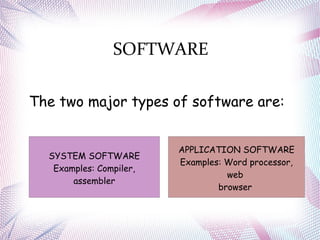
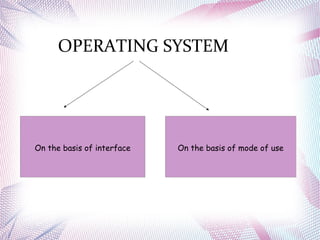
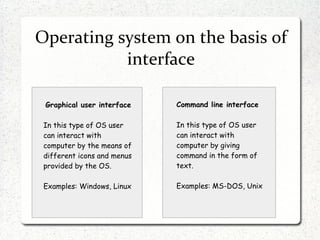
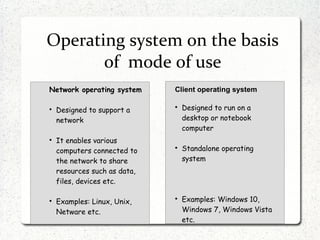
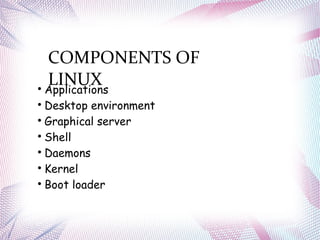
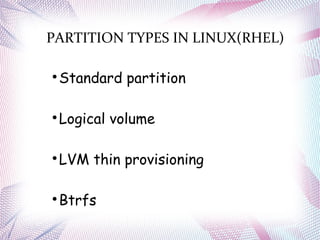
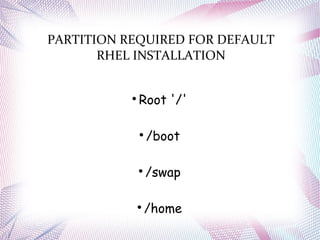
The document discusses different operating systems including Linux, Windows, Netware and Unix. It describes that an operating system is system software that manages computer hardware and resources. It provides functions like device management, process management, memory management etc. Operating systems can be classified based on interface like graphical or command line, and based on usage like network OS or client OS. Examples of different Windows and Linux operating systems are provided along with their components and key principles. The document also discusses OS upgrading, updating and dual boot systems.