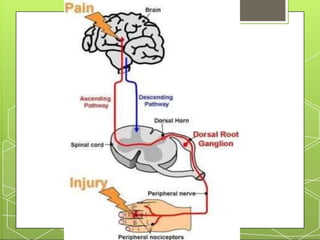
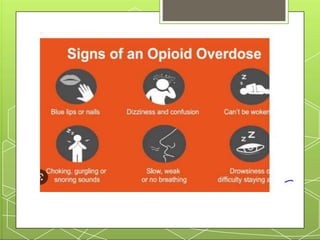
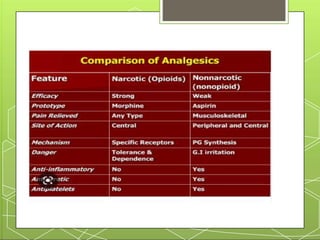
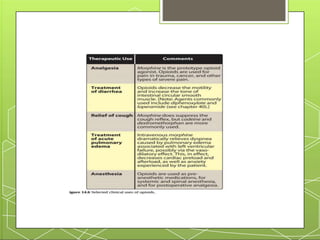
This document provides an overview of narcotic analgesia and summarizes key points about pain mechanisms, opioid and non-opioid analgesics, and the nursing process for administering analgesics. It describes how chemicals released during tissue damage stimulate pain receptors, causing nerve impulses that are sensed as pain in the brain. Opioid analgesics work in the central nervous system by binding to mu and kappa receptors, reducing pain sensation. Common opioid analgesics include morphine, codeine, and fentanyl. Non-opioid analgesics like NSAIDs reduce inflammation and pain at peripheral sites. The nursing process for administering analgesics includes assessing pain and vital signs, monitoring for side effects, providing patient education, and intervening as needed.