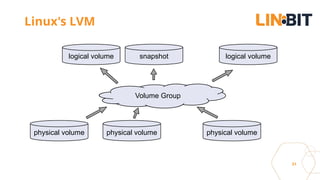
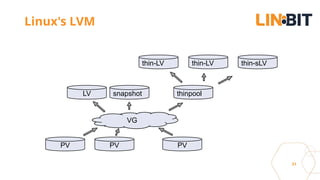
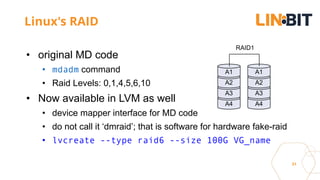
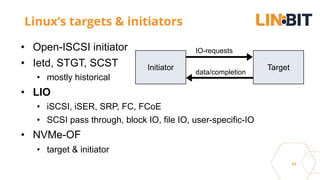
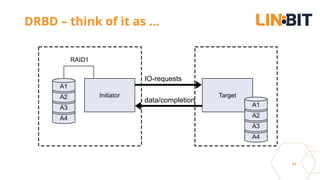
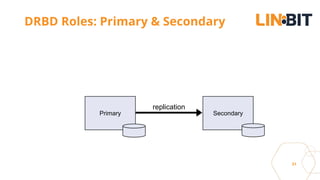
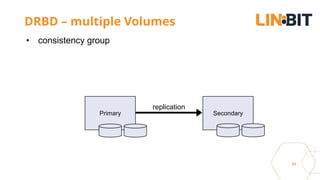
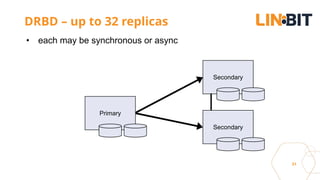
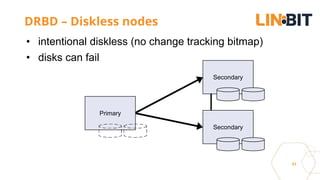
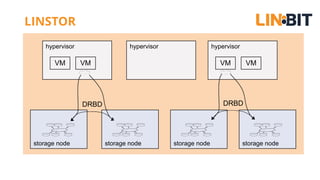
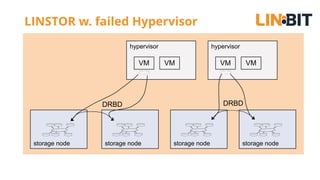
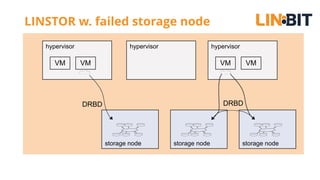
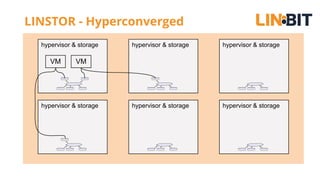
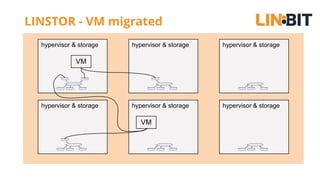
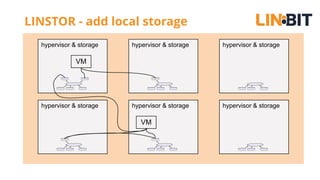
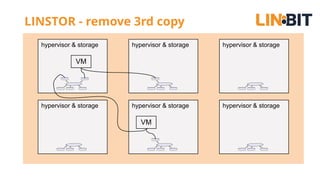
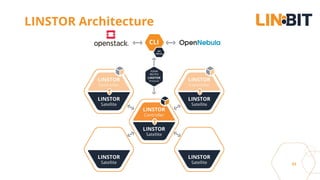
This document discusses Linux storage technologies like LVM, RAID, SSD caching, deduplication, targets and initiators that can provide persistent container storage. It describes DRBD for replicating block devices across nodes, LINSTOR for building storage from generic nodes to provide storage for container orchestrators, and LINBIT's work with Intel on a data management platform using LINSTOR with Swordfish API and NVMe-oF support.