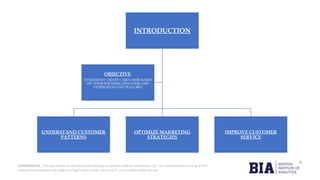
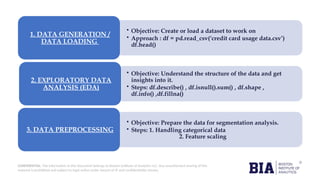
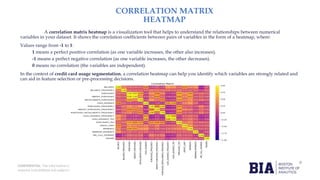
The document details a capstone project on credit card usage segmentation by Boston Institute of Analytics, focusing on developing unsupervised learning models to group customers based on their spending behavior. It outlines the project's objectives, including data loading, exploratory data analysis, preprocessing, and clustering using algorithms like k-means, with an emphasis on visualizing results for actionable insights. The findings aim to enhance marketing strategies and improve customer service through personalized offerings based on distinct customer segments.