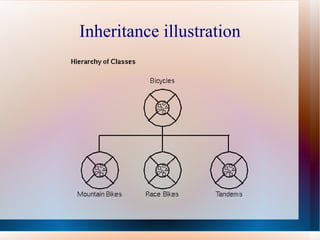
This document provides an overview of object-oriented programming concepts in Java including inheritance, polymorphism, abstraction, and encapsulation. It also discusses control structures like if/else statements and switches as well as repetition structures like while, do-while, and for loops. Arithmetic operations in Java like addition, subtraction, multiplication, and division are also mentioned.