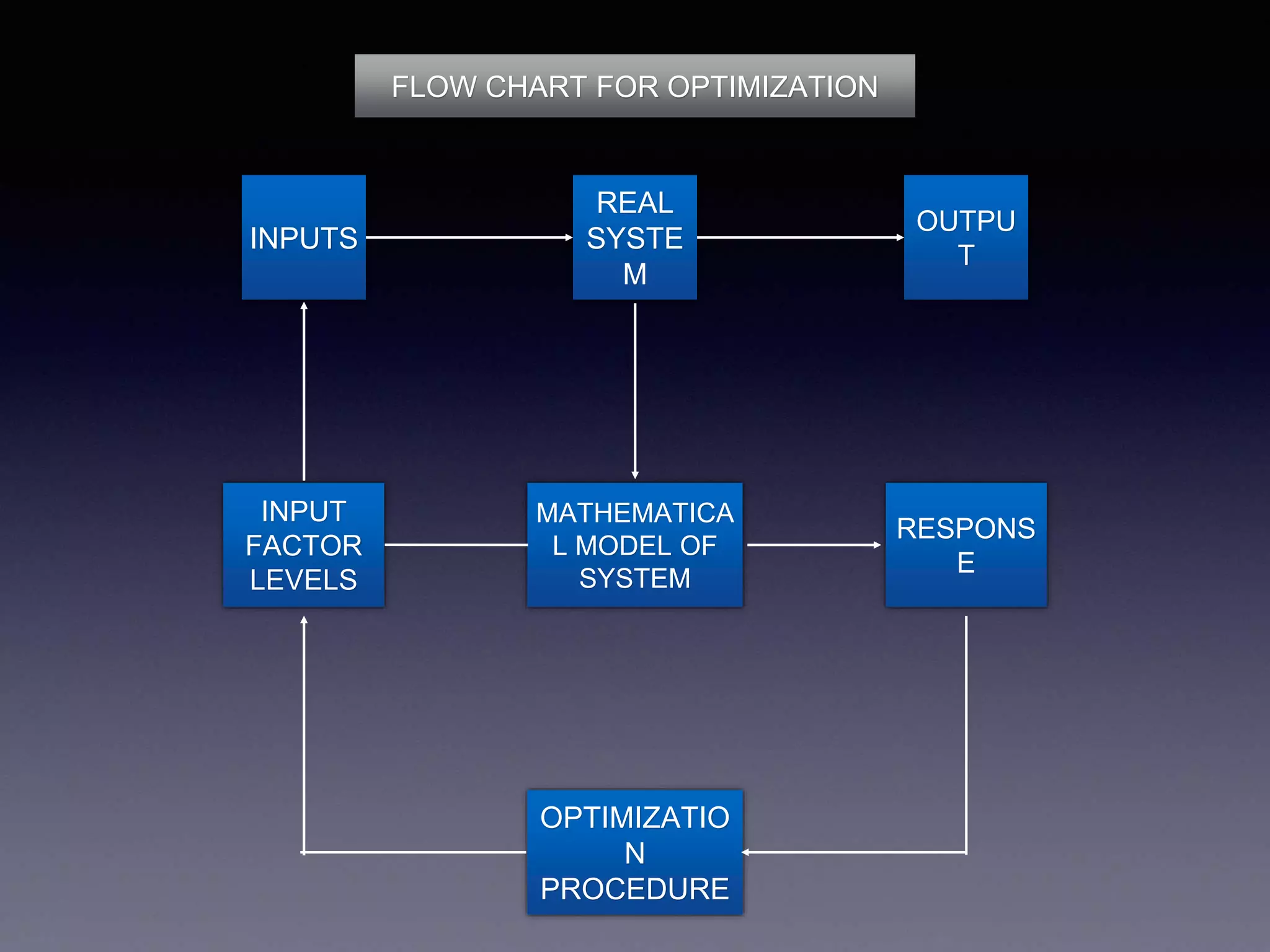
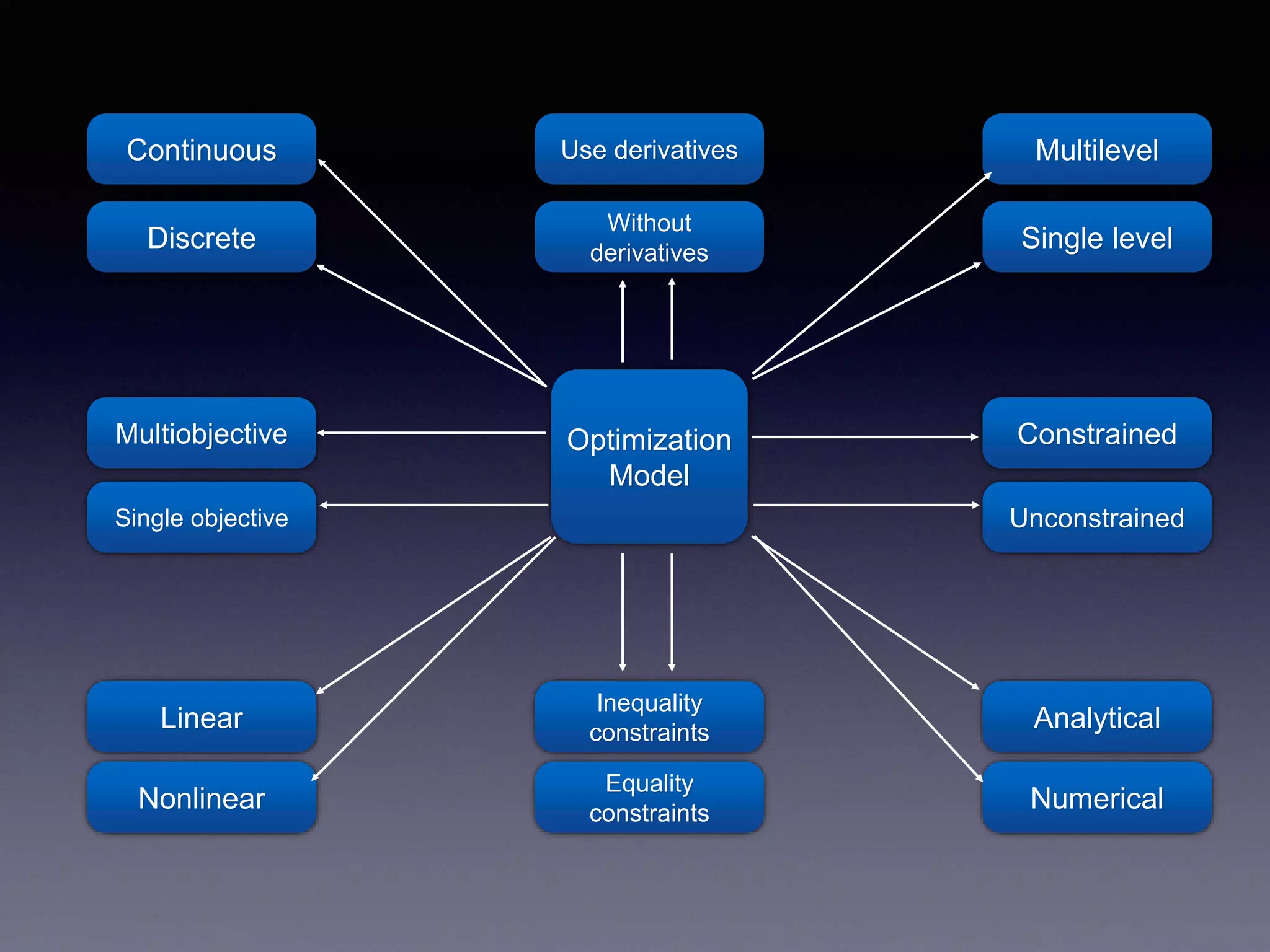
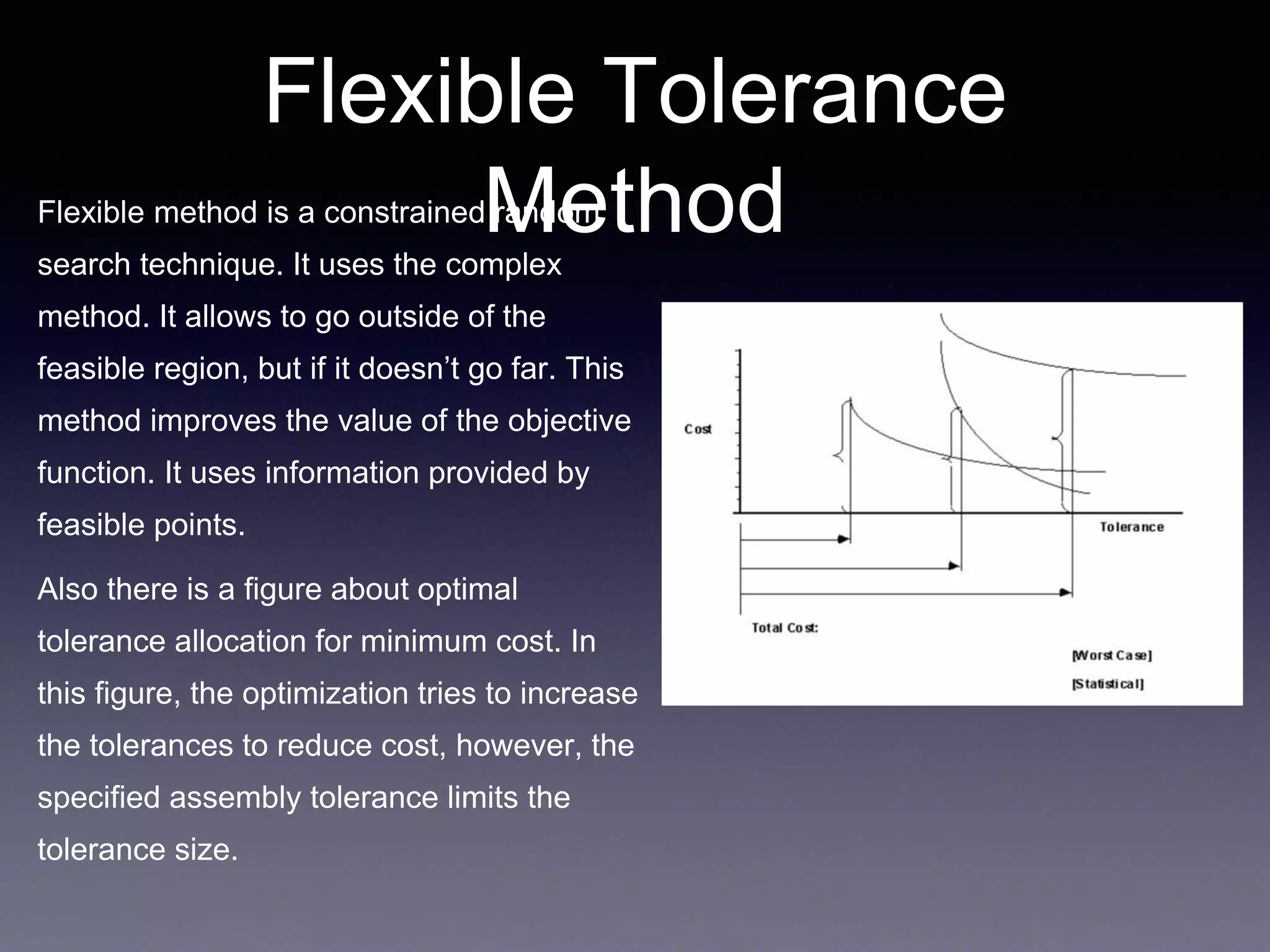
This document discusses optimization of objects and systems. It defines optimization as making something as fully perfect by finding alternative solutions to problems. It discusses how optimization is used everyday consciously or subconsciously to reach the best possible outcome with available resources. The document outlines different types of optimization problems including linear and nonlinear, single and multi-objective, constrained and unconstrained. It also discusses analytical and numerical optimization methods, including those with and without derivatives like the complex method, flexible tolerance method, and hillclimb method. Numerical methods are useful for problems that cannot be solved analytically. The document concludes with discussing methods that use first and second derivatives like Newton's method and sequential quadratic programming methods.















![REFERENCES
[1] http://adcats.et.byu.edu/Publication/87-5/WAM2.html
[2] József Farkas, Károly Jármai, Analysis and Optimum Design
of Metal Structures](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/optimizationn-190422151332/75/Optimization-19-2048.jpg)
