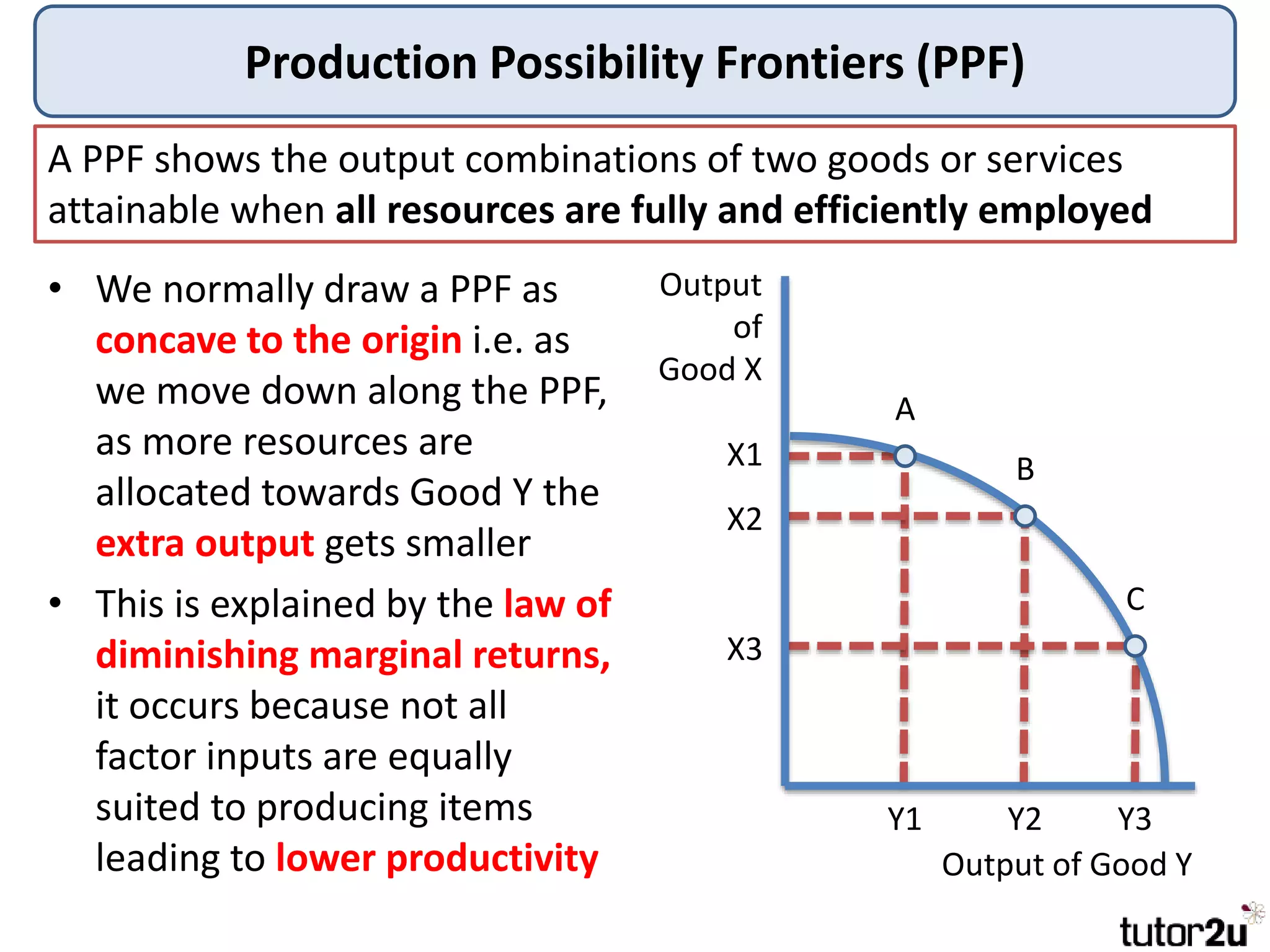
