1. The document discusses strategies for teaching reading comprehension, including balanced literacy, explicit instruction of comprehension strategies, and assessment to inform instruction.
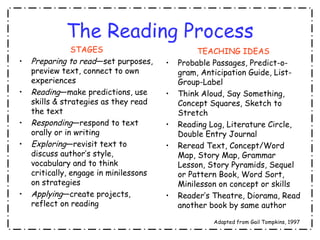
2. It outlines the reading process and various comprehension strategies like previewing, self-questioning, making connections, and summarizing.
3. Examples are provided for how to teach each strategy, including think-alouds, anticipation guides, double-entry journals, and more. The goal is for students to become strategic, active readers.