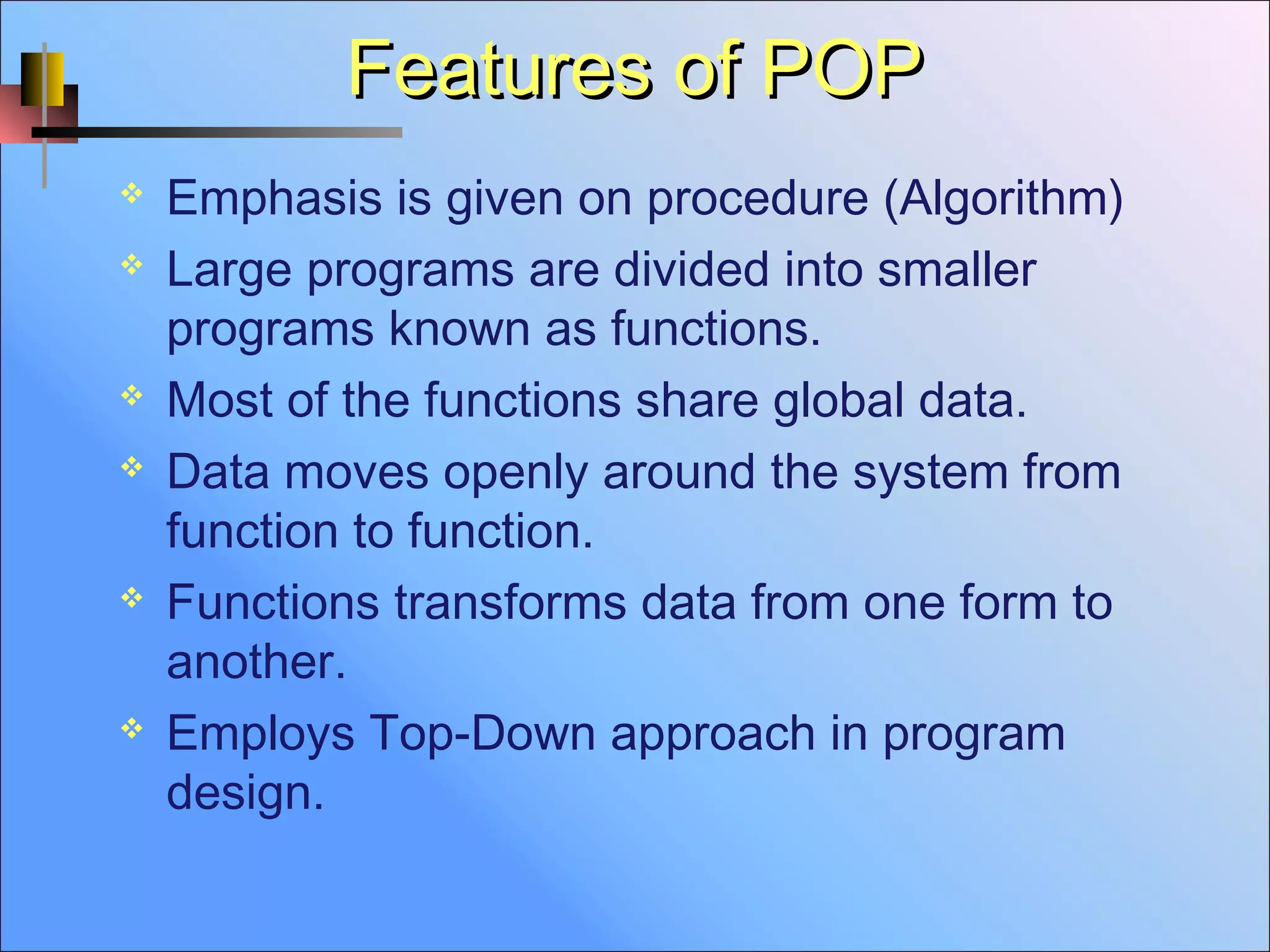
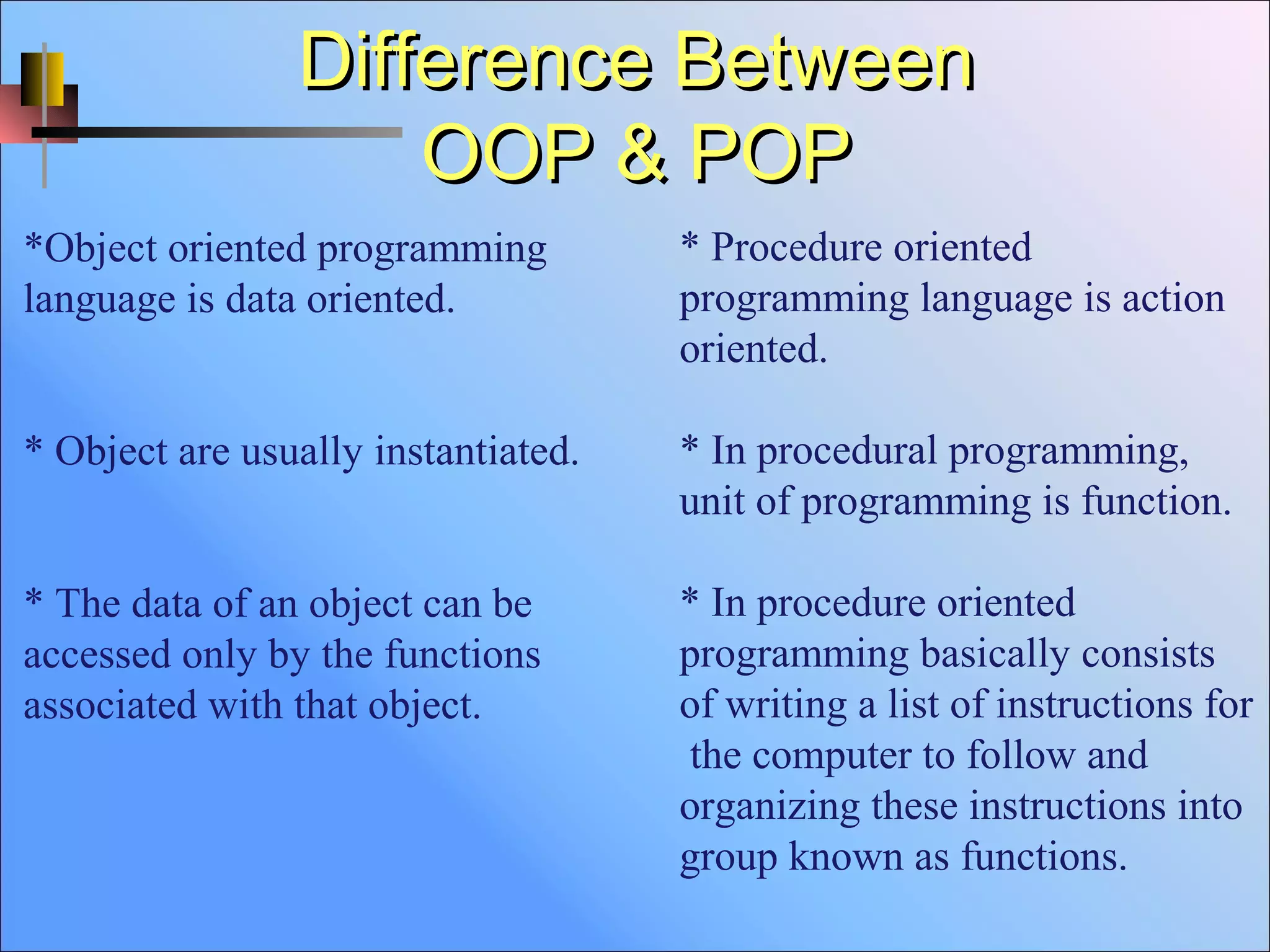
Object-oriented programming (OOP) is an approach that creates partitioned memory areas for both data and functions as templates that can be copied on demand (Object-oriented programming). Classes define user-defined data types that contain data members and member functions, and objects are run-time instances of classes. OOP emphasizes data over procedures and divides programs into small, reusable modules called objects. In contrast, procedural programming (POP) views problems as sequences of tasks and divides the program into functions that can access shared global data and transform data without encapsulation. OOP focuses more on data protection and tying data to the functions that operate on it.