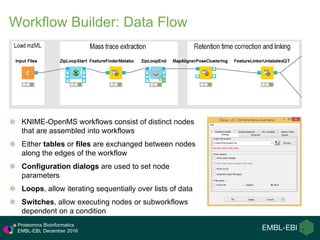
The document provides an overview of OpenMS, an open-source framework for computational mass spectrometry, highlighting its modularity, workflow capabilities, and integration with various tools such as KNIME and Galaxy. It details different workflows for protein identification and quantification, including label-free methods, and discusses the extensive collection of software tools available within OpenMS. Additionally, it emphasizes the framework's compatibility across different operating systems and its application in large-scale proteomics research.