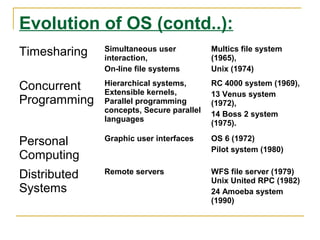
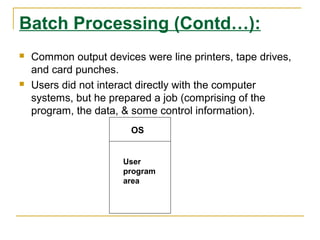
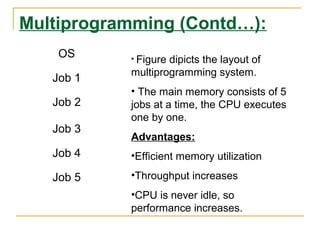
This document provides an overview of operating systems including definitions, functions, evolution, and types. It defines an operating system as software that enables computer hardware to work and interfaces between applications and hardware. Key points covered include: the structure of OS with hardware, software, system programs and applications; evolution from batch processing to timesharing and personal computing; main functions like memory management and I/O control; and types of single-user and multi-user operating systems. Examples discussed are Windows, Linux, Unix, and DOS.