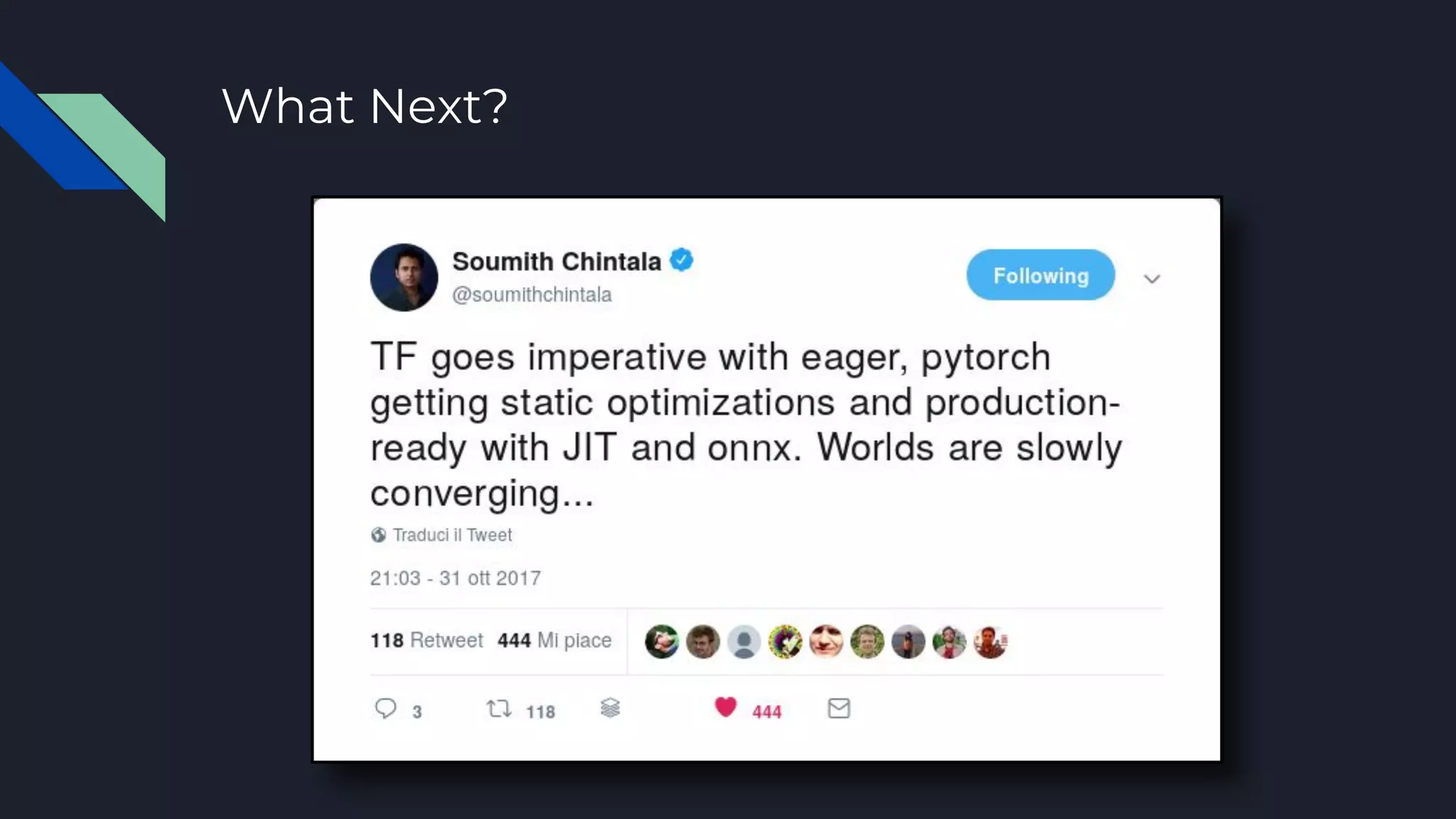
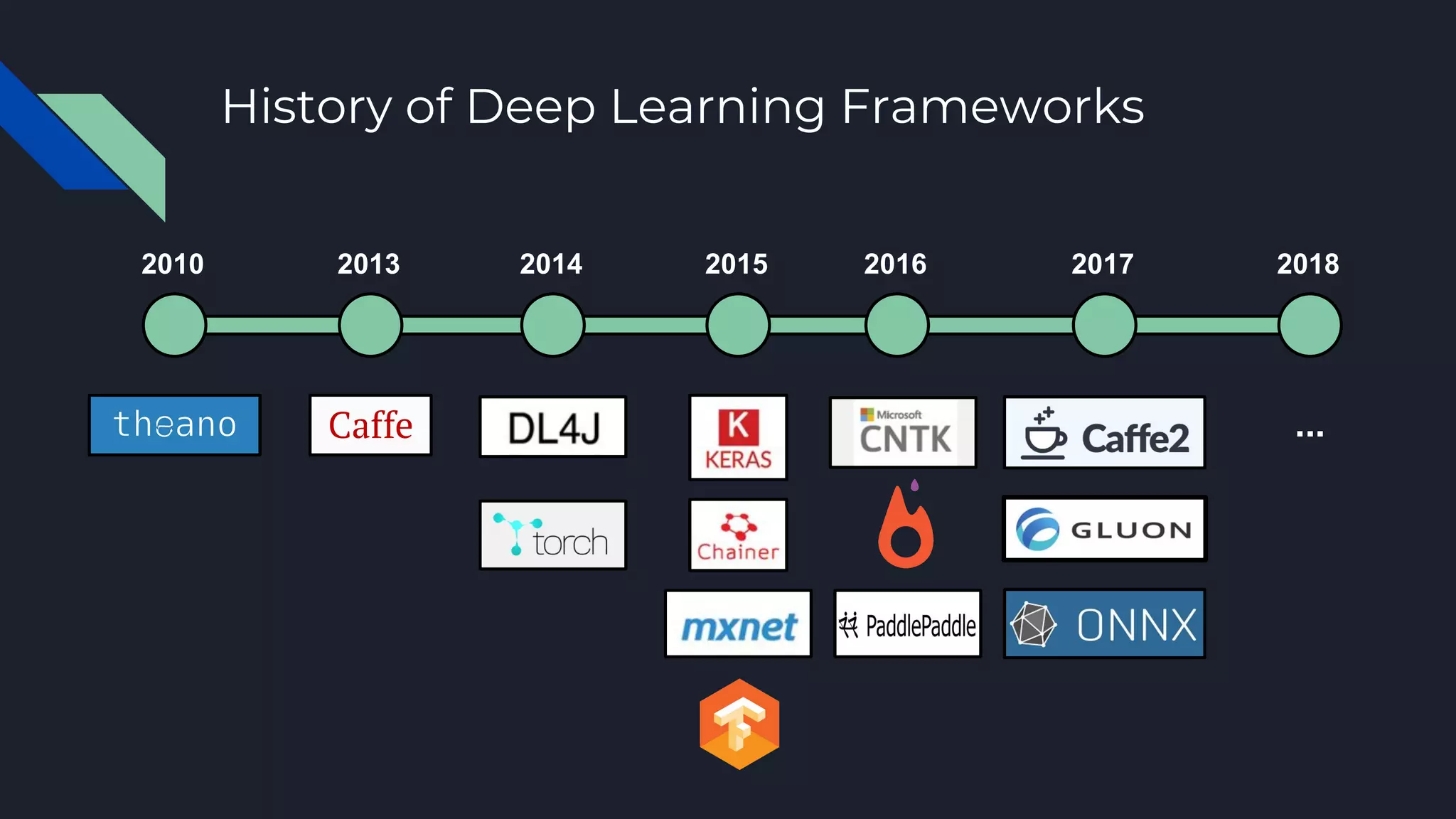
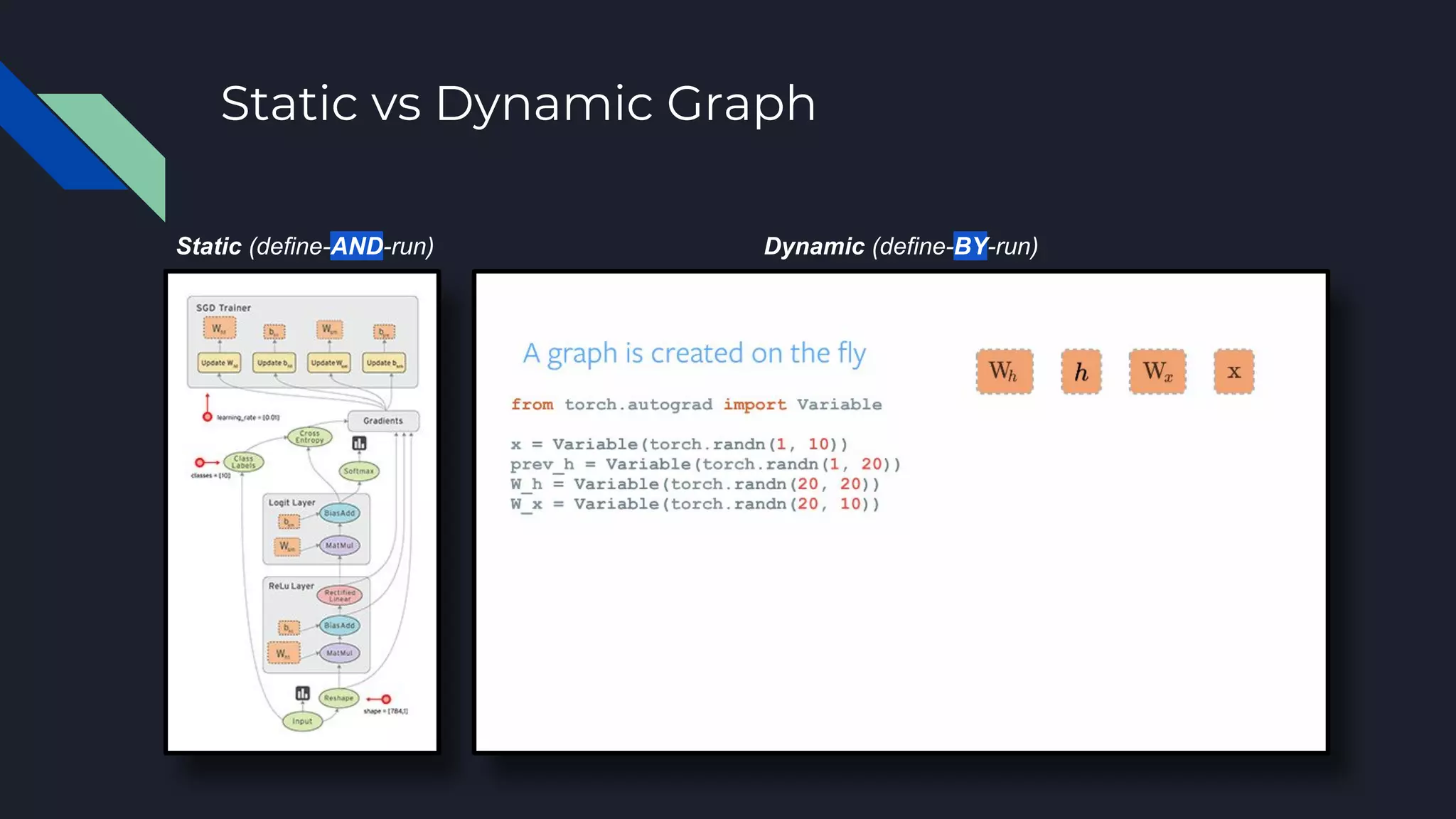
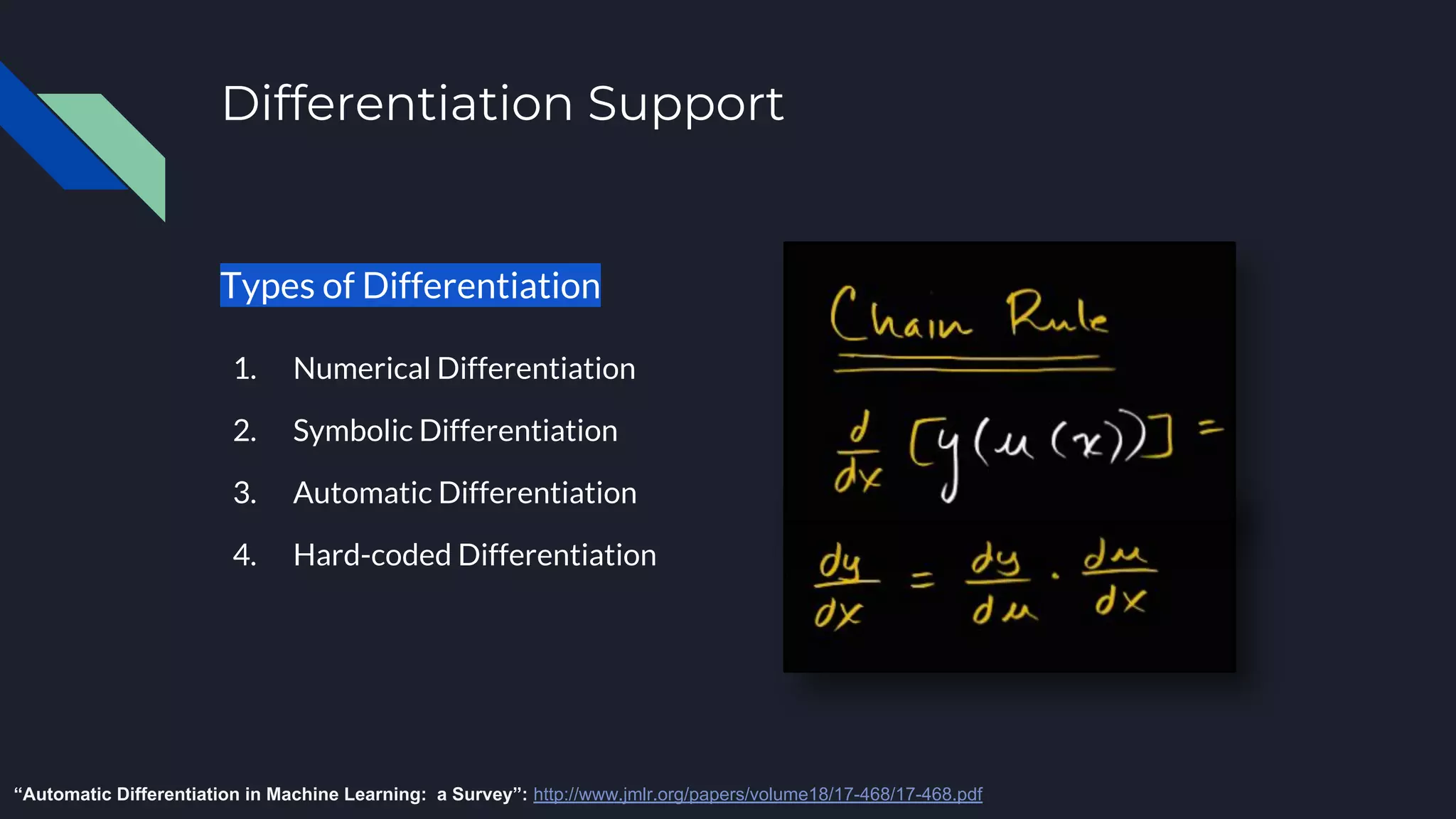
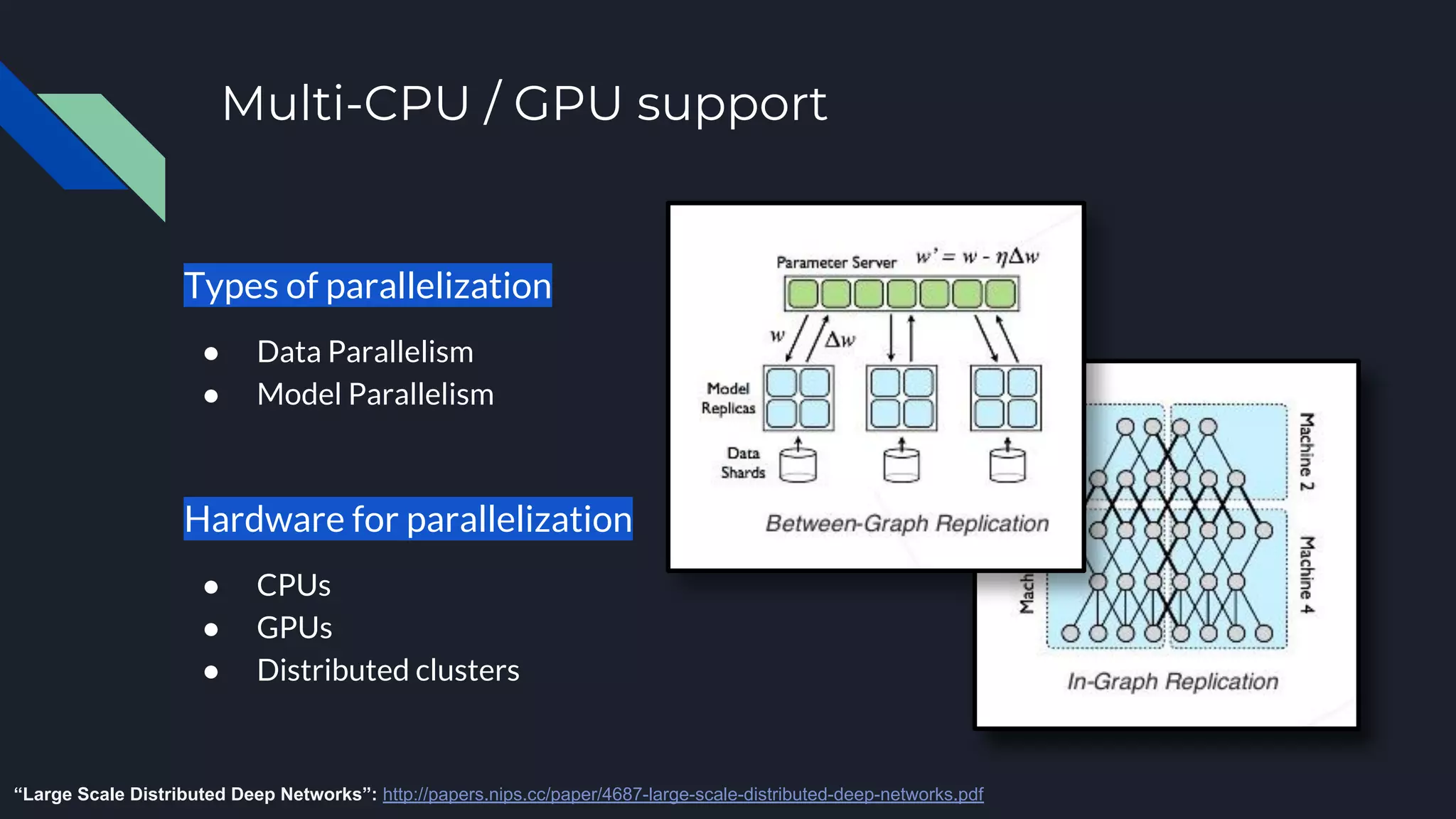
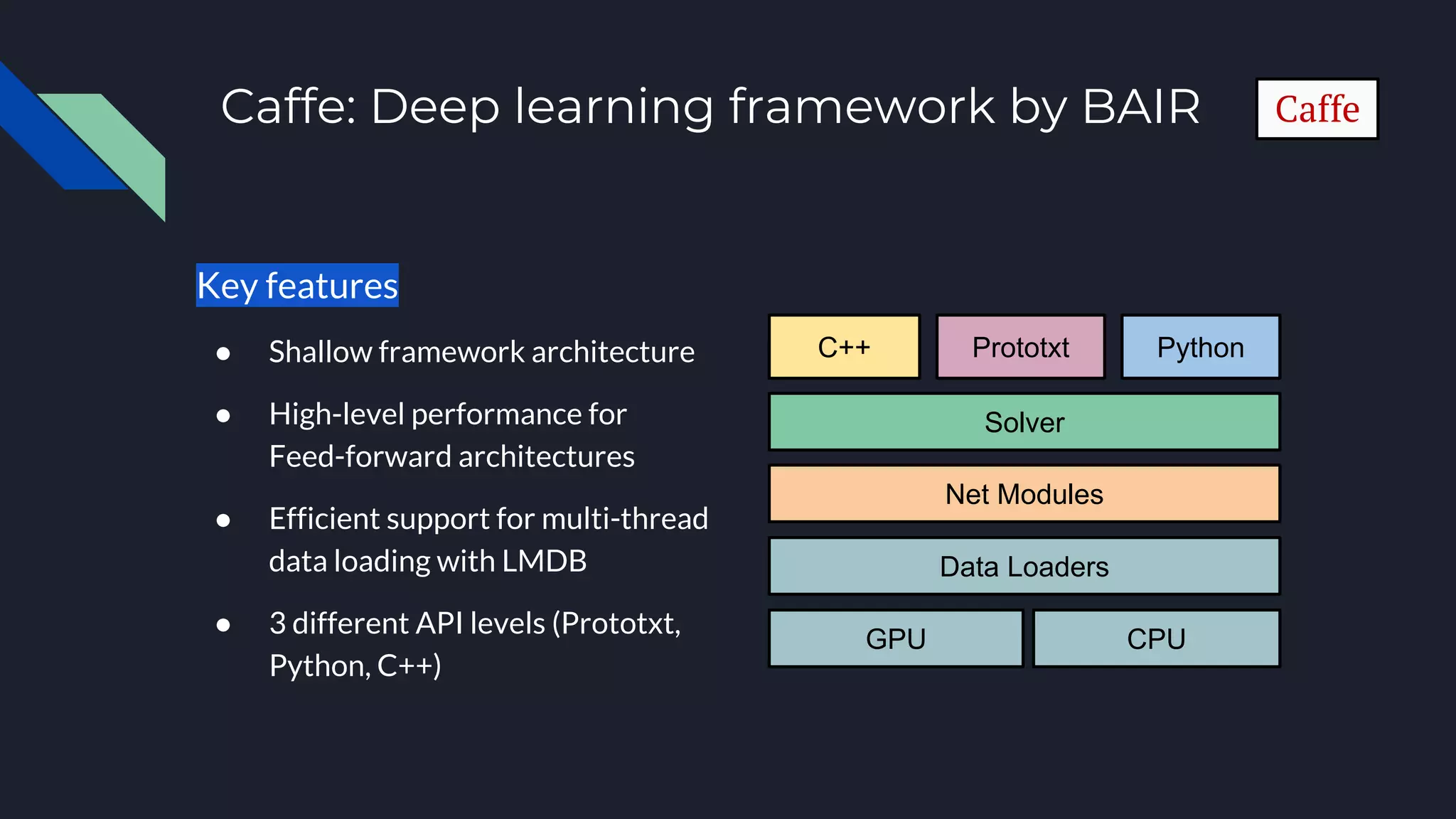
This document provides an overview of open-source deep learning frameworks. It discusses the history and evolution of frameworks from 2010 to present. The main frameworks covered are Caffe, TensorFlow, and PyTorch. Each framework is characterized by features like differentiation support, hardware acceleration, model types, and licensing. Practical advice is given to choose a framework based on the task and existing resources rather than sticking to one for all projects. The document aims to help researchers and practitioners understand and select among leading deep learning software options.











![[Hands-on (15 minutes)] Training a
ConvNet with Caffe](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/frameworksfordeeplearning-190107120355/75/Open-Source-Frameworks-for-Deep-Learning-an-Overview-27-2048.jpg)


![[Hands-on (15 minutes)] Training a
ConvNet with Tensorflow](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/frameworksfordeeplearning-190107120355/75/Open-Source-Frameworks-for-Deep-Learning-an-Overview-31-2048.jpg)

![[Hands-on (15 minutes)] Training a
ConvNet with Pytorch](https://image.slidesharecdn.com/frameworksfordeeplearning-190107120355/75/Open-Source-Frameworks-for-Deep-Learning-an-Overview-35-2048.jpg)