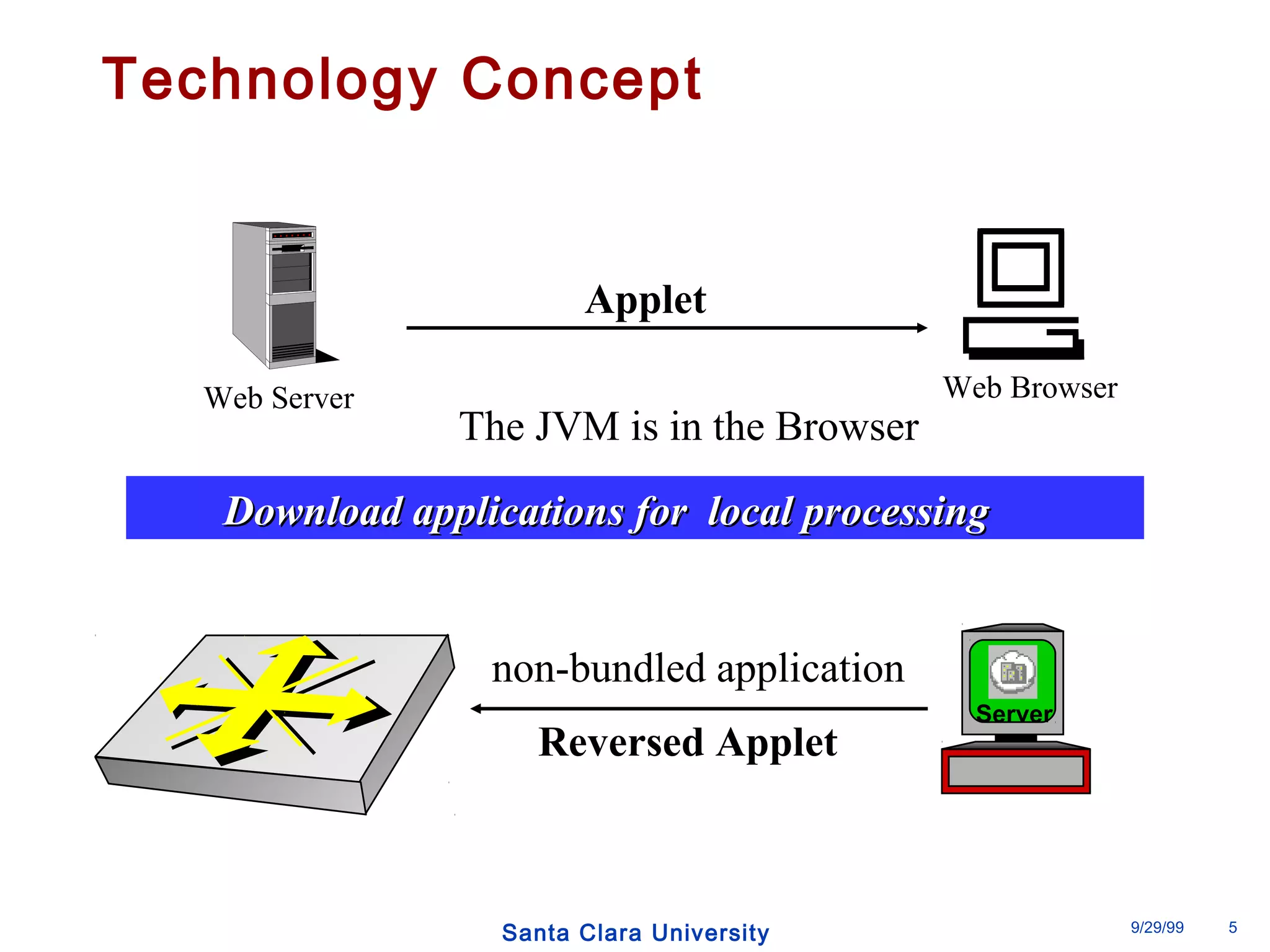
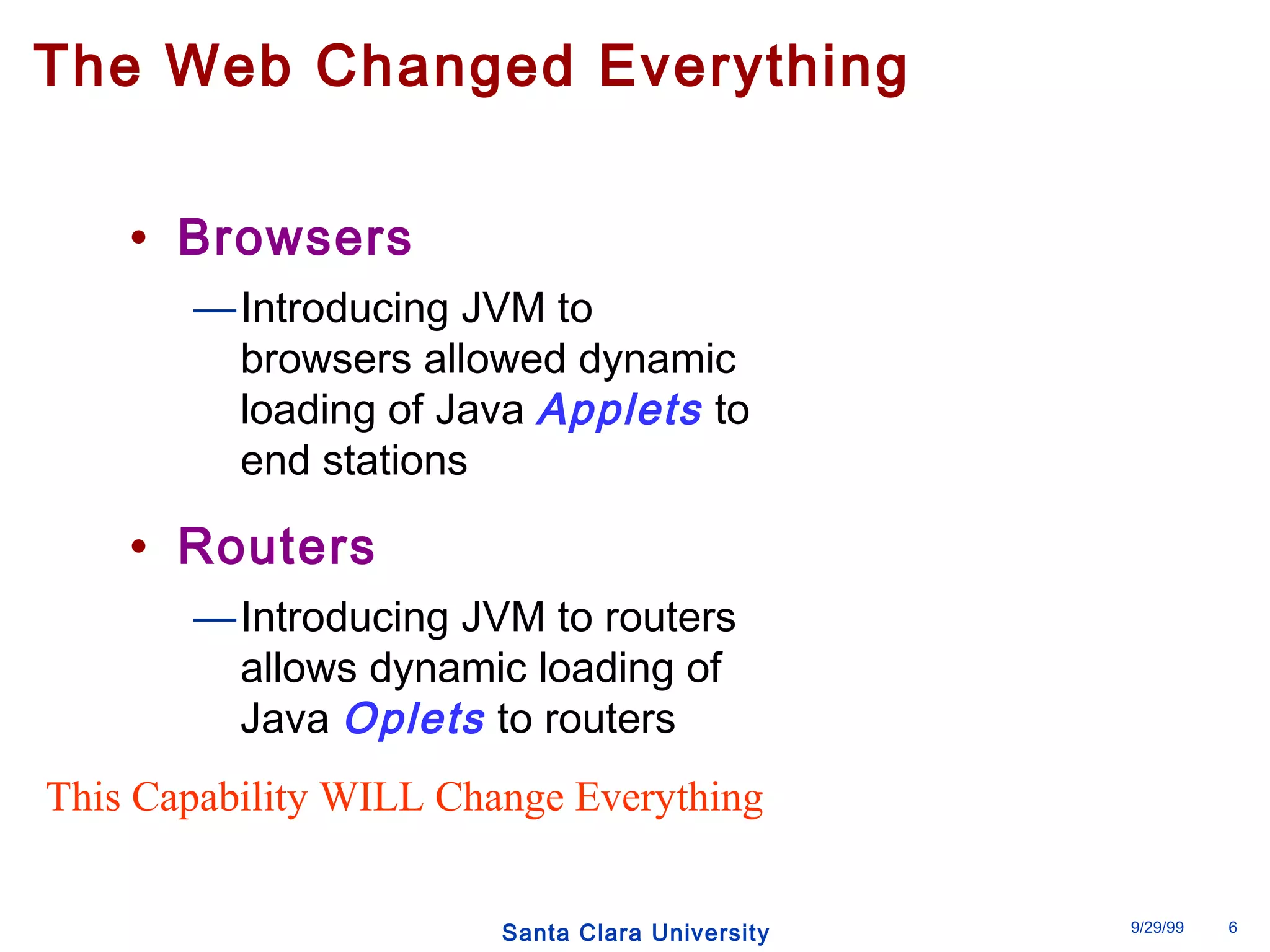
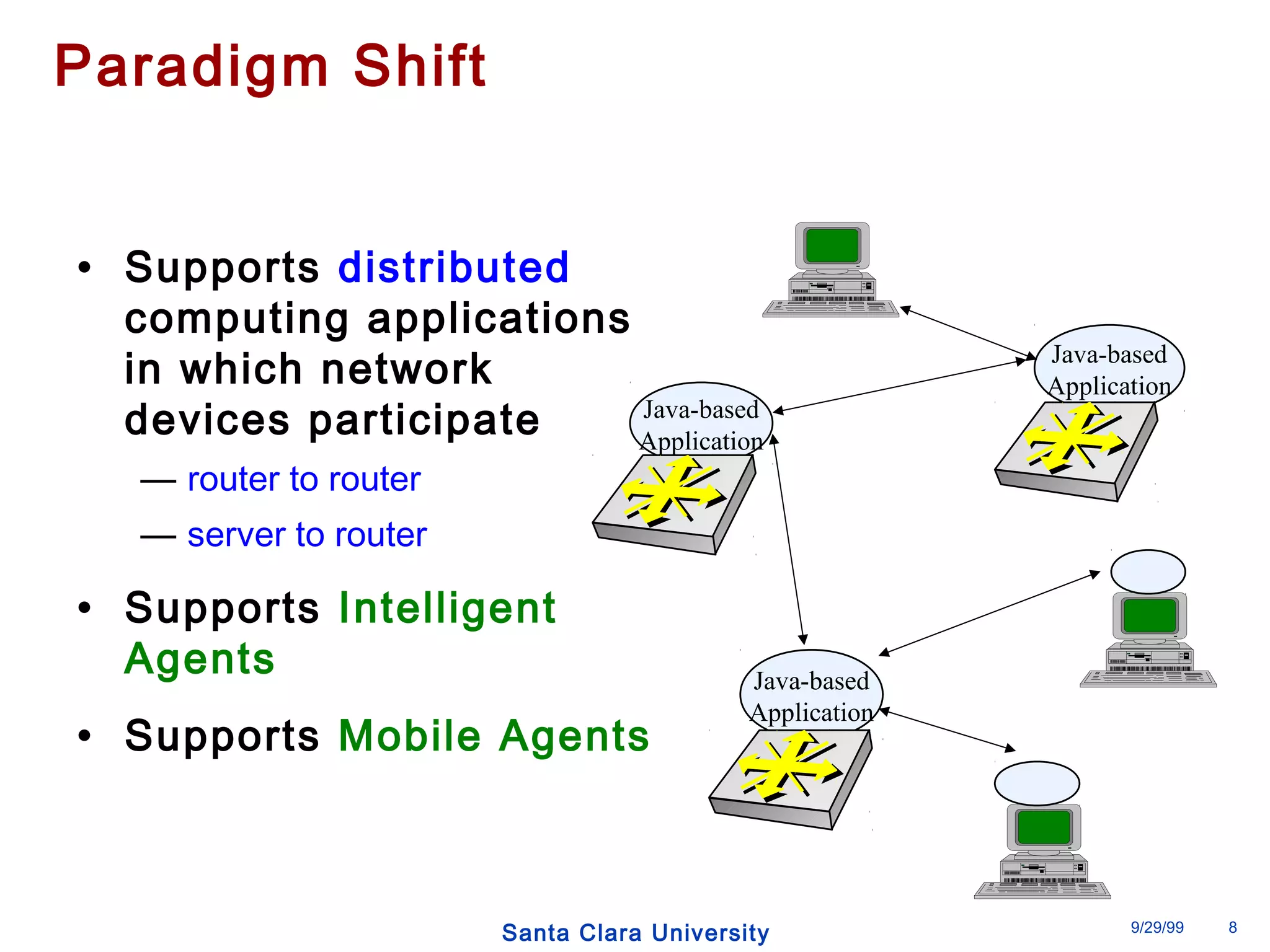
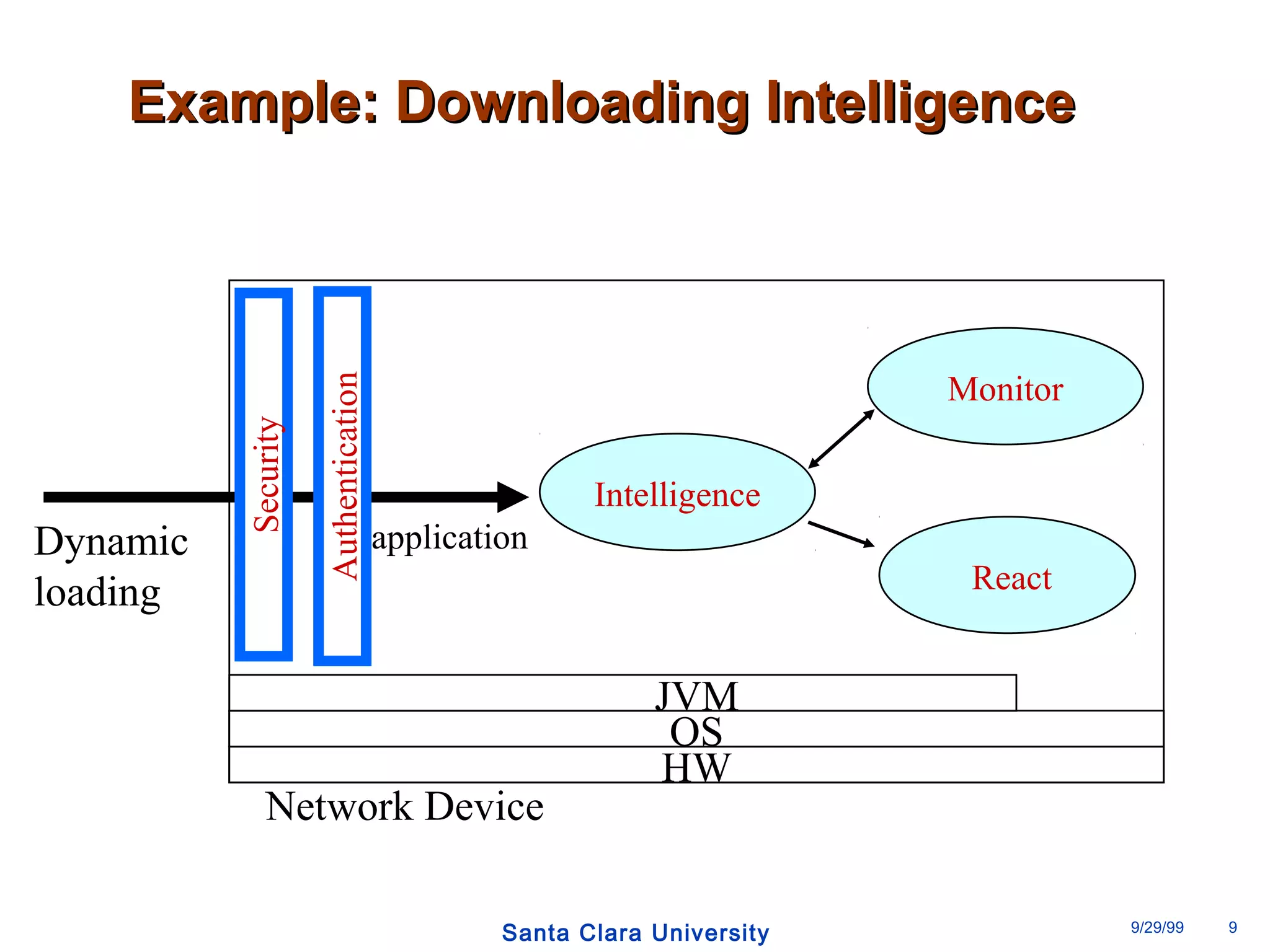
