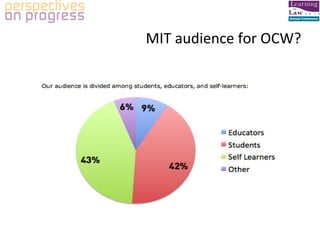
OER refers to open educational resources which include full courses, course materials, and other learning content that can be freely accessed and used online. MIT's OpenCourseWare initiative is an example of an institutional OER program that makes course materials from over 1,900 courses freely available on the web. Educators use OER in a variety of ways like reusing content, adapting course syllabi, and combining OER materials with other resources. There are benefits to creating OER like lowering costs for students and fostering pedagogical innovation through customizable learning materials.