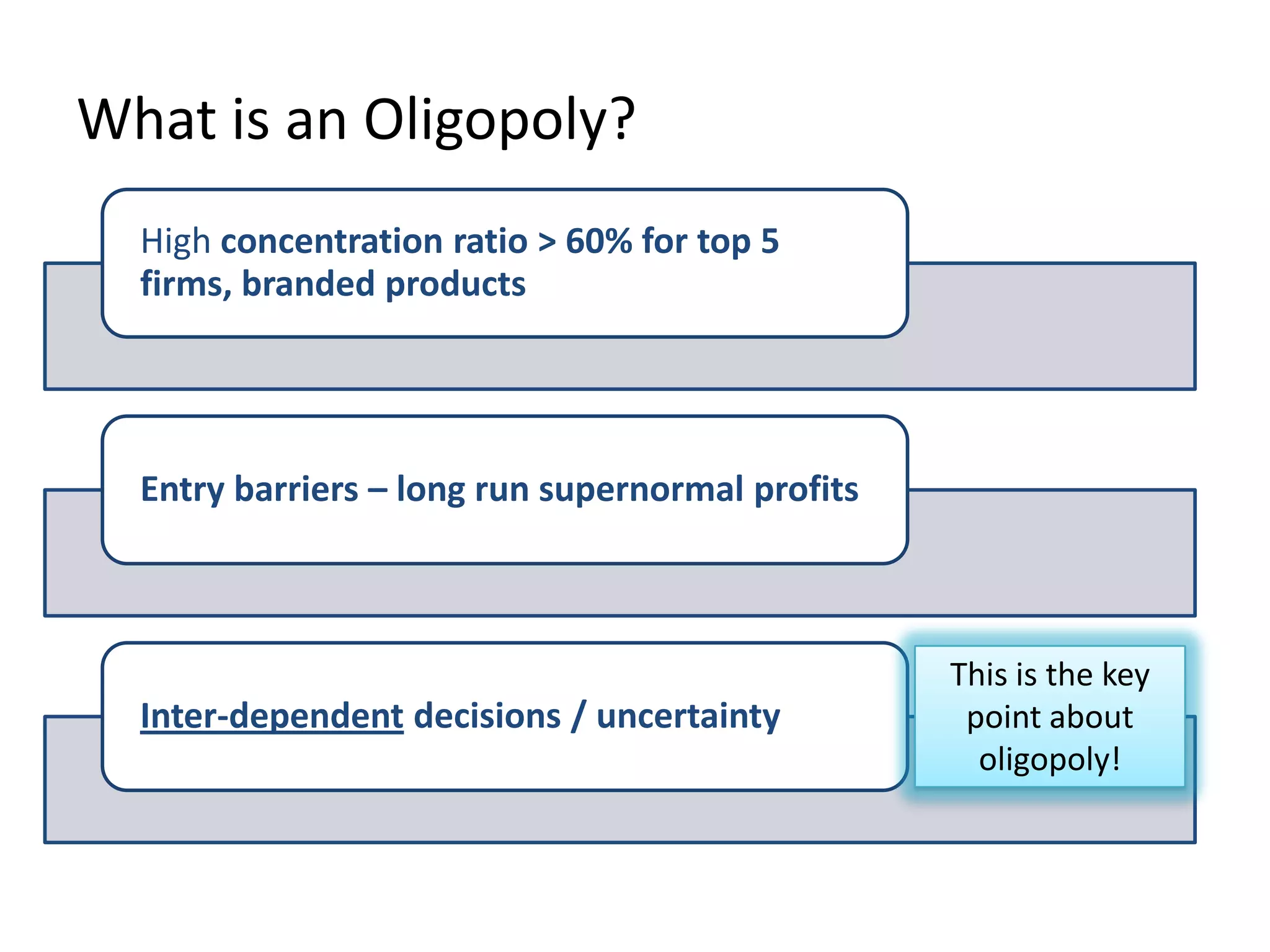
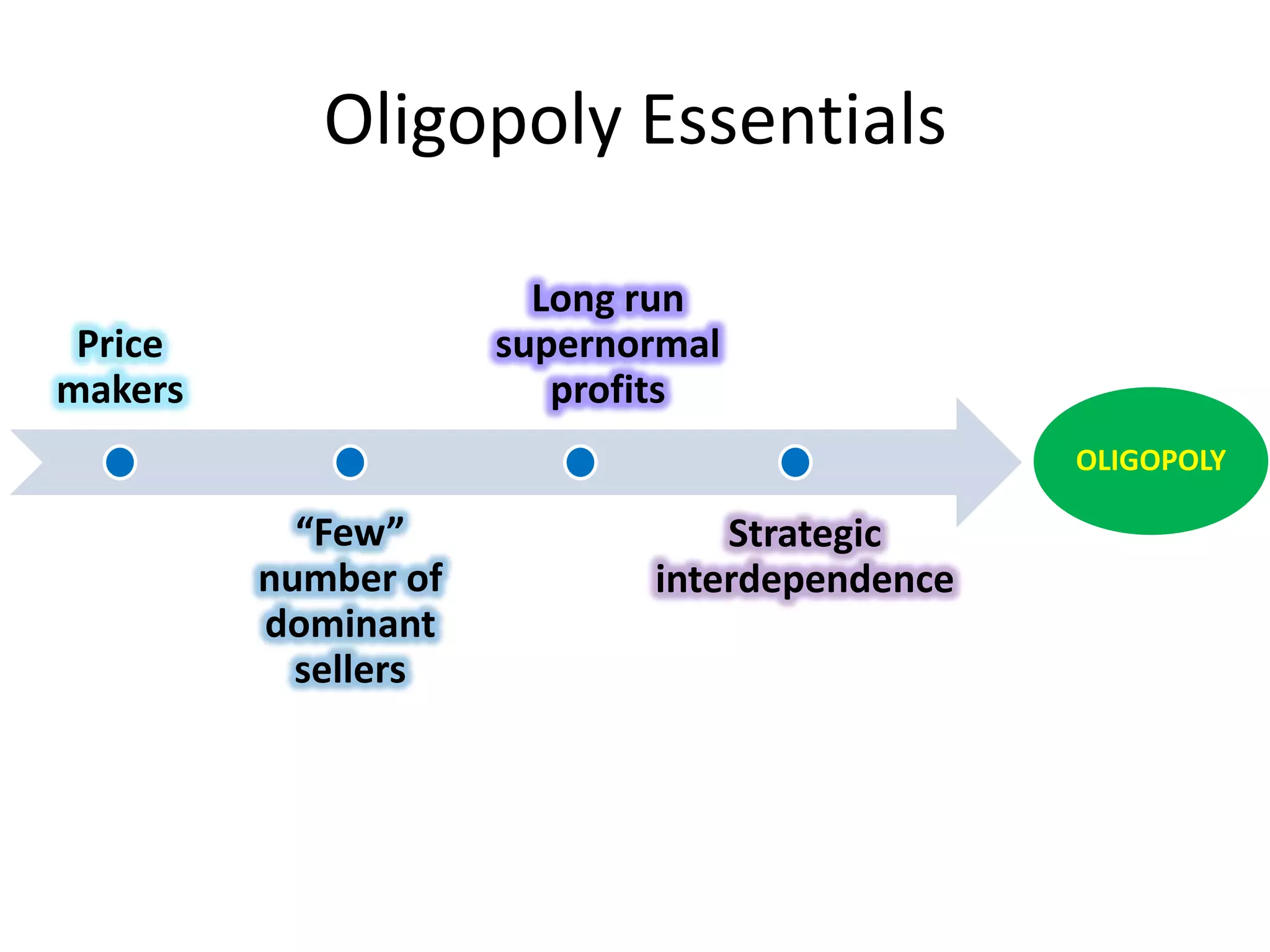
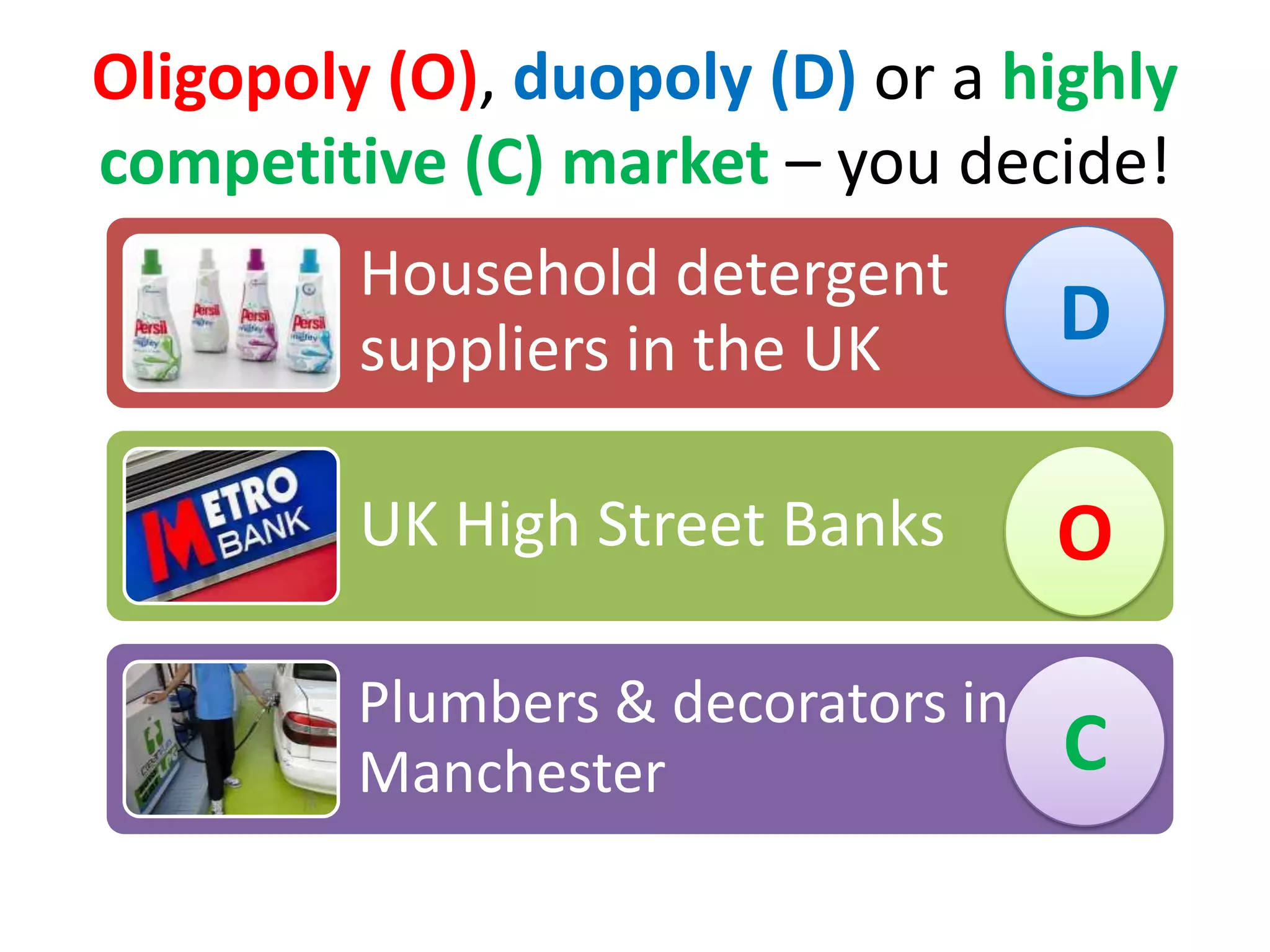
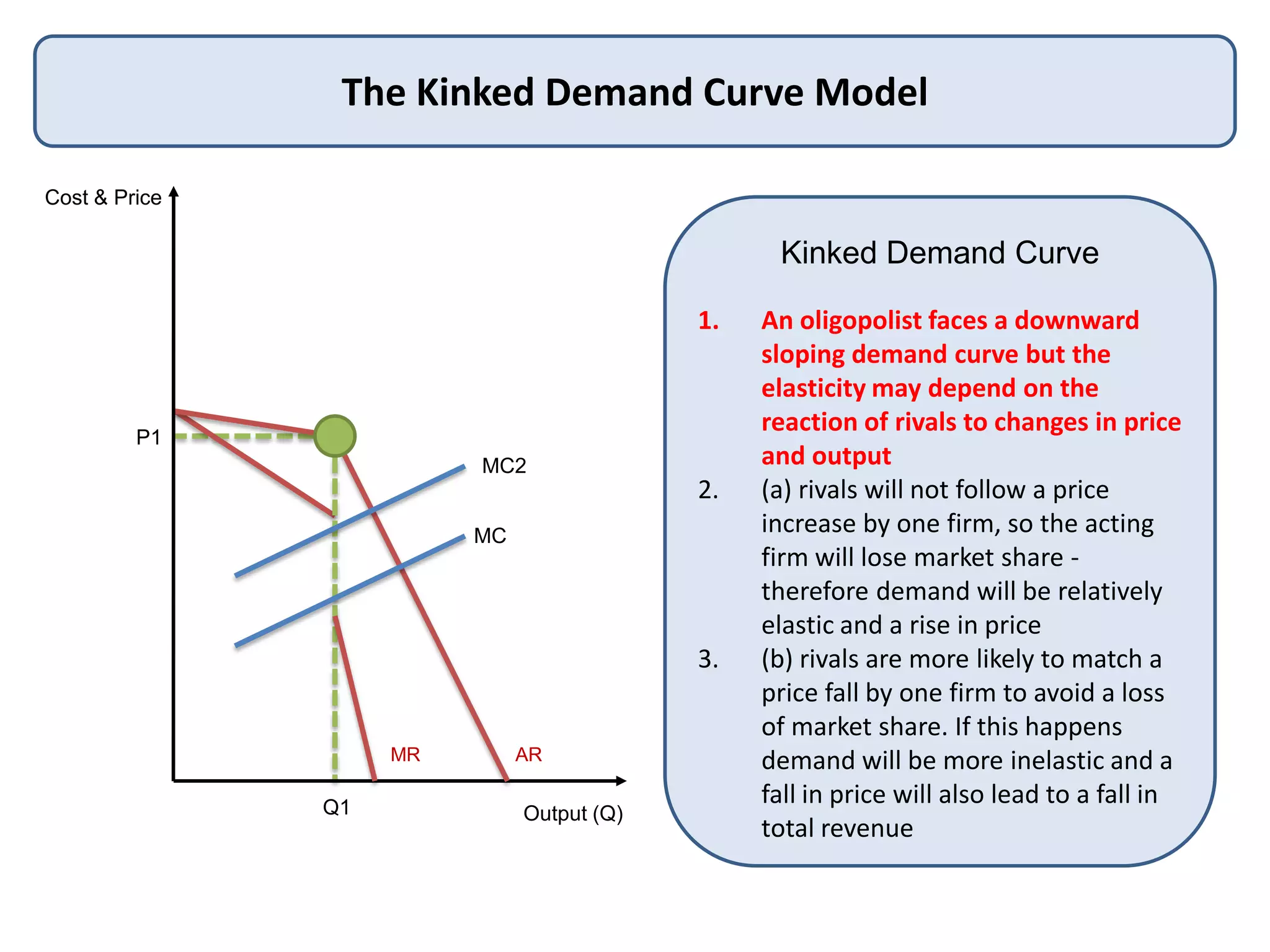