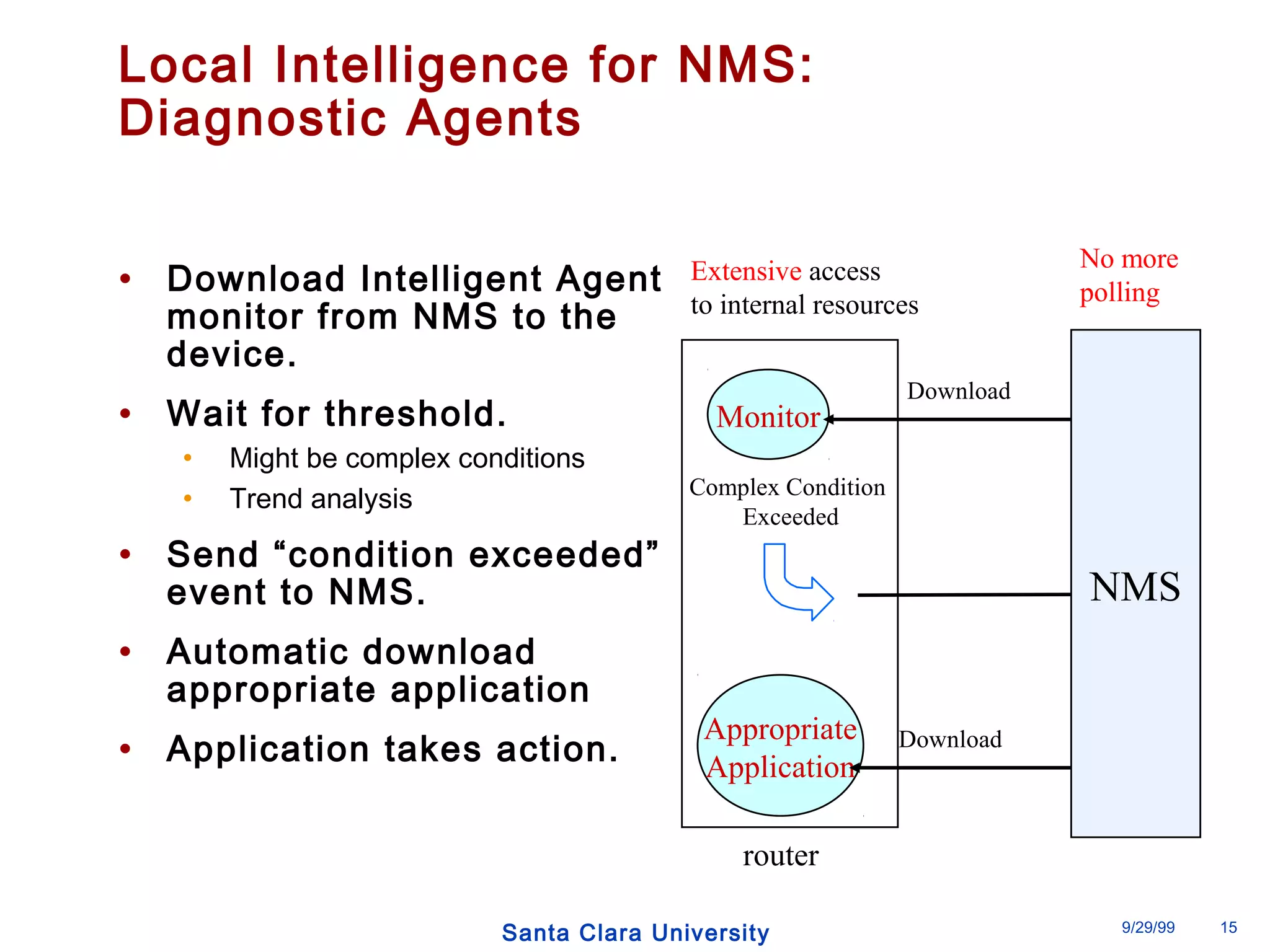
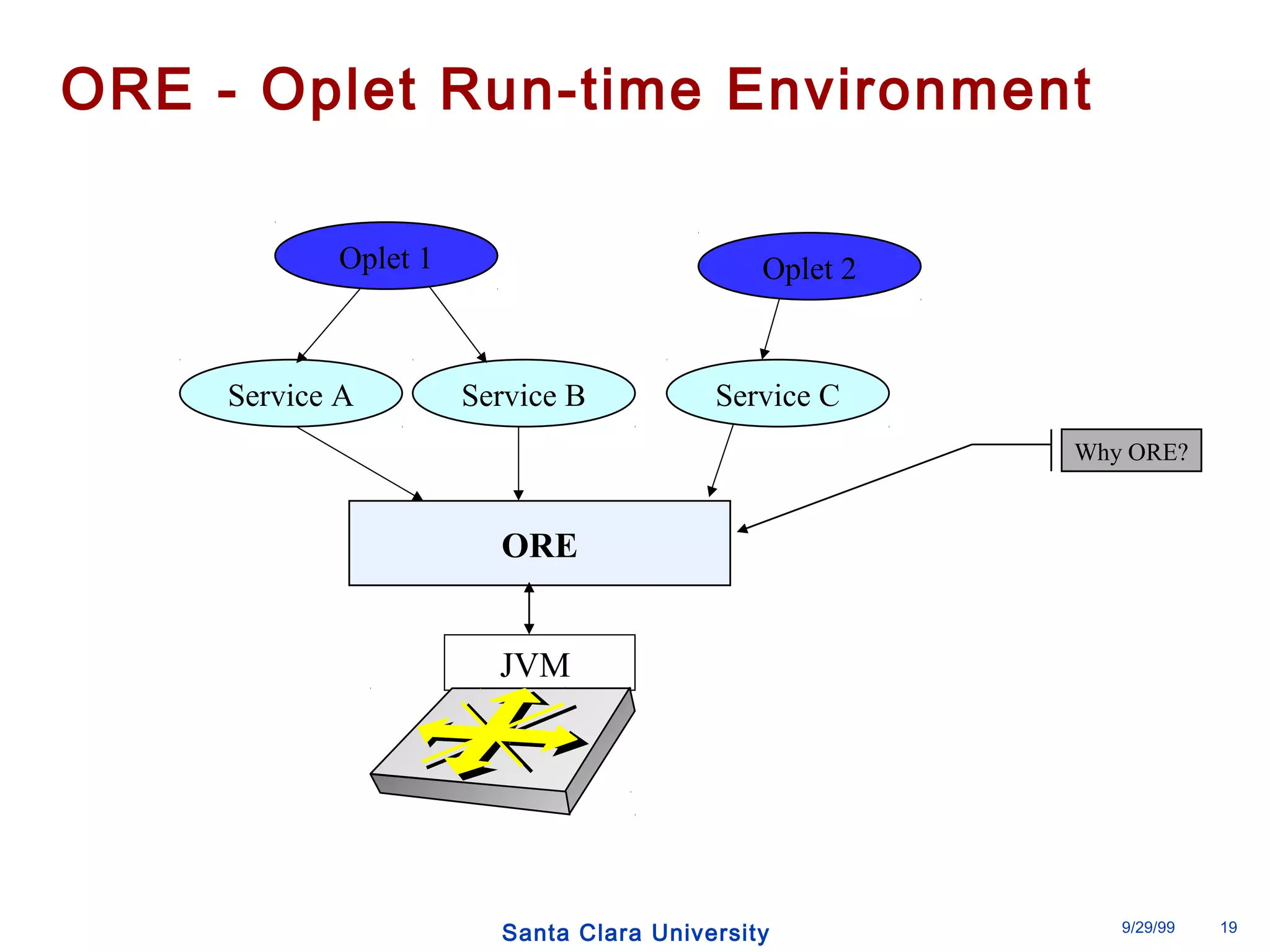
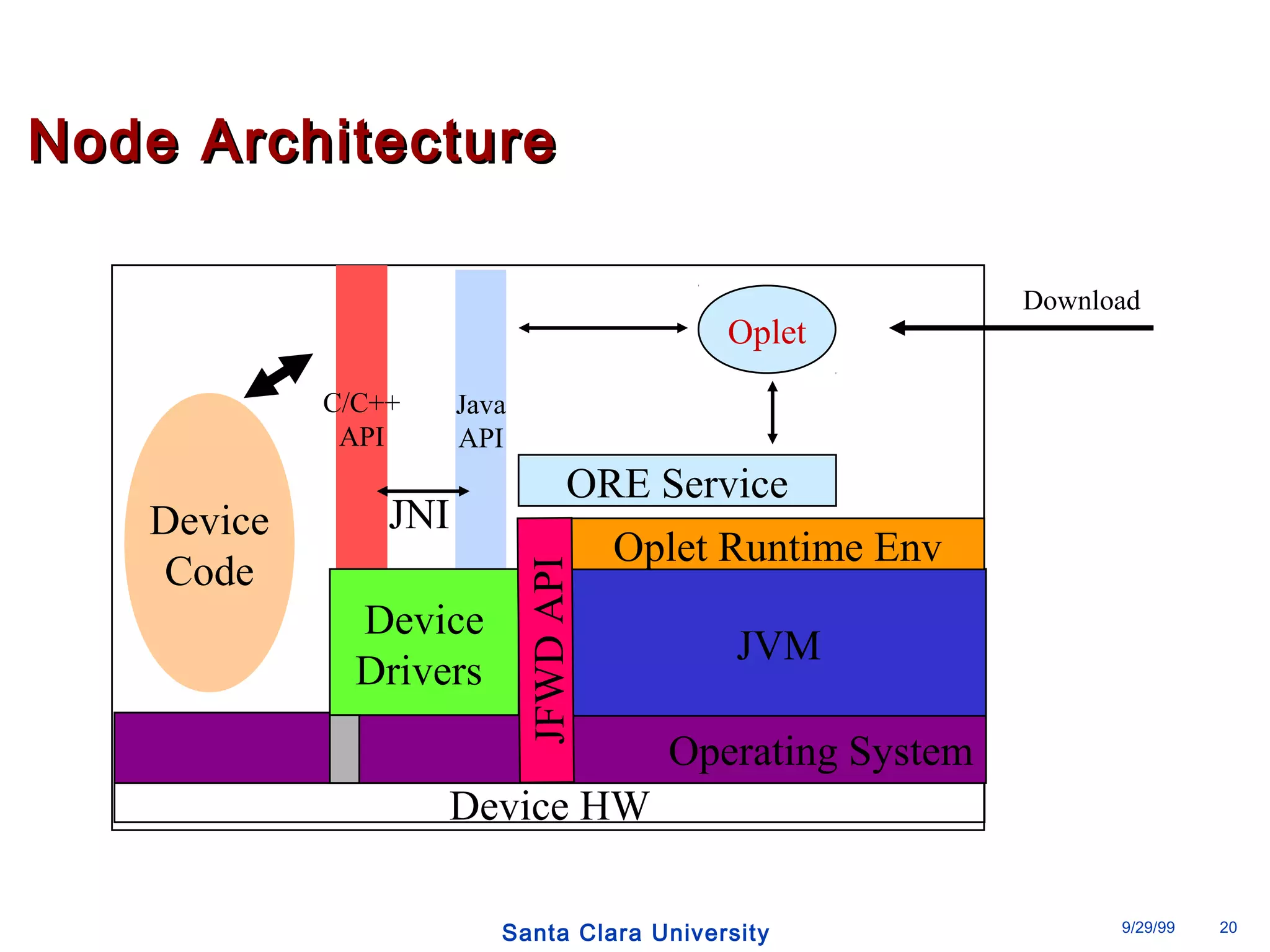
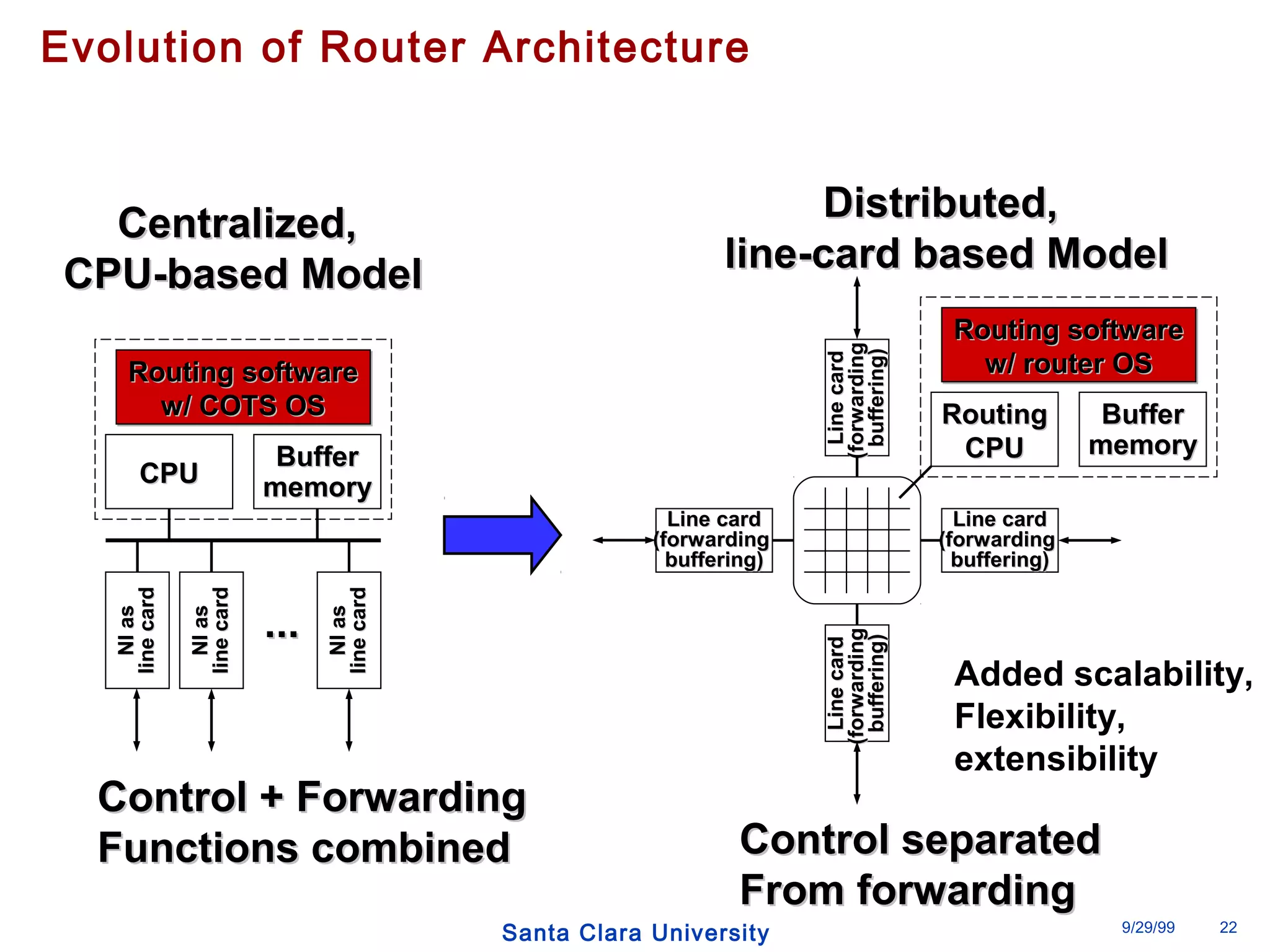