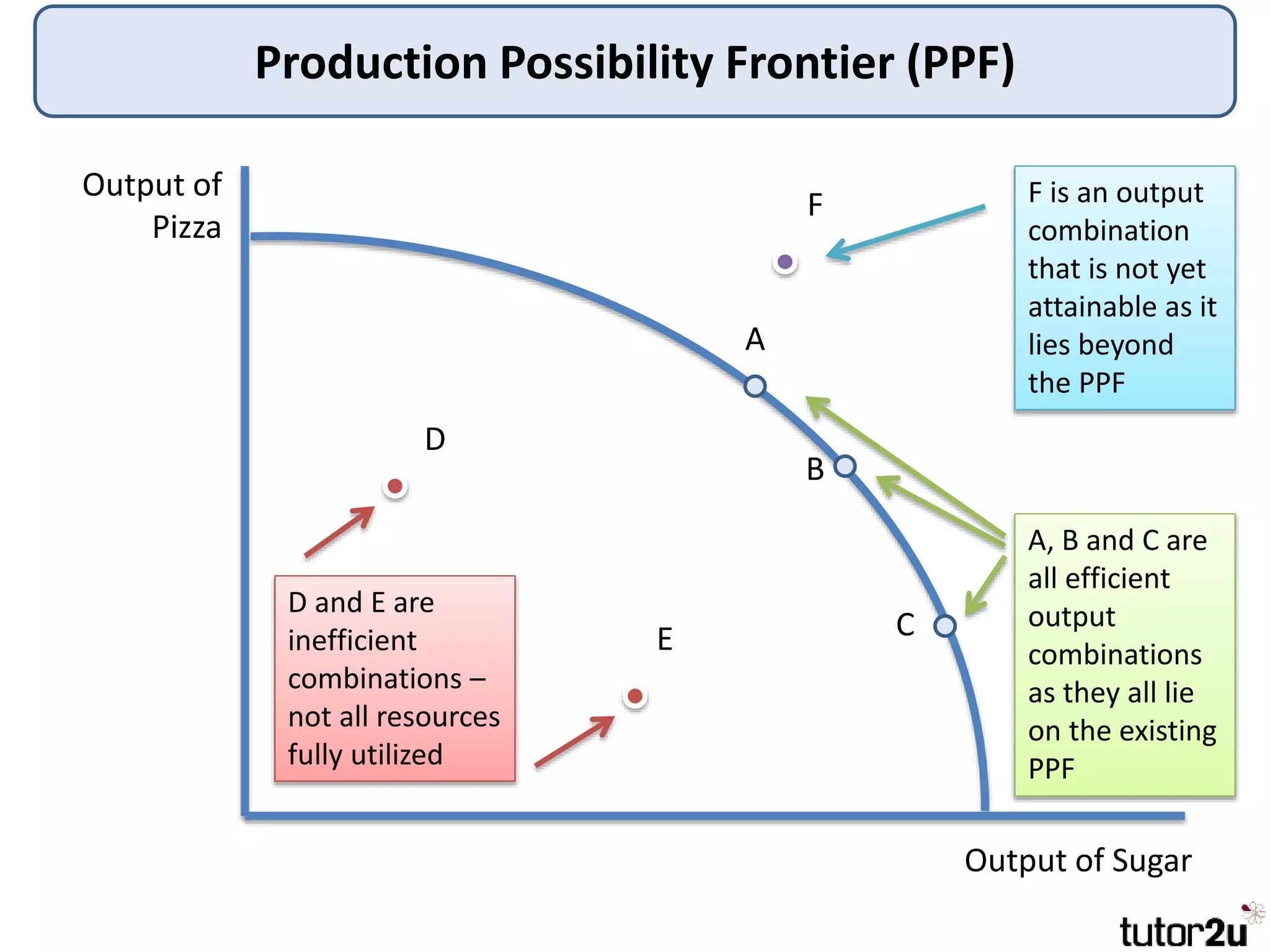
