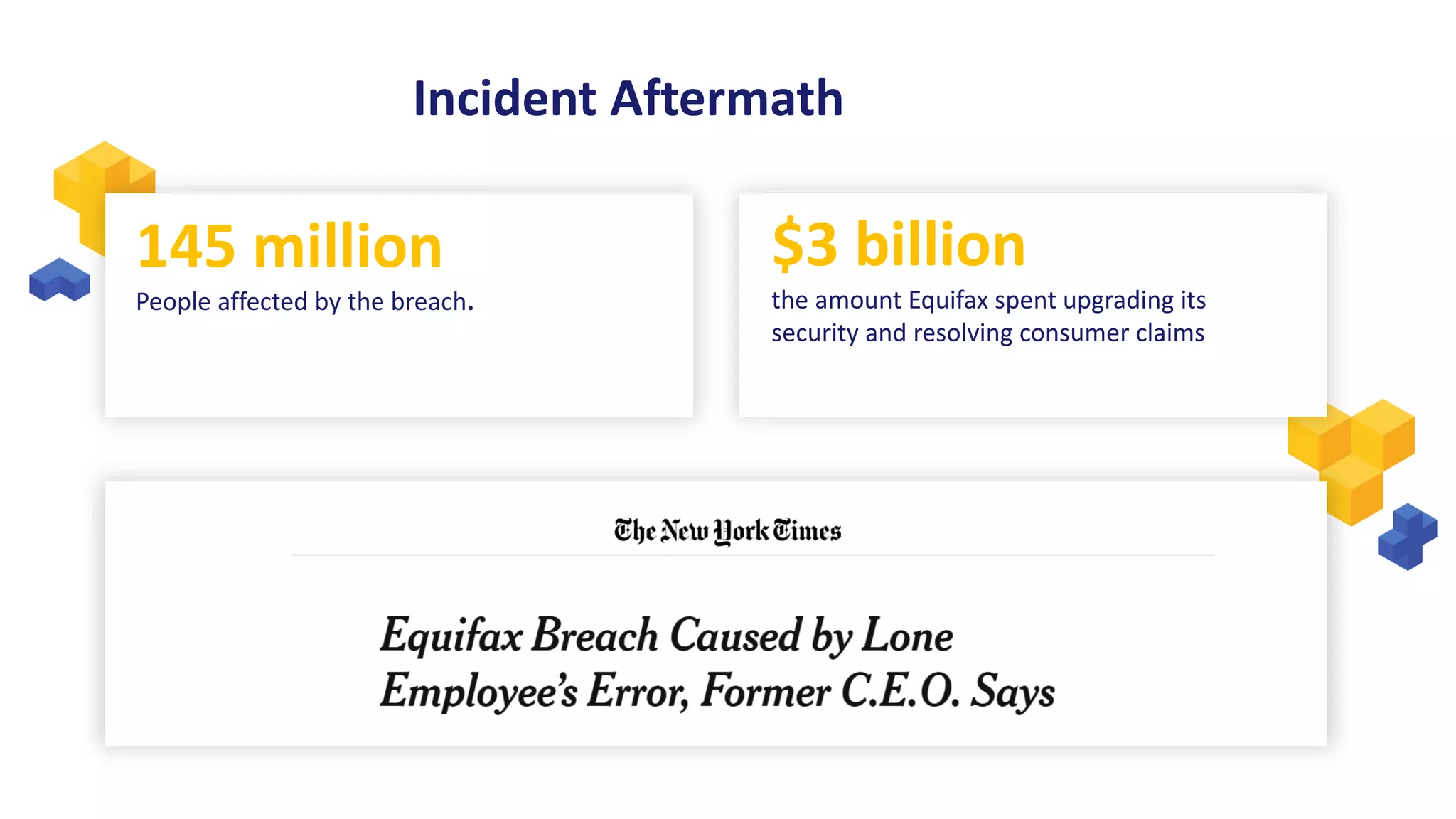
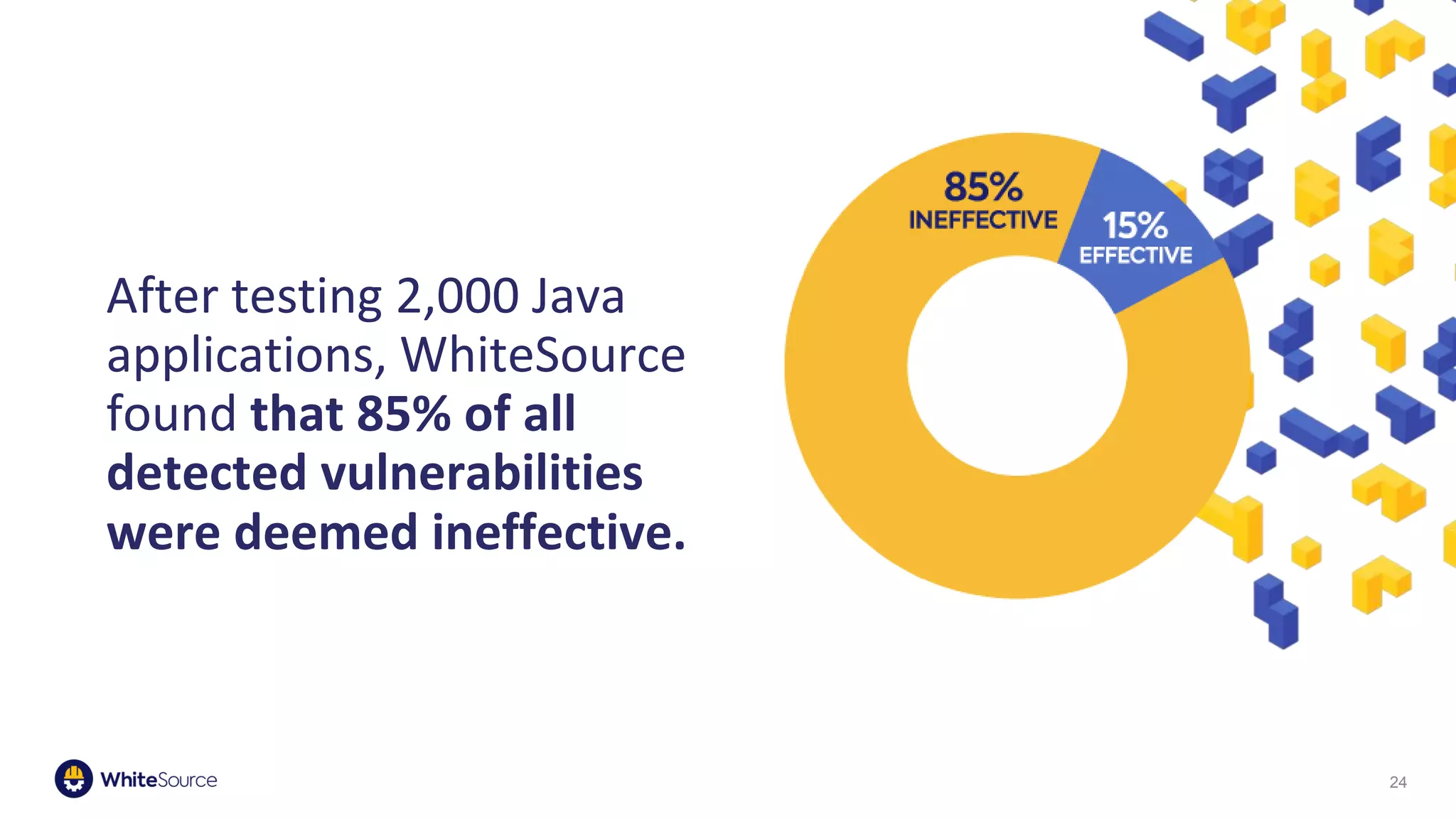
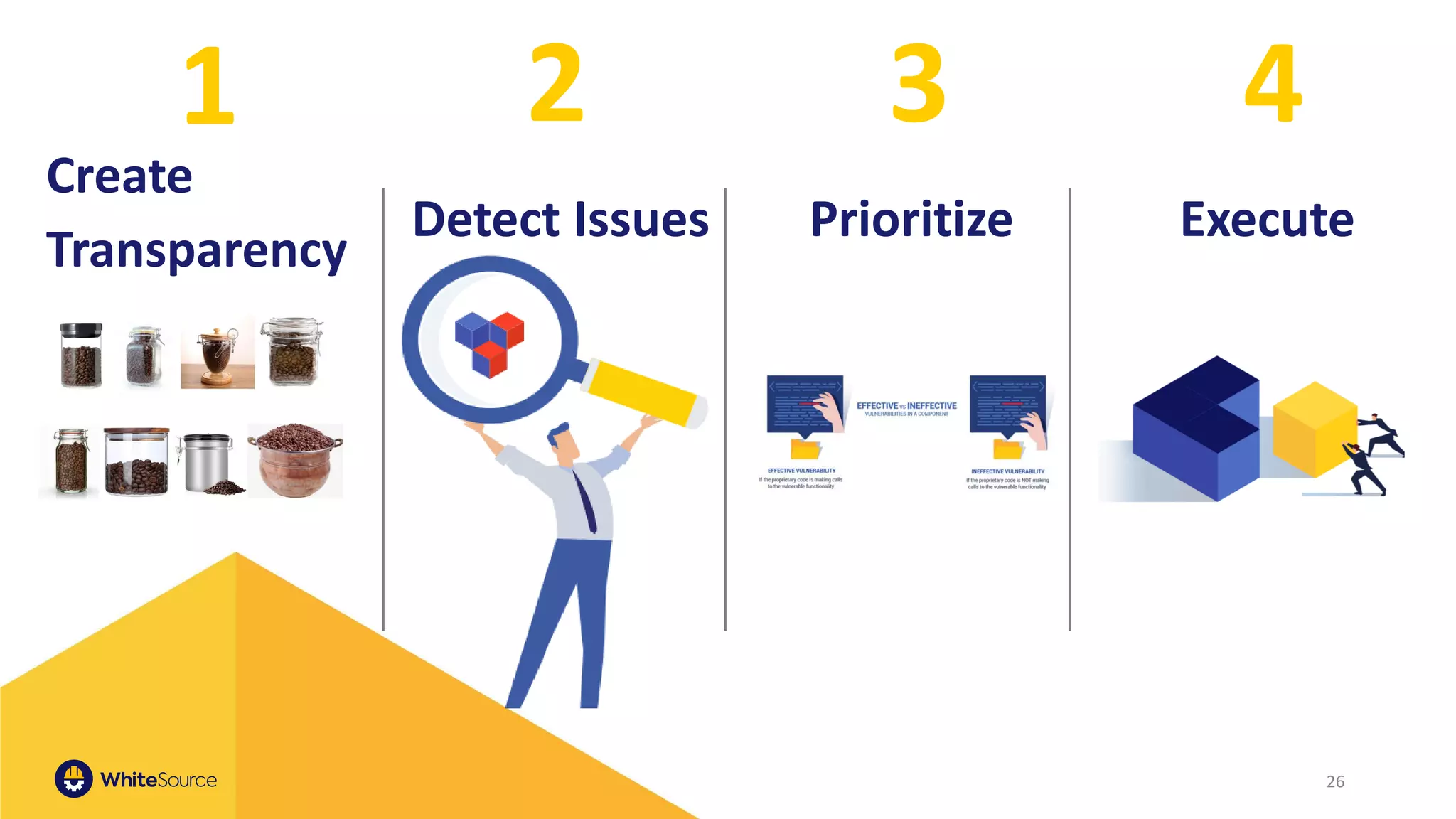