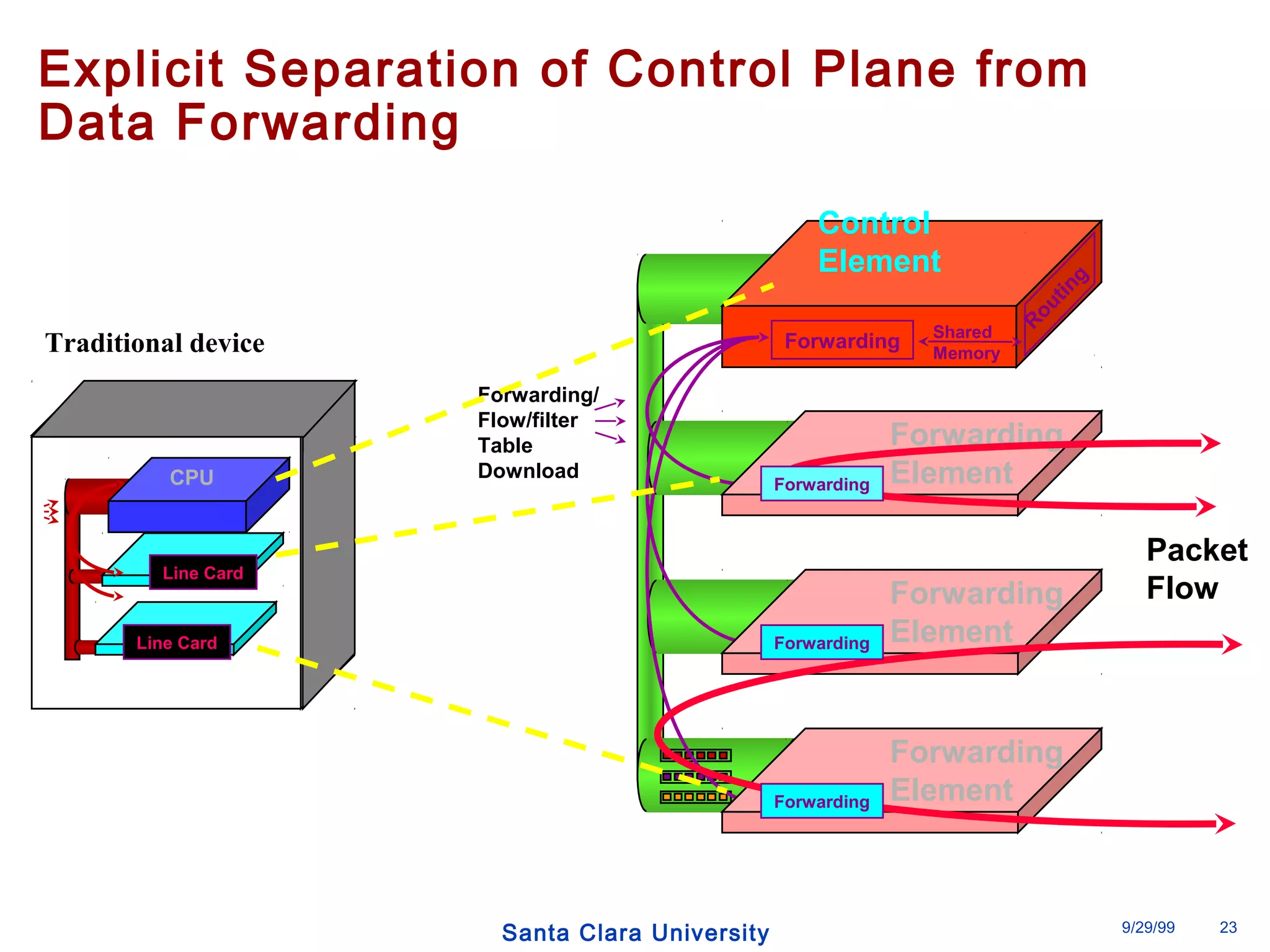
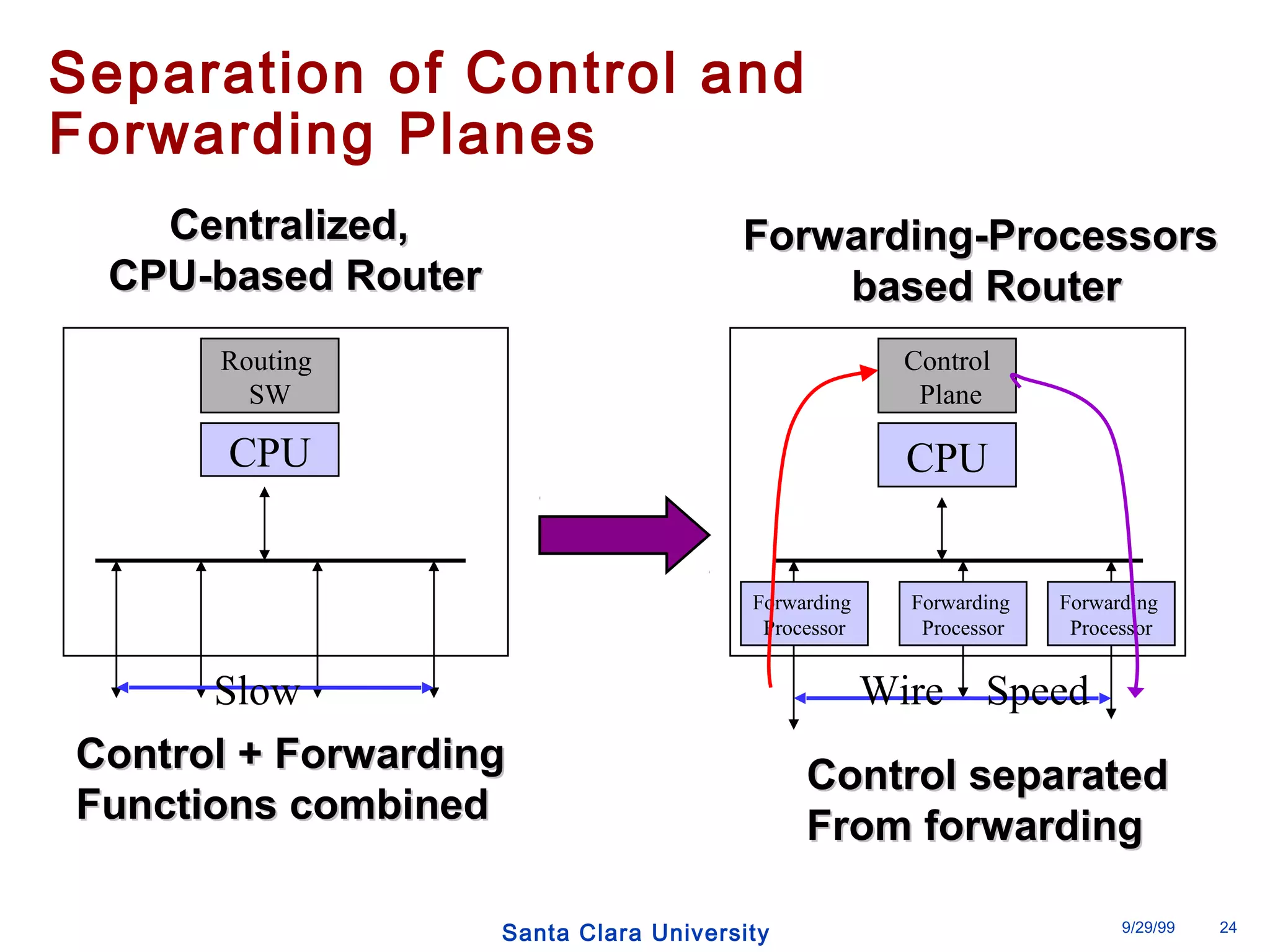
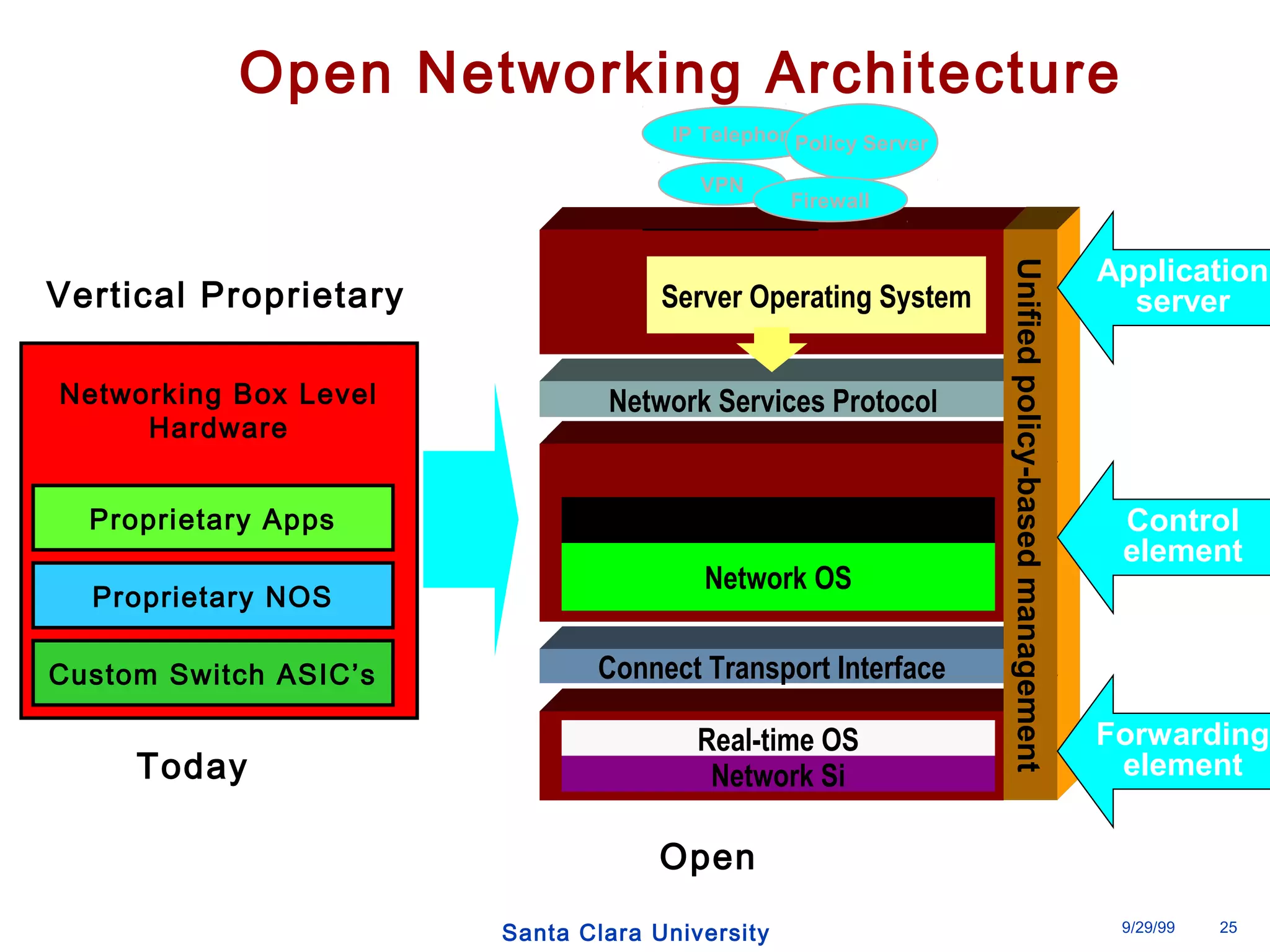
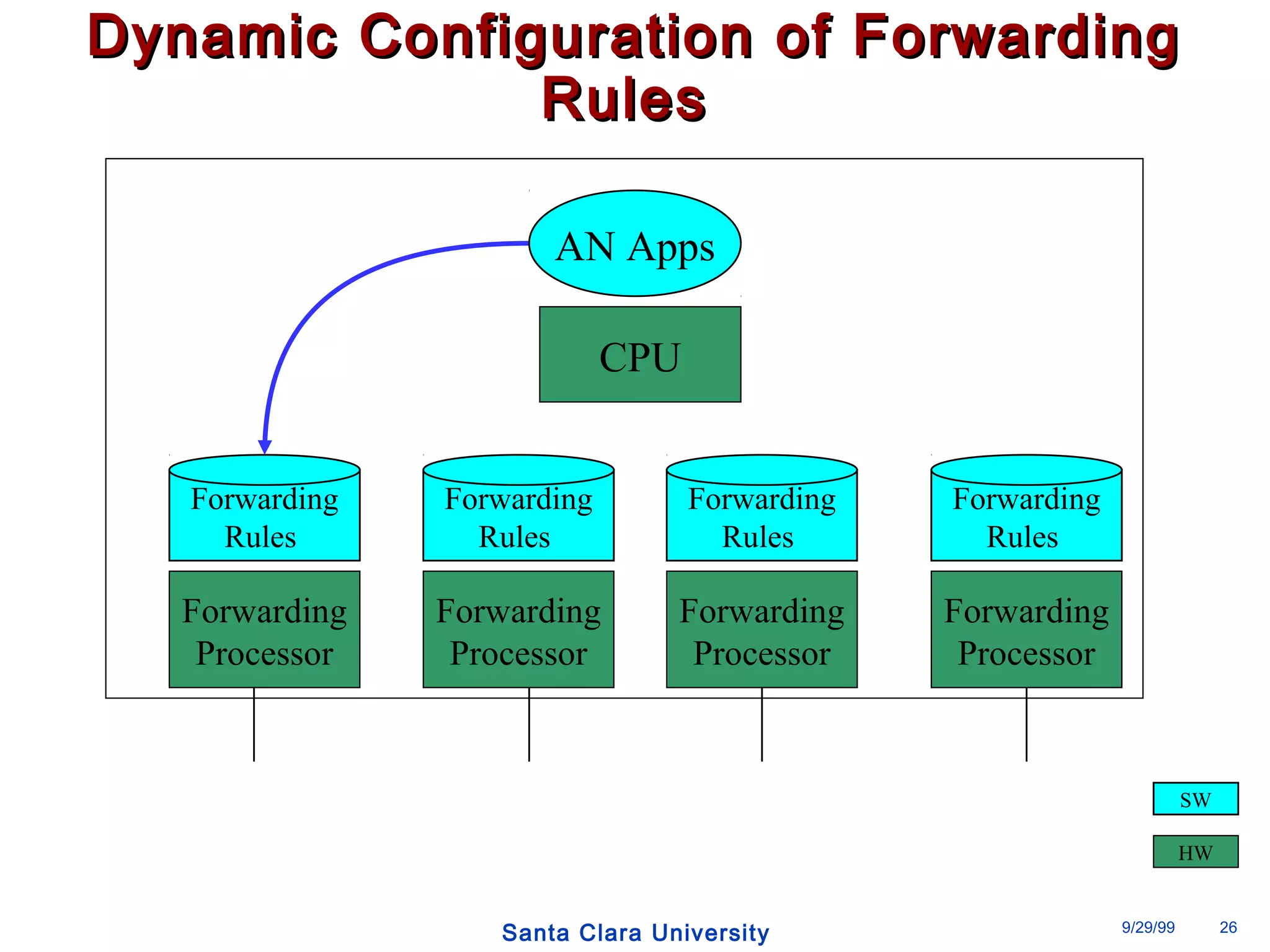