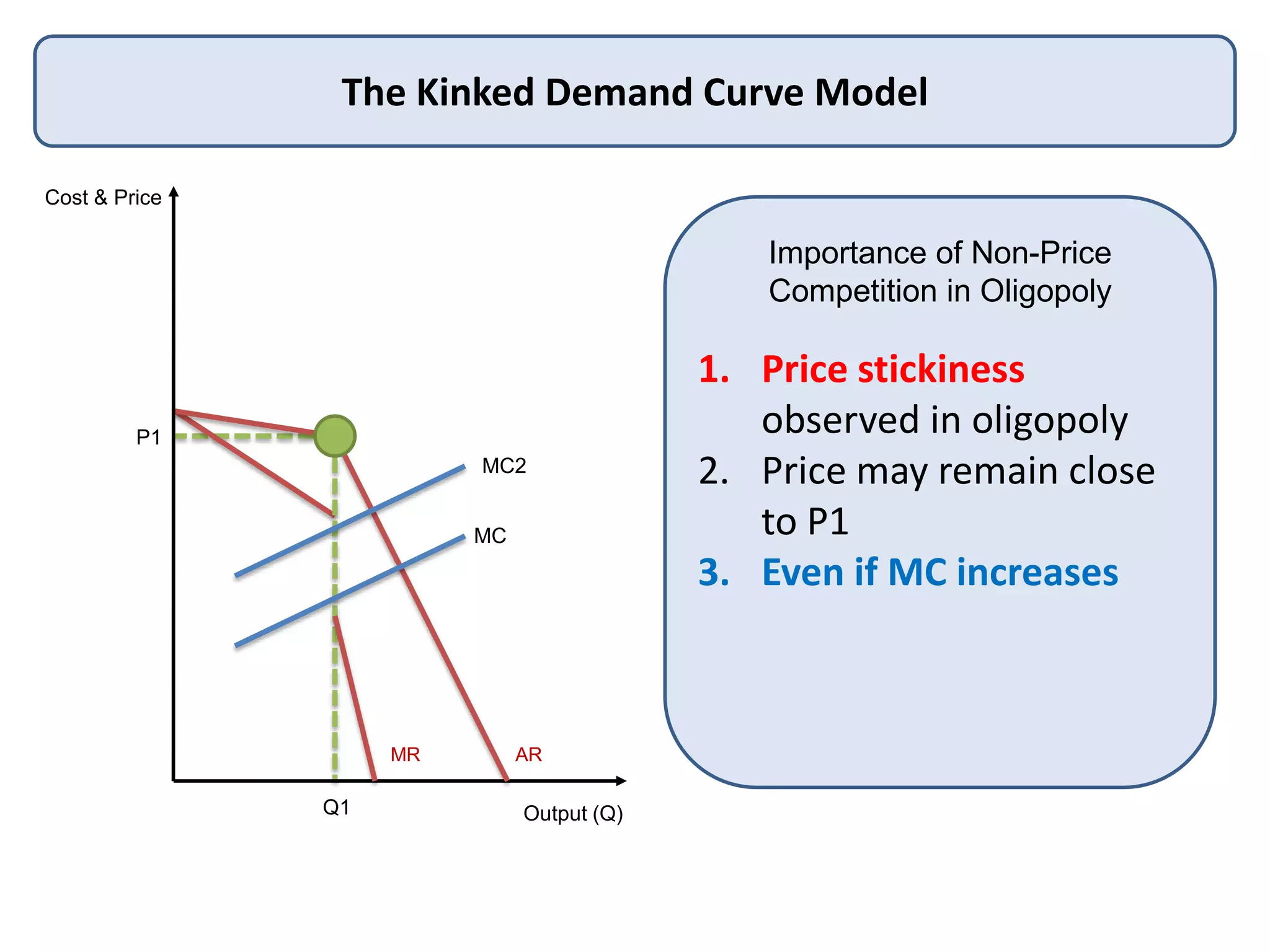
This document defines oligopoly and key aspects of oligopolistic markets. It notes that oligopoly is characterized by a high concentration ratio of the top firms controlling over 60% of the market, branded products, and significant barriers to entry that allow long-run supernormal profits. It emphasizes that in oligopoly, firms' decisions are interdependent and uncertain since each firm is aware of and influences its competitors. Non-price competition through factors like innovation, quality, and customer service is particularly important in oligopoly due to price stickiness near marginal cost.