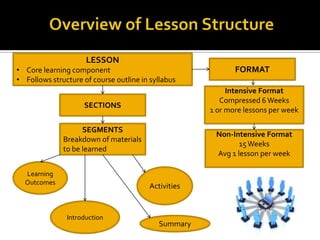
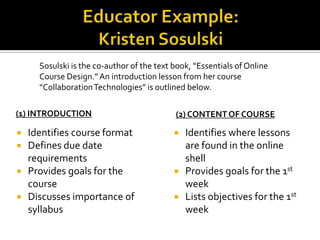
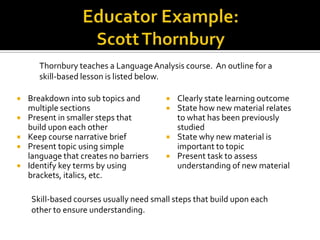
The document provides guidance for educators on developing effective online course content and lesson structure. It recommends that educators (1) structure lessons and content around clear learning outcomes, (2) chunk information into small, digestible segments, and (3) use a variety of multimedia materials and interactive activities to engage learners. Examples of effective course outlines from two educators demonstrate how to apply these principles.