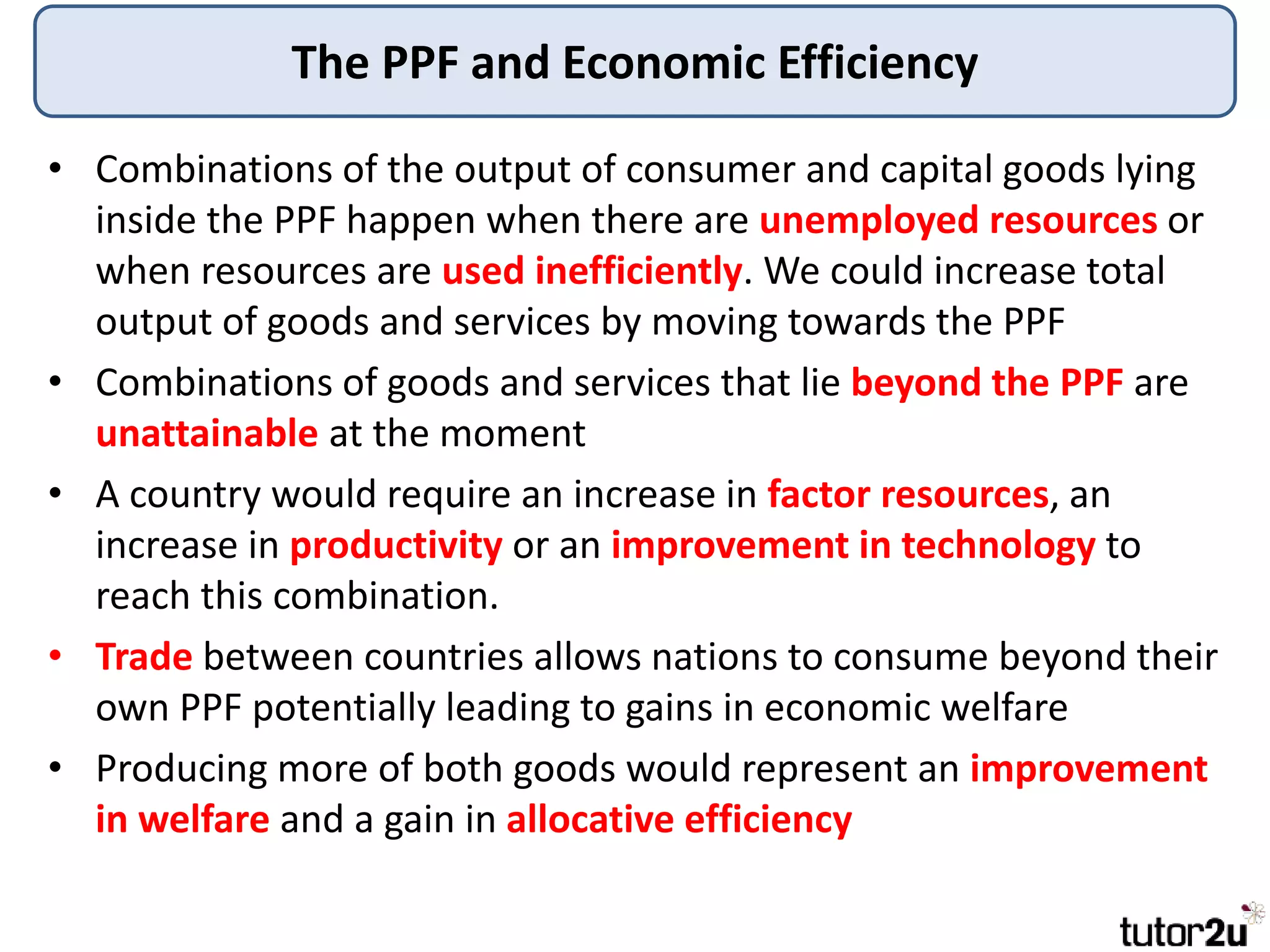
