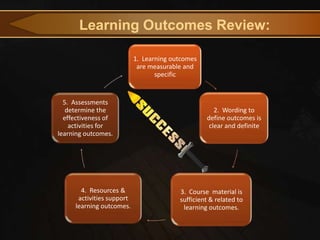
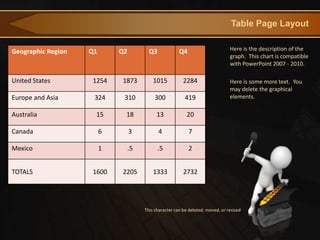
This document provides an agenda for an online course design presentation. It includes an introduction to key concepts like learning outcomes, the online syllabus, course structure, language and writing style, and visual design basics. The presentation covers how to build an online course foundation through defining measurable learning outcomes and creating a comprehensive syllabus. It also includes a tour of an example online course site and tips for clear writing and effective visual presentation.