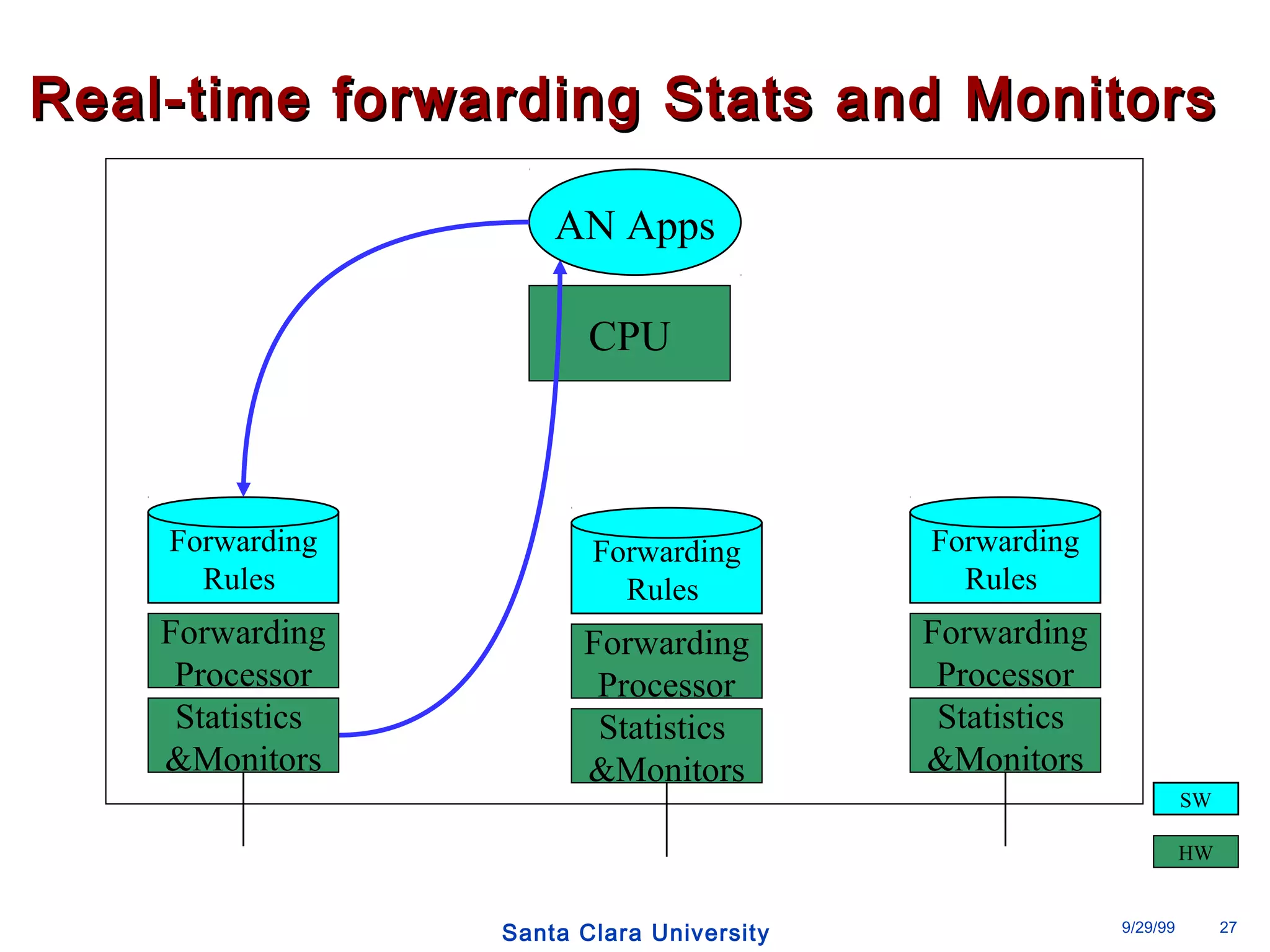
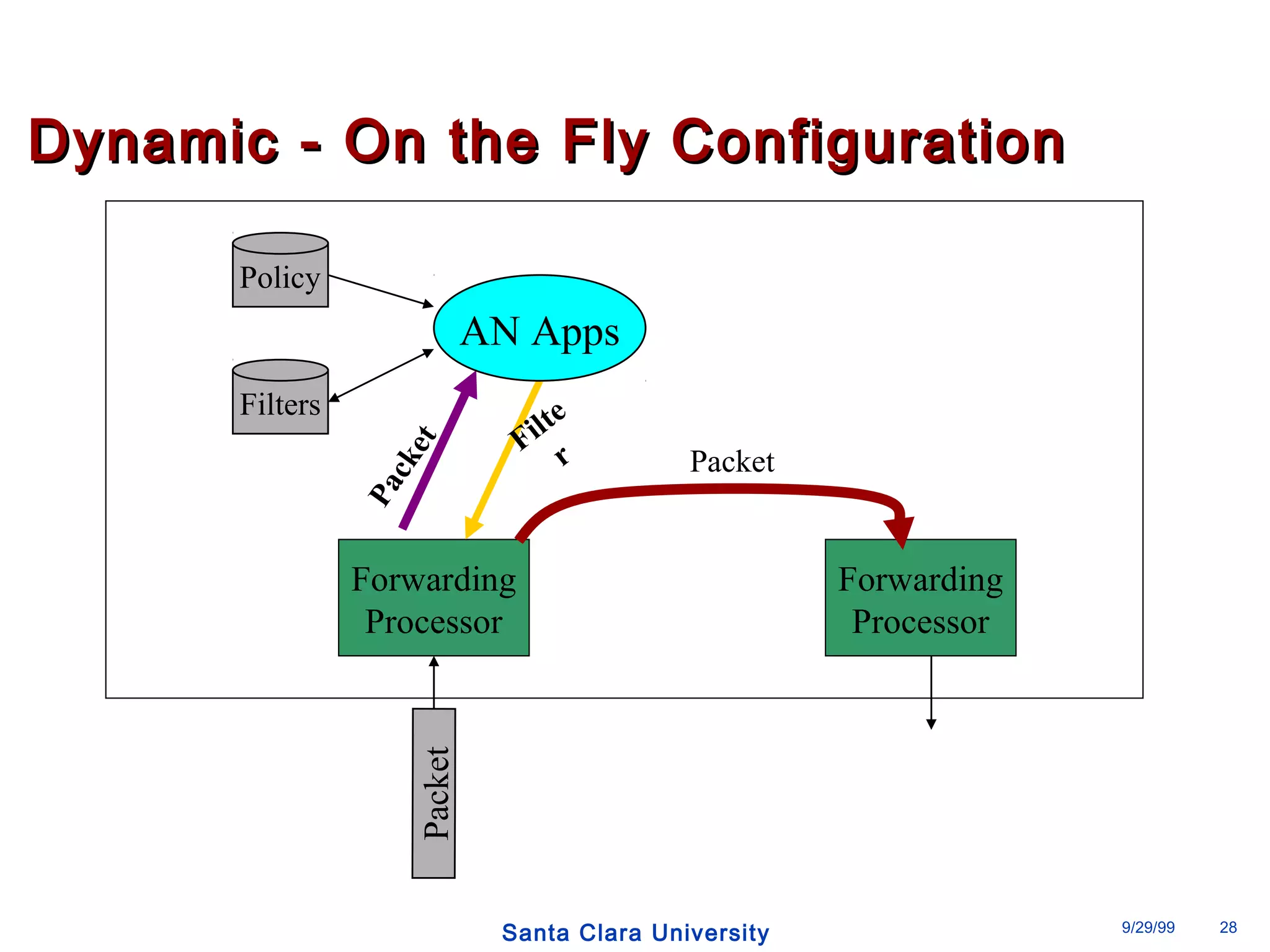
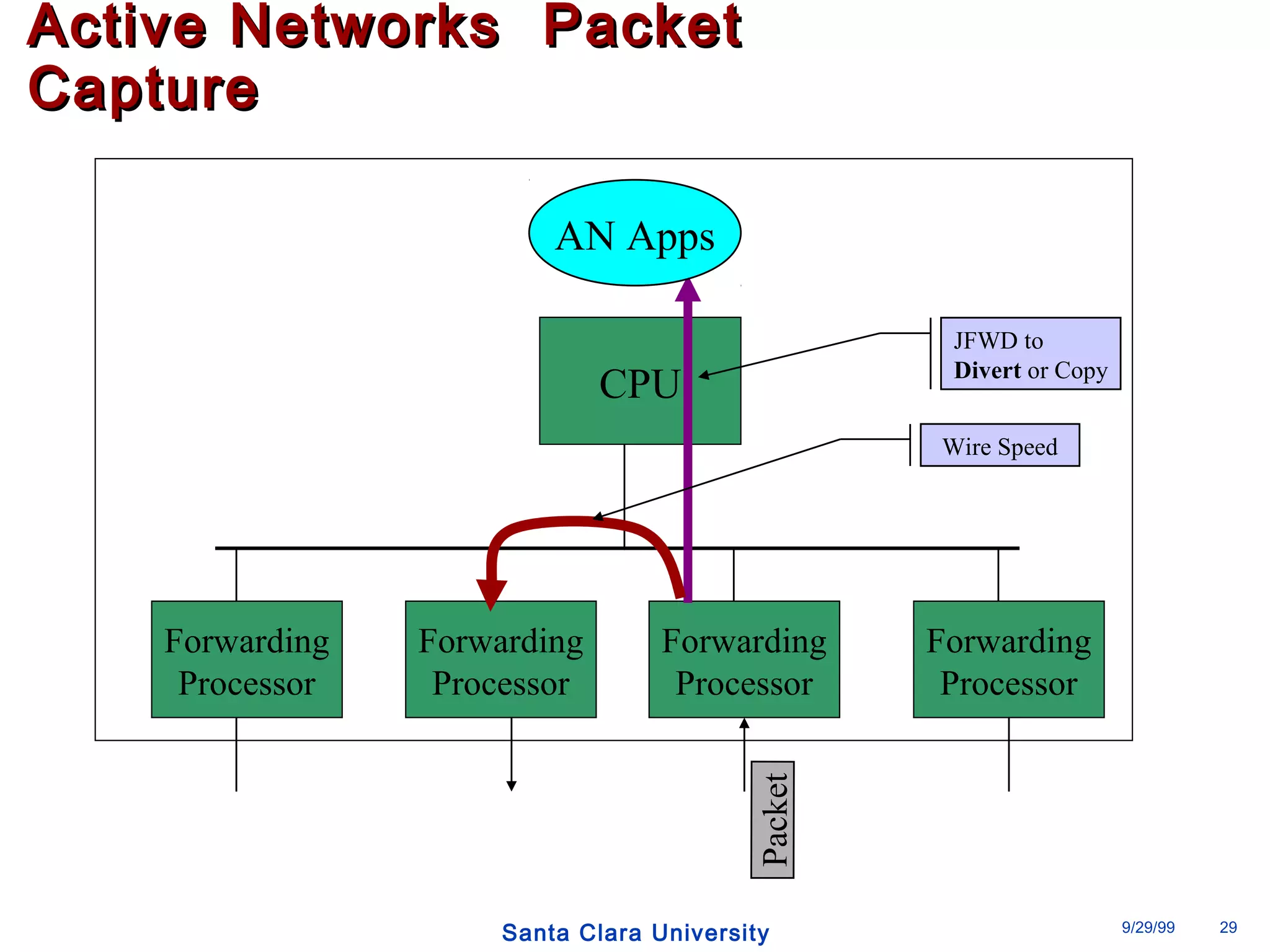
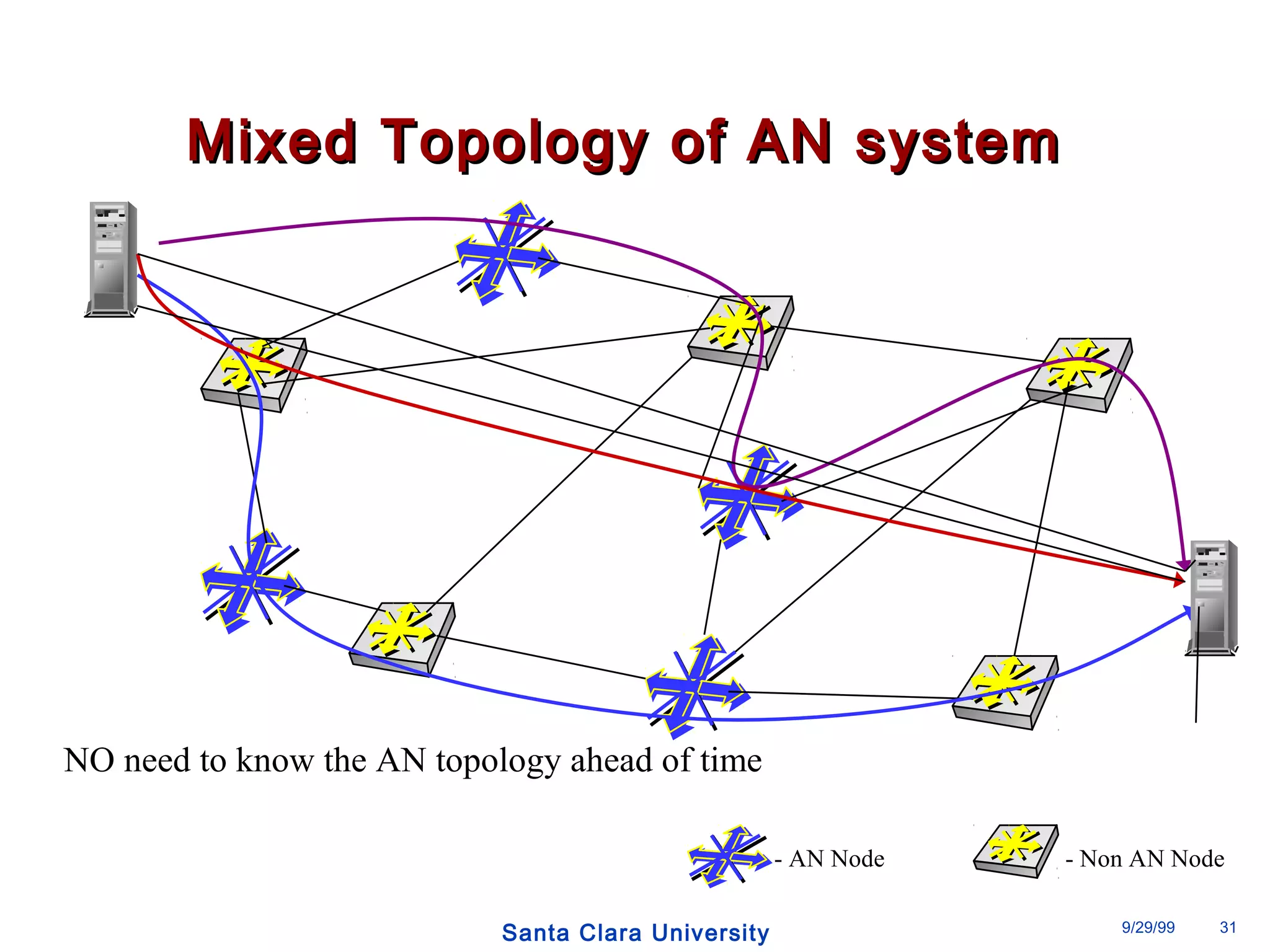