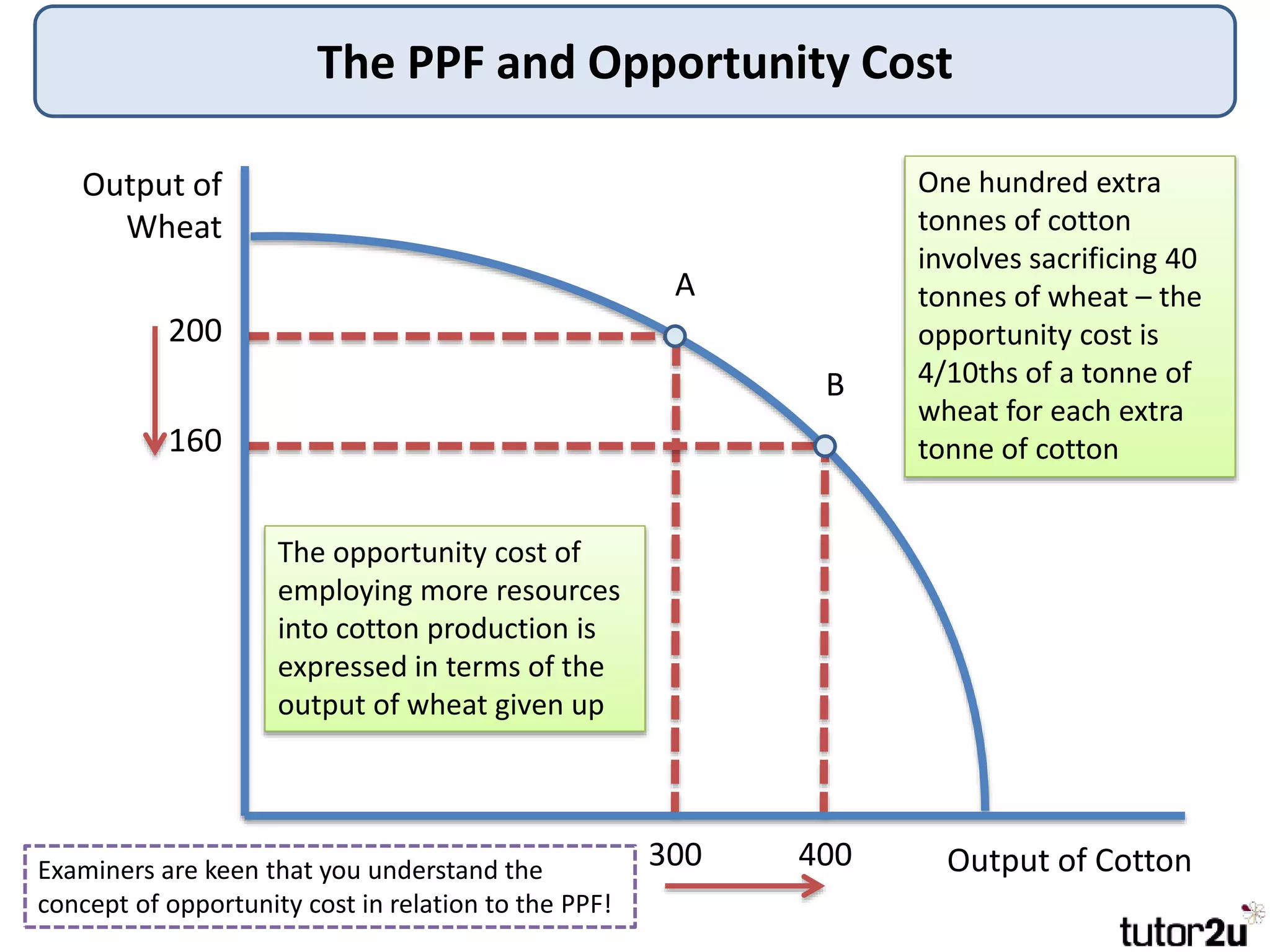
