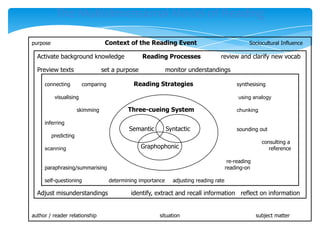
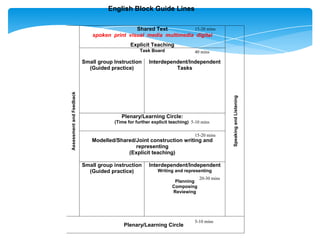
This document discusses comprehension as one of the most challenging issues for reading teachers. It notes that comprehension is important for true reading, and that proficient readers actively engage with texts using various strategies to gain meaning. The document then lists and describes numerous reading strategies that can be explicitly taught to improve comprehension, such as predicting, inferring, connecting ideas, and monitoring understanding. It concludes by questioning where comprehension instruction fits within the English block structure in schools.