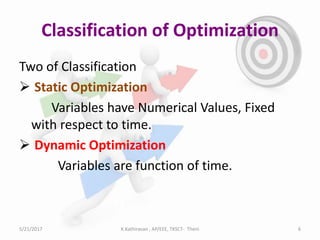
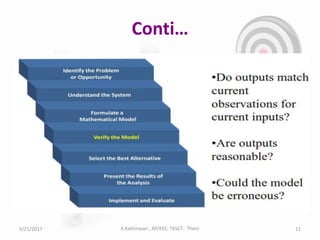
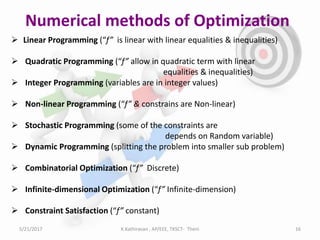
The document discusses optimization techniques for power system problems. It defines optimization as finding the maximum and minimum of functions, and describes how optimization is used in fields like electrical networks, economics, and transportation. It outlines various optimization methods like linear programming, quadratic programming, and nonlinear programming. The document also discusses how artificial intelligence techniques like expert systems, neural networks, genetic algorithms, and particle swarm optimization can be applied to solve complex power system optimization problems. Overall, the document provides an overview of optimization techniques and their importance and applications in solving power system engineering issues.