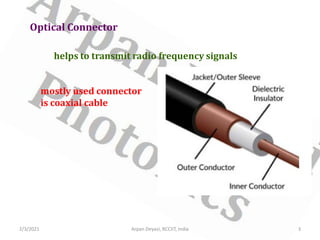
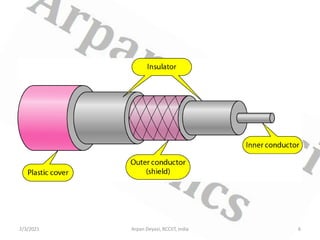
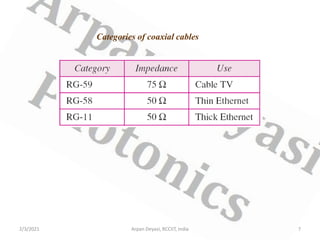
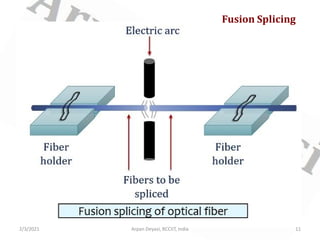
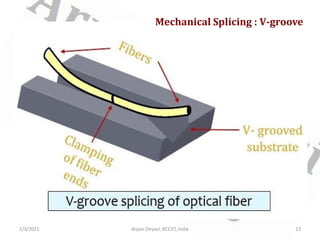
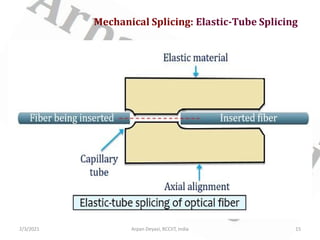
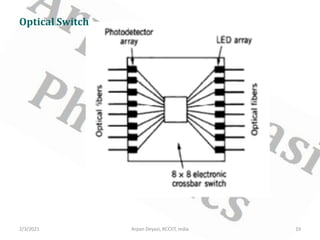
This document discusses optical waveguide components including connectors, splices, switches. It describes how optical connectors are used to transmit signals and lists features of fiber optic connectors. It also discusses different types of splices for joining optical fibers including fusion splicing and mechanical splicing. Additionally, it defines optical switches and their uses in selectively operating fibers/circuits. It lists types of optical switching and classifications of switches including mechanical and non-mechanical.