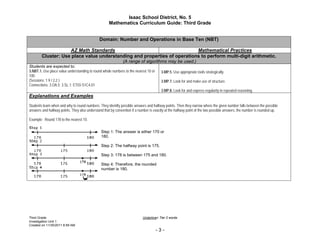
The document provides an overview of Unit 1 of the third grade mathematics curriculum for the Isaac School District. It focuses on representing numbers in different ways and relationships between numbers. The unit covers addition, subtraction, and place value over 16 sessions. It includes essential questions, vocabulary, Arizona state standards, and examples for how students can explore numerical patterns and operations with multiples of 10 to develop fluency.