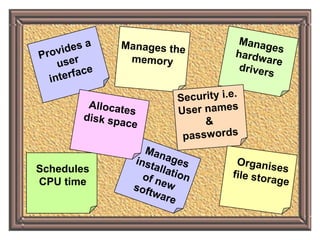
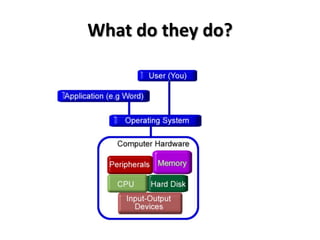
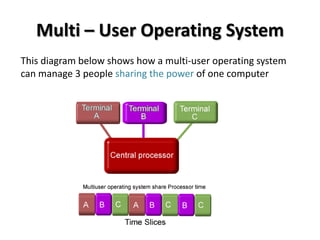
The document discusses operating systems, their functions, and examples. It explains that an operating system schedules CPU time, loads and runs applications, communicates with hardware, and provides security and file management. The document also discusses multi-user operating systems and how they allow powerful computers to be shared among multiple users simultaneously.