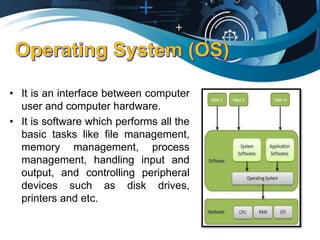
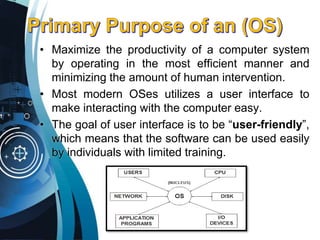
This document discusses computer viruses and operating systems. It begins by defining an operating system as an interface between the user and computer hardware that manages tasks like file handling and device control. A GUI is described as a graphics-based user interface using elements like windows and icons. Computer viruses can spread via flash drives, email attachments, and internet downloads. Some notable viruses mentioned include ILOVEYOU from 2000, Blaster worm of 2003, and MyDoom of 2004. Types of viruses include boot sector, direct action, and resident viruses. The document concludes by recommending antivirus software and caution when downloading files to prevent virus infections.