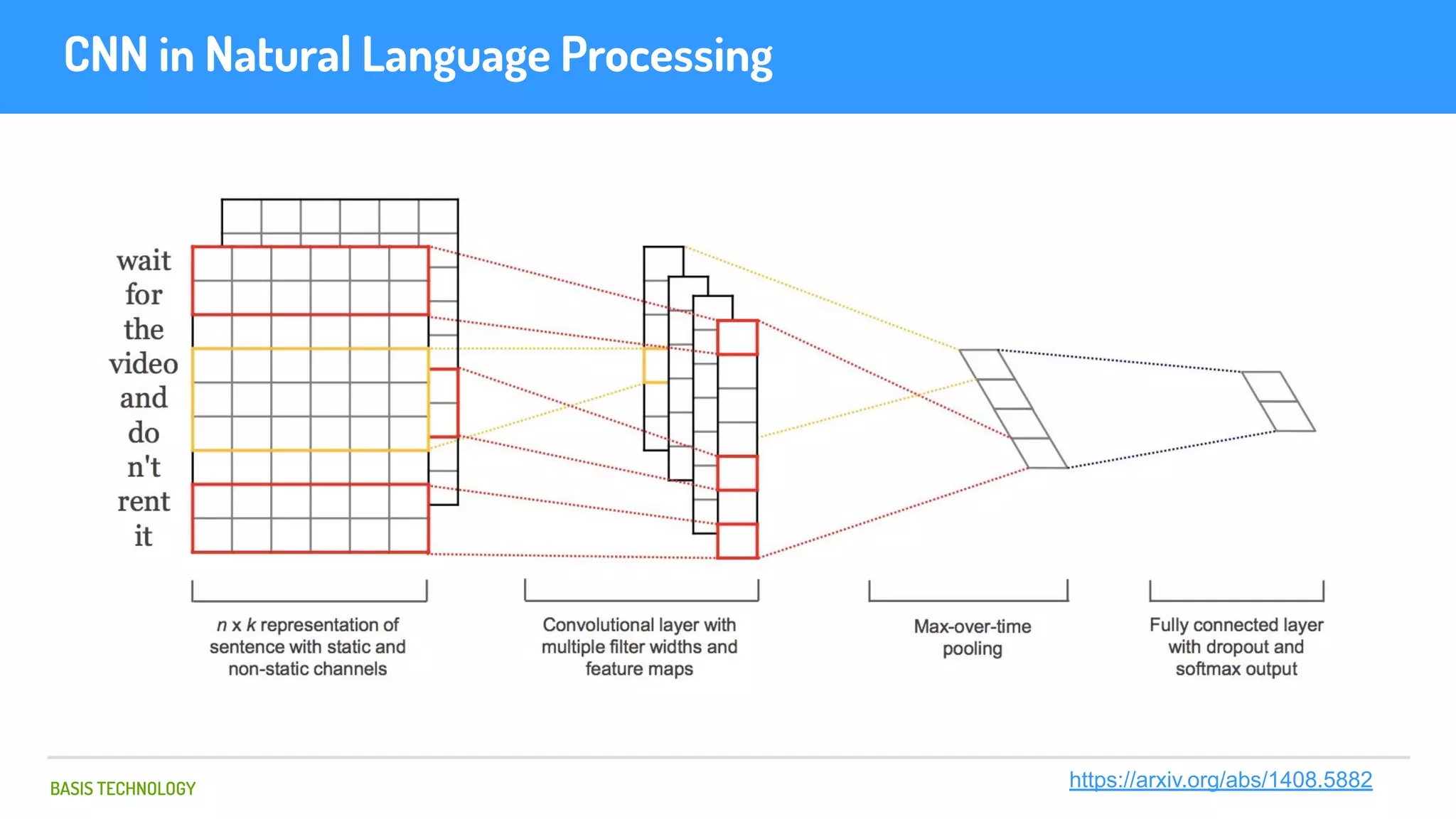
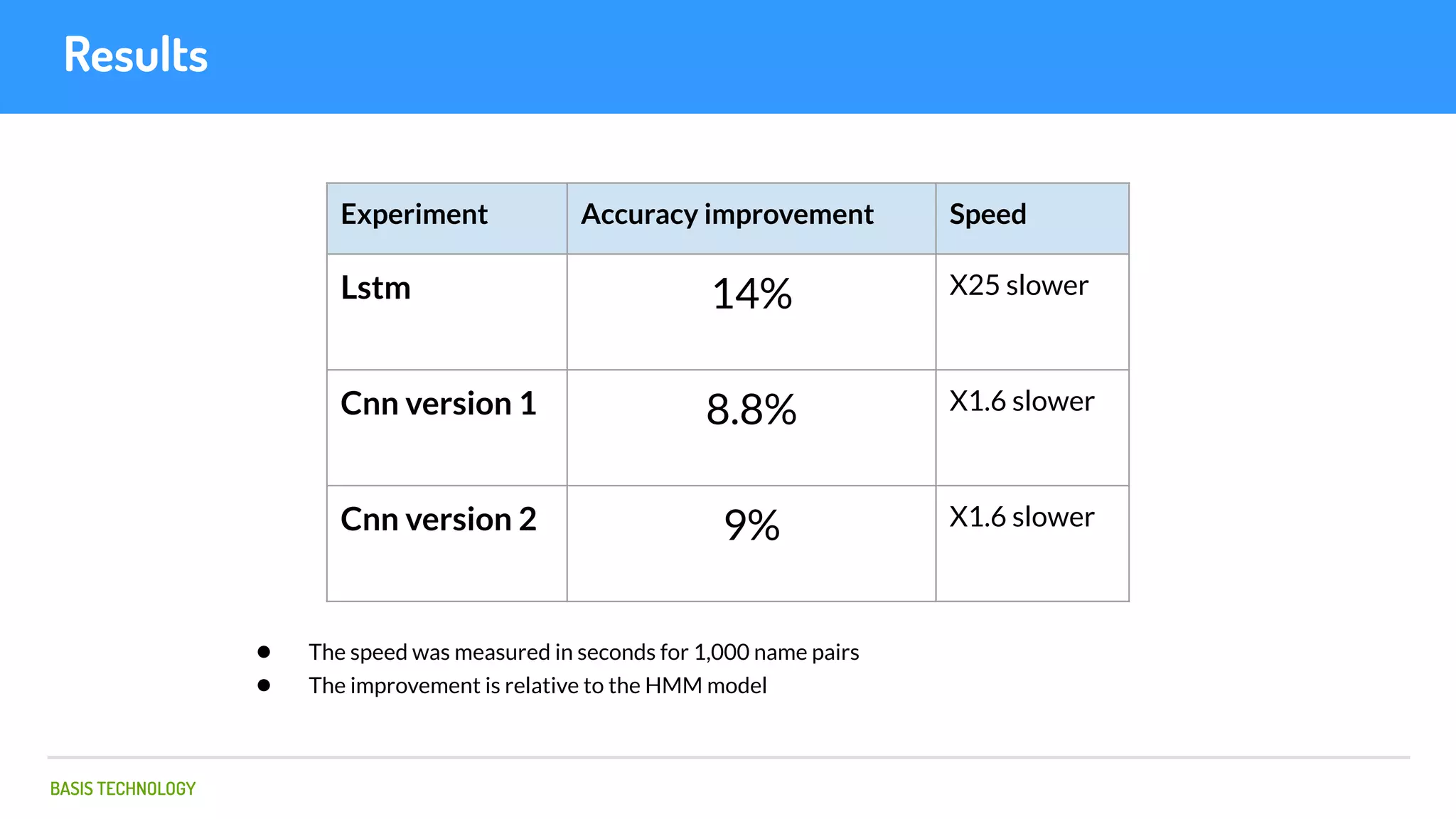
The document discusses name matching techniques using neural networks. It describes how earlier techniques like Hidden Markov Models (HMMs) had limitations in capturing context around character sequences in names. The researchers at Basis Technology developed a sequence-to-sequence model using long short-term memory (LSTM) neural networks to transliterate names between languages. While more accurate, the LSTM model was slower than HMMs. To address this, they explored using a convolutional neural network which provided speed improvements while maintaining accuracy gains over HMMs. The researchers concluded that name matching remains an open problem but data-driven neural approaches hold promise for continued advances.