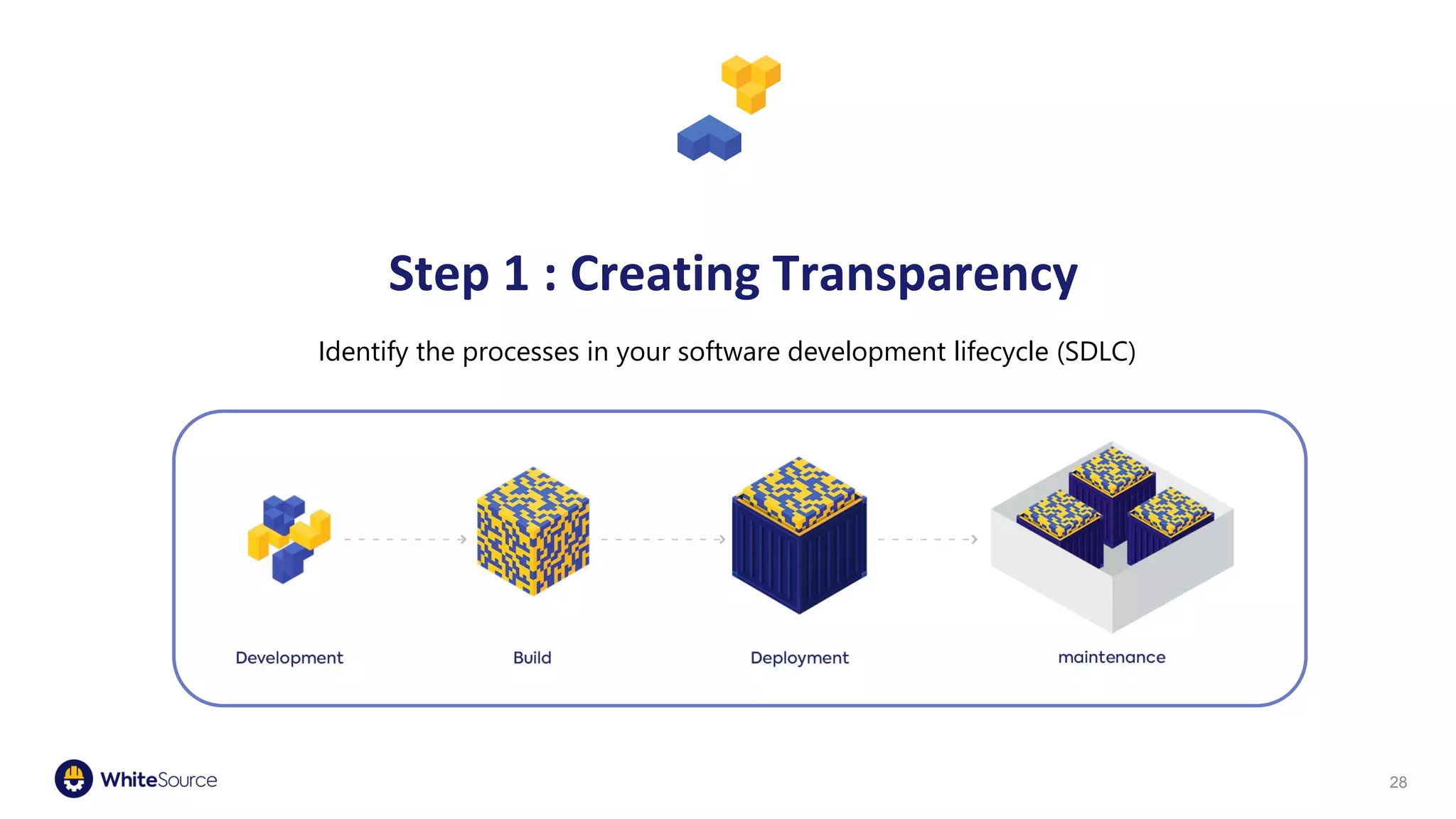
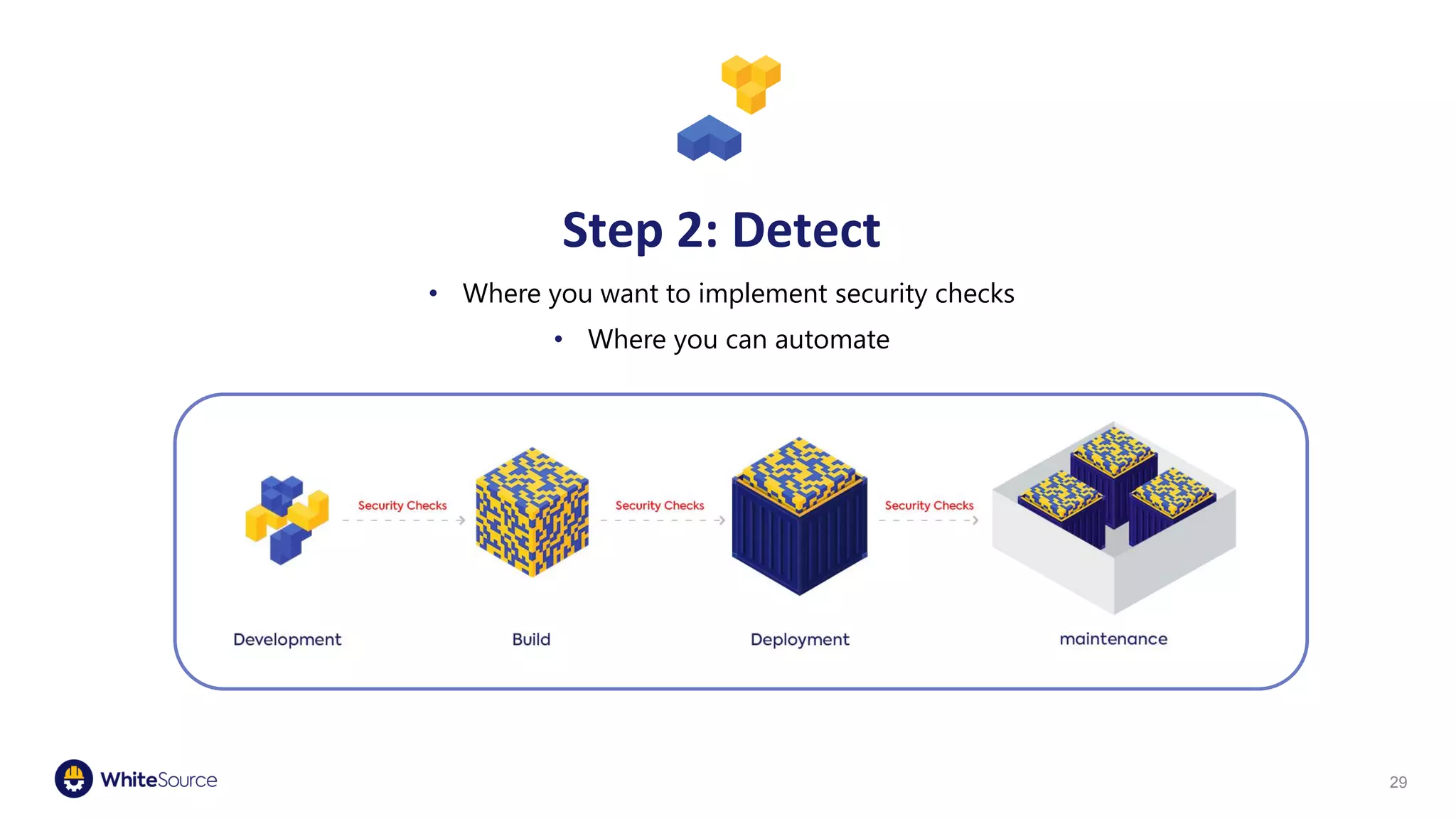
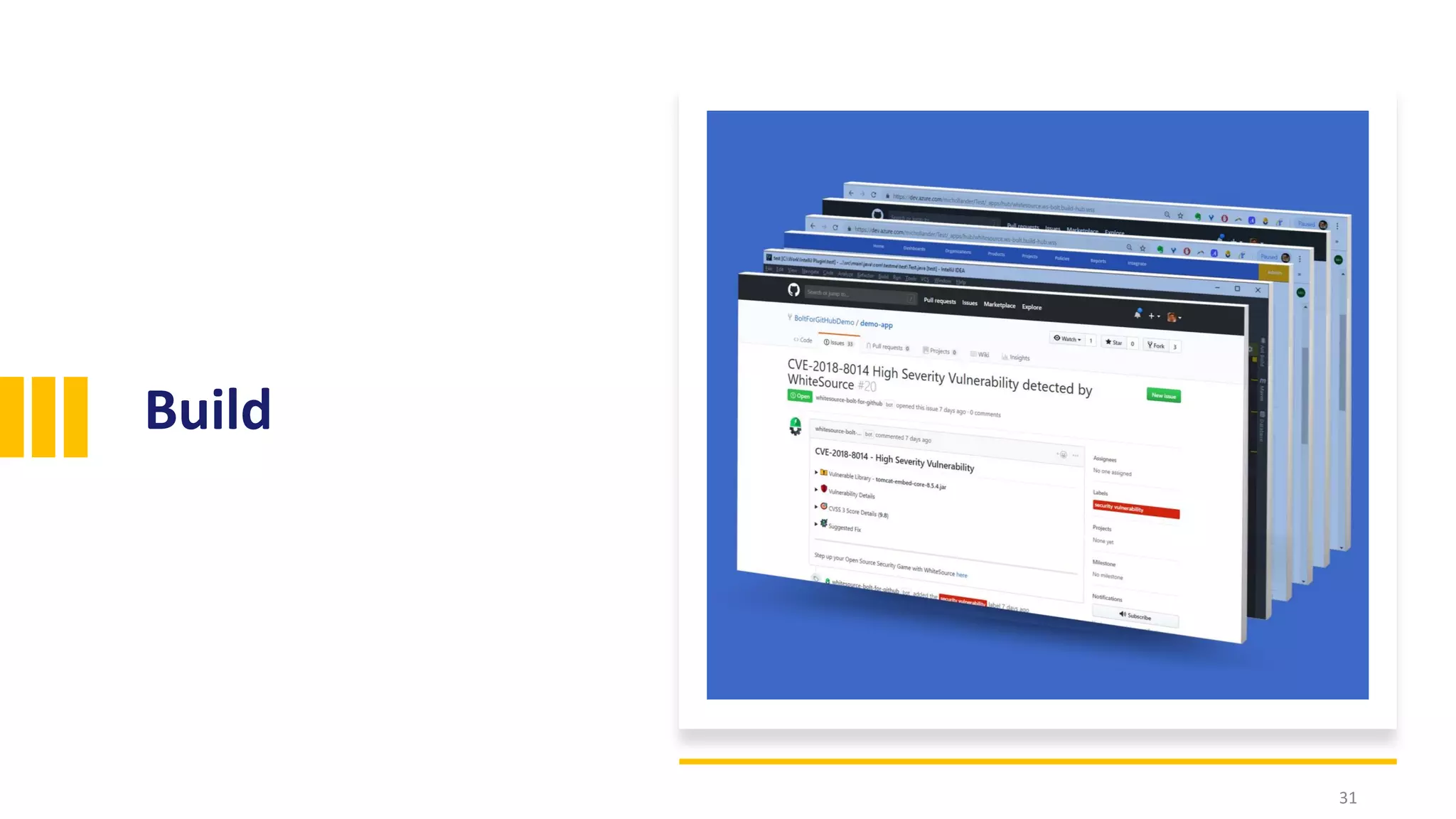
