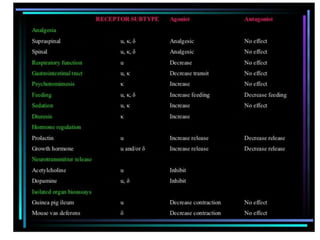
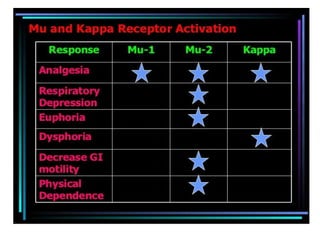
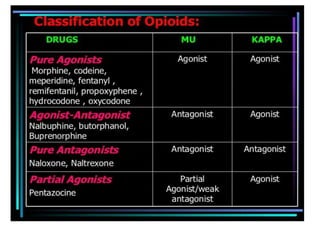
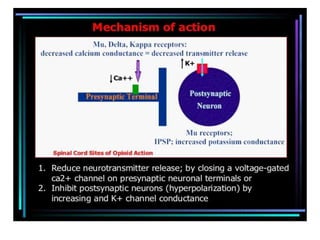
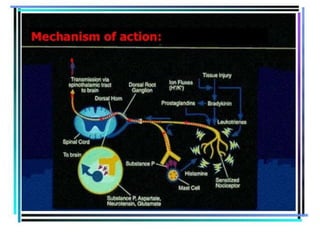
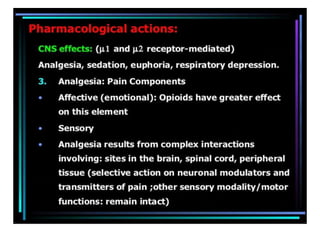
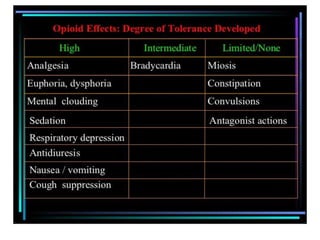
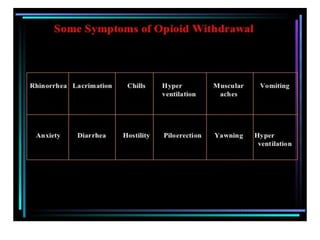
1. Mu opioid receptors mediate positive reinforcement following direct or indirect activation and are central to understanding addiction. Recent data from native neurons confirms that mu receptor signaling is strongly dependent on the agonist.
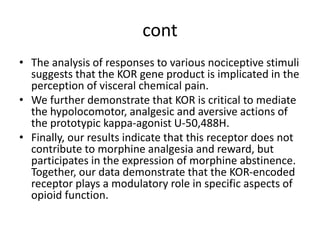
2. Kappa opioid receptors (KOR) are widely expressed in the central nervous system where they mediate opioid analgesia and mood effects. Knockout mice studies show that KOR contributes to perception of visceral pain and mediates the effects of the kappa agonist U-50,488H but not morphine analgesia or reward.
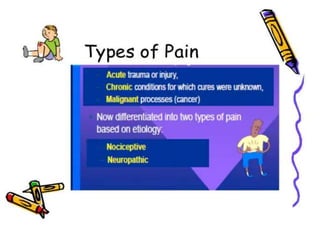
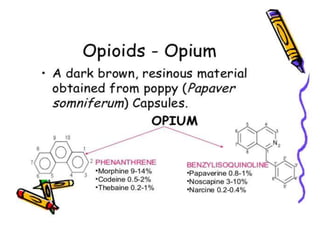
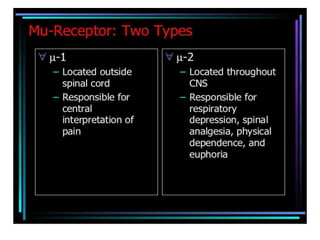
3. Kappa receptors are located throughout the central nervous system including the hypothalamus, periaqueductal gray and claustrum as well as the