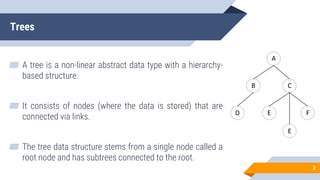
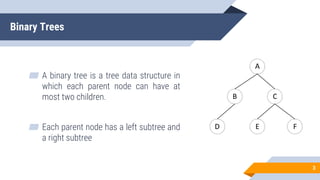
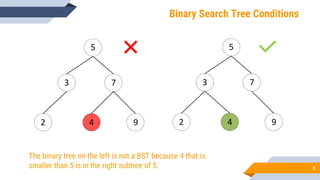
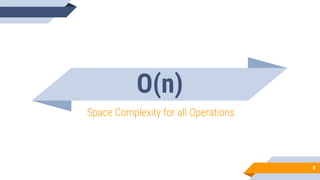
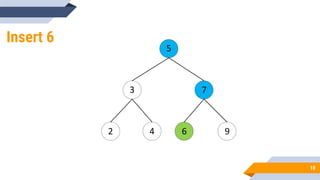
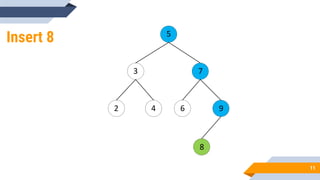
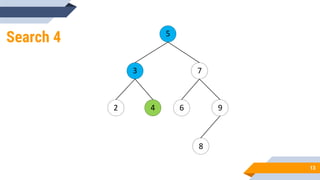
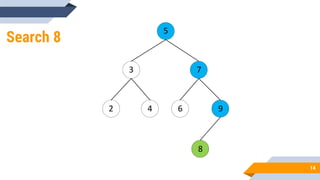
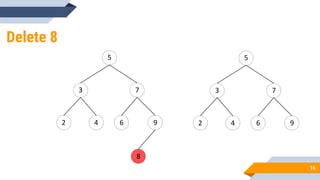
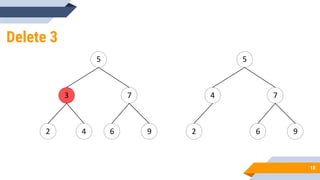
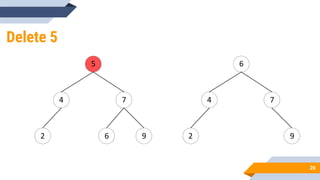
The document discusses binary search trees (BSTs). It defines BSTs as data structures that allow maintaining a sorted list of numbers in a way that allows searching in O(log n) time. The key properties of BSTs are that the left subtree of a node contains only nodes with values smaller than the node, and the right subtree contains only larger values. The document outlines common BST operations like searching, insertion, and deletion and explains how they make use of the BST properties to achieve efficient O(log n) time complexity on average. Examples are provided to illustrate each operation. Applications of BSTs include indexing for databases and dynamic sorting.