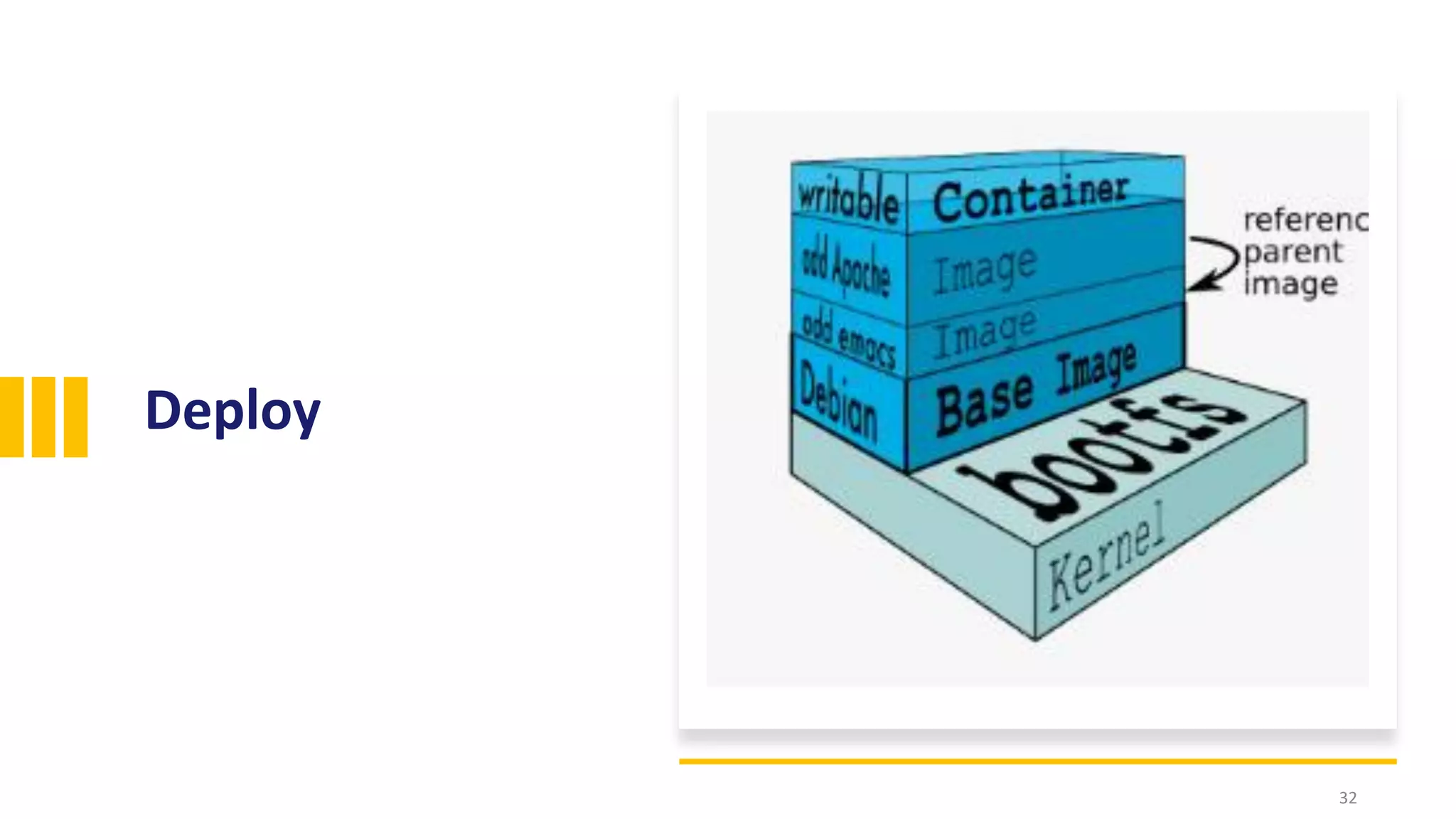
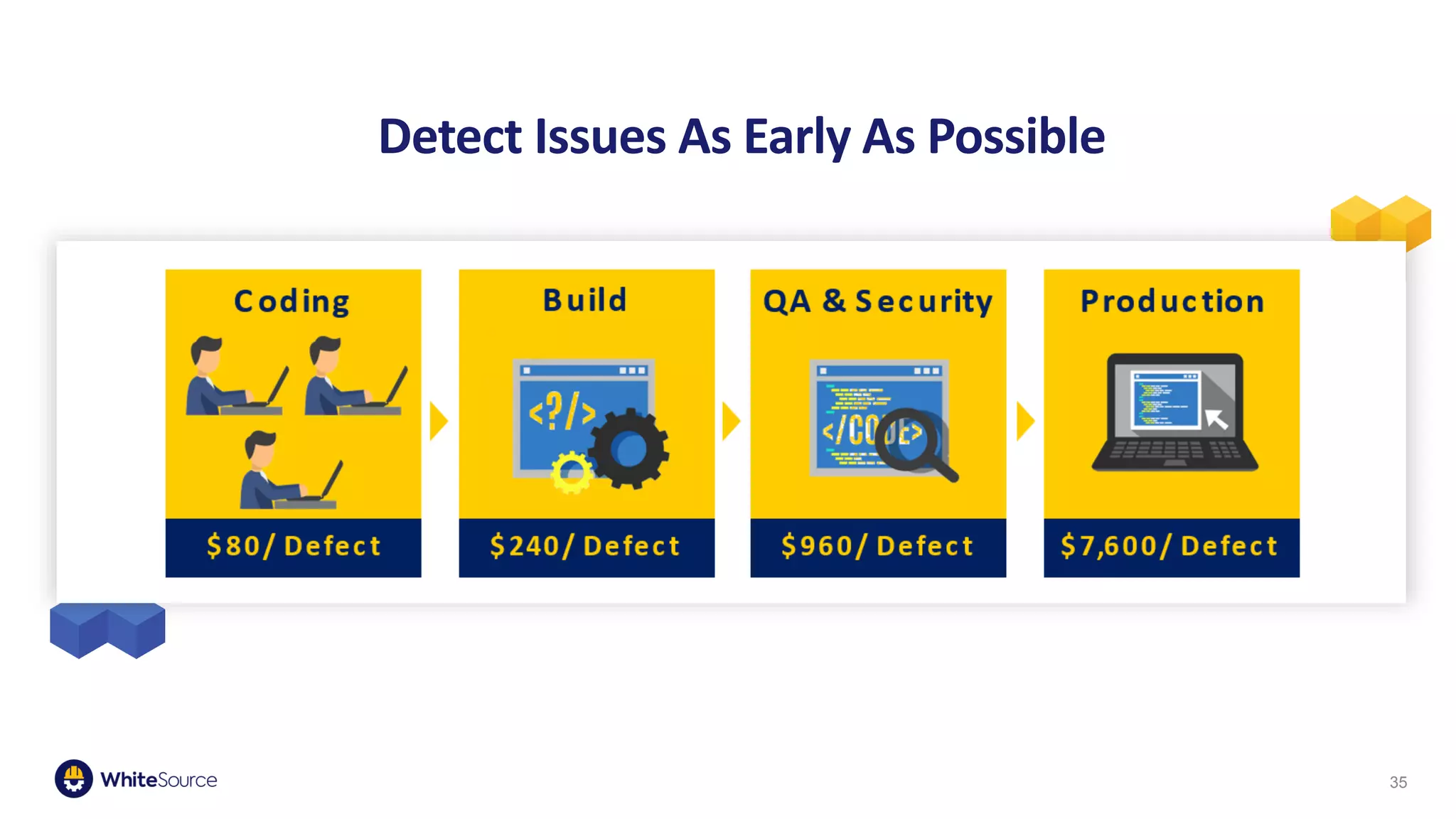
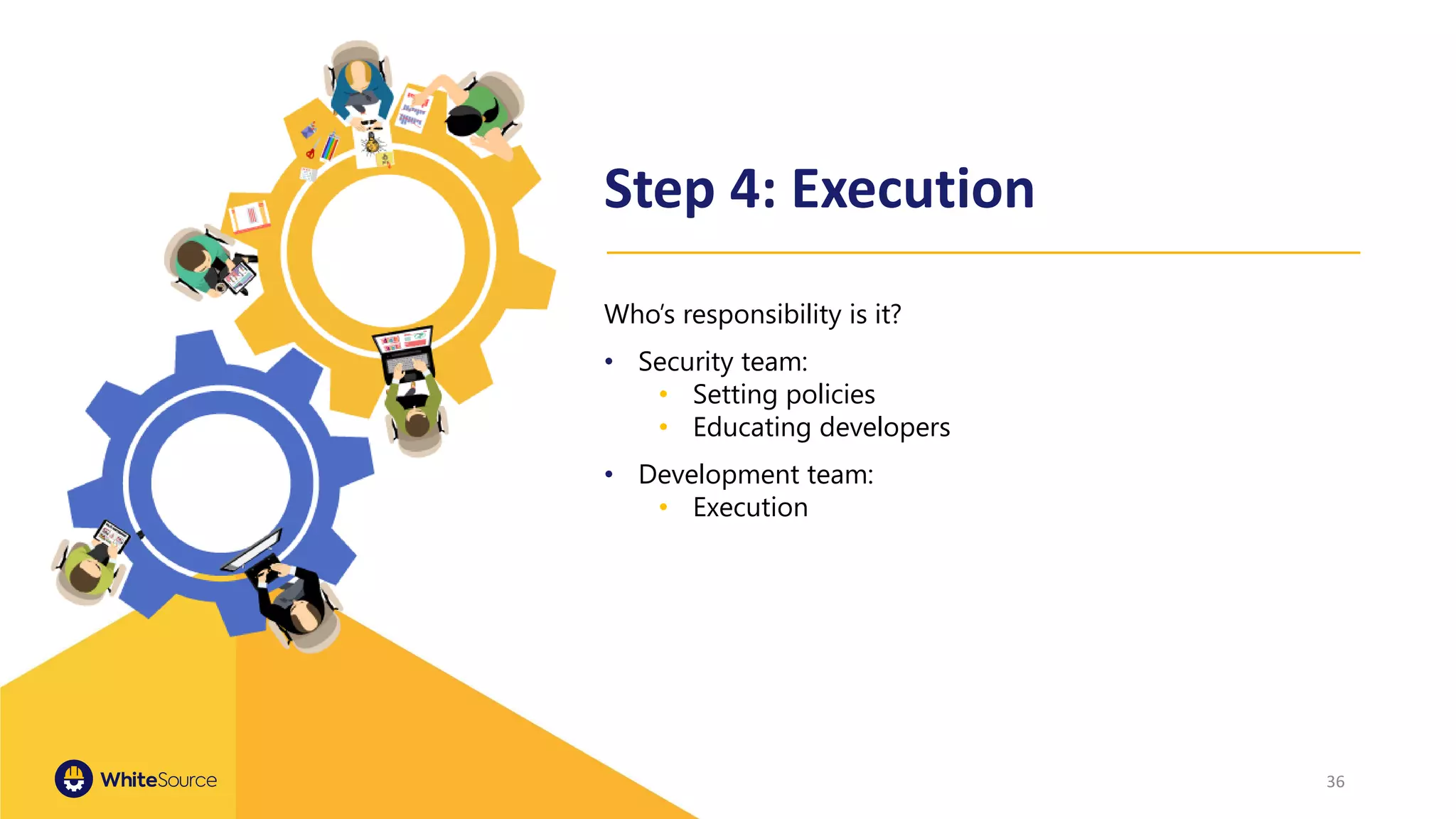
The document discusses the significance of open source security, focusing on the Equifax breach which affected 145 million individuals due to a known vulnerability in the Apache Struts framework. It highlights the lessons learned from this breach and emphasizes the importance of transparency, detection of vulnerabilities, prioritization, and execution in maintaining secure software practices. Additionally, the document provides insights into the challenges faced by SmallComp during a merger and acquisition process, involving compliance with open source licenses.