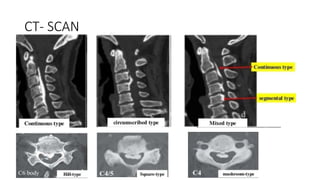
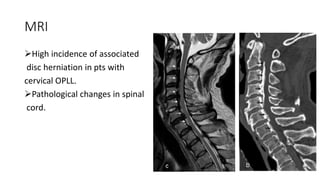
This document provides information on ossification of the posterior longitudinal ligament (OPLL). It describes the anatomy and function of the PLL, defines OPLL as ectopic ossification of the PLL, and discusses the epidemiology, pathogenesis, clinical presentation, diagnostic evaluation, treatment options, and prognosis of OPLL. Key points include that OPLL most commonly affects the cervical spine, causes myelopathy, and surgical treatment may involve anterior corpectomy or posterior laminoplasty depending on the location and severity of ossification.