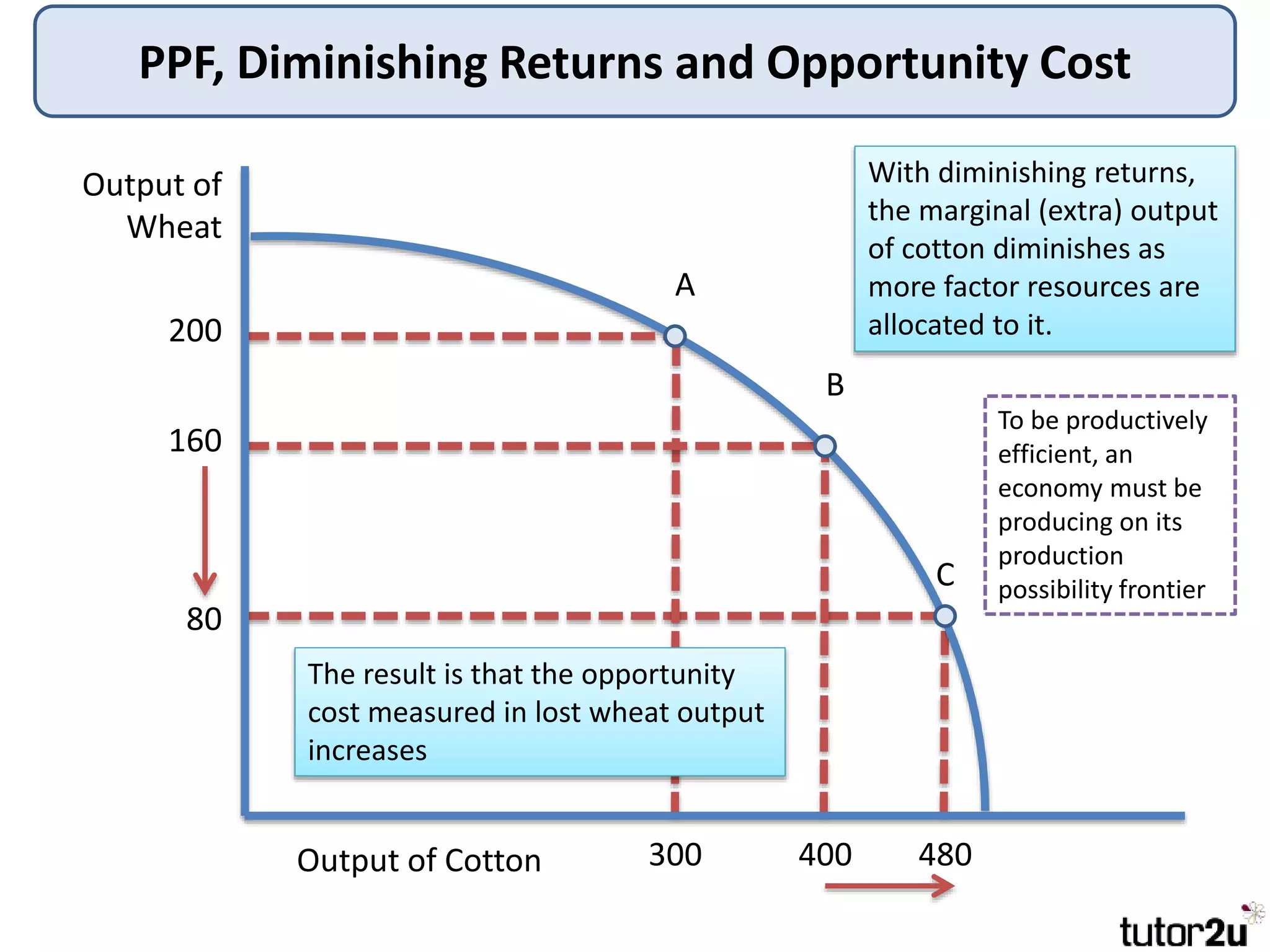