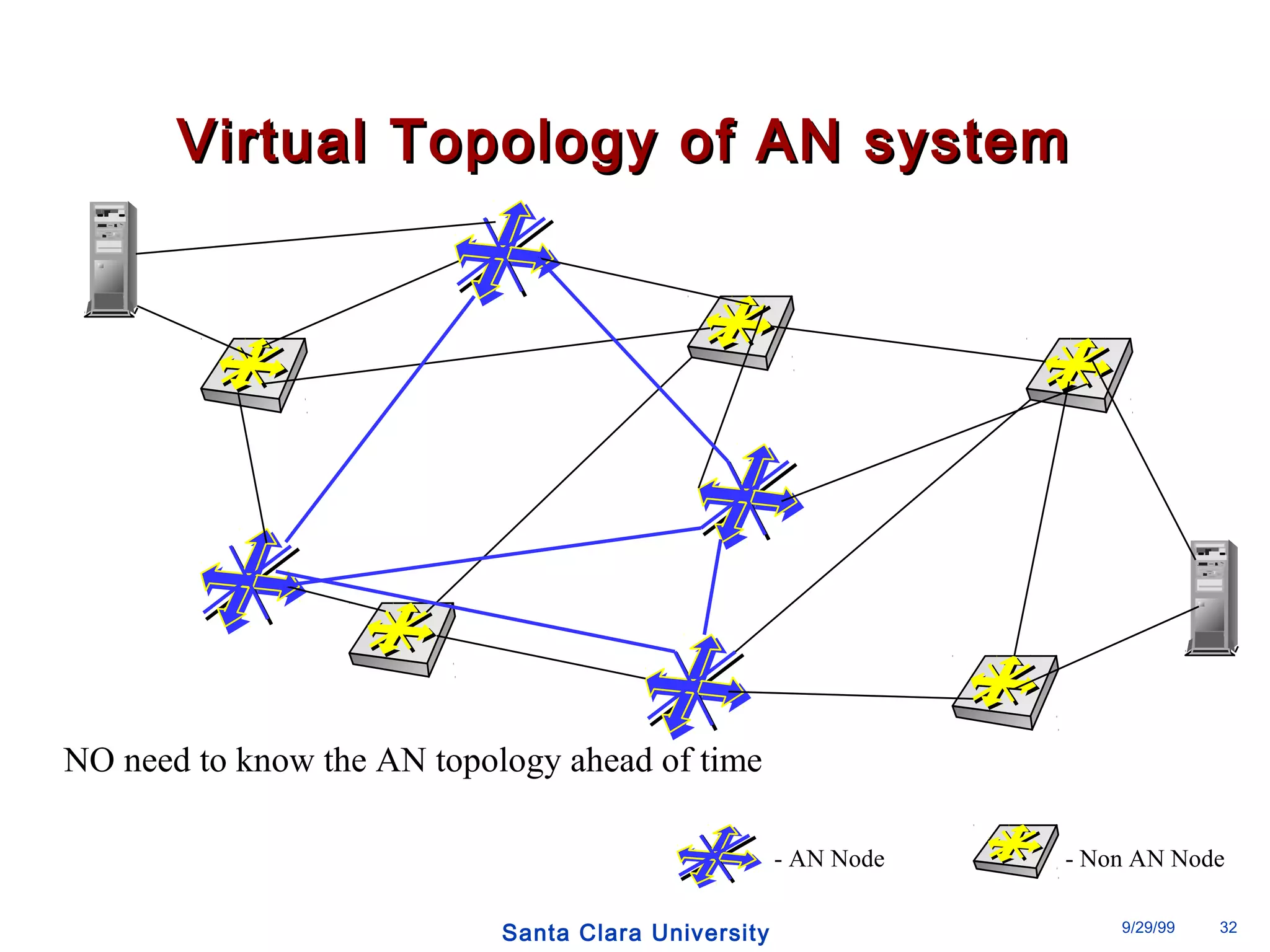
The document discusses an open programmable architecture for Java-enabled network devices that allow local processing and dynamic application loading, shifting the paradigm towards intelligent, adaptable network devices. It highlights the technological advancements made, including the integration of Java into routers and the development of dynamic agents that improve network intelligence and application collaborations. The architecture supports secure, flexible, and innovative applications, positioning Java-based solutions as a foundation for future networking advancements.