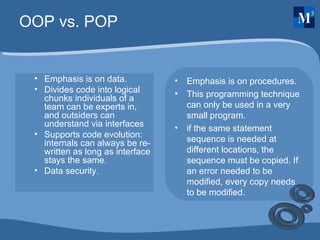
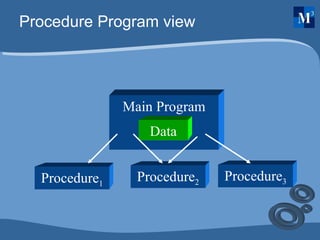
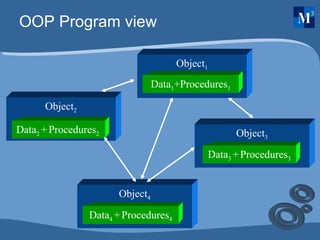
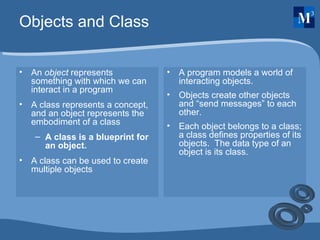
OOP concepts such as objects, classes, abstraction, encapsulation, inheritance, and polymorphism are discussed and compared to procedural programming. Objects are instances of classes that contain both data and procedures. Abstraction allows programmers to focus on the overall concepts without implementation details. Encapsulation wraps data and access within a class. Inheritance allows new classes to inherit properties from parent classes. Polymorphism allows different objects to respond differently to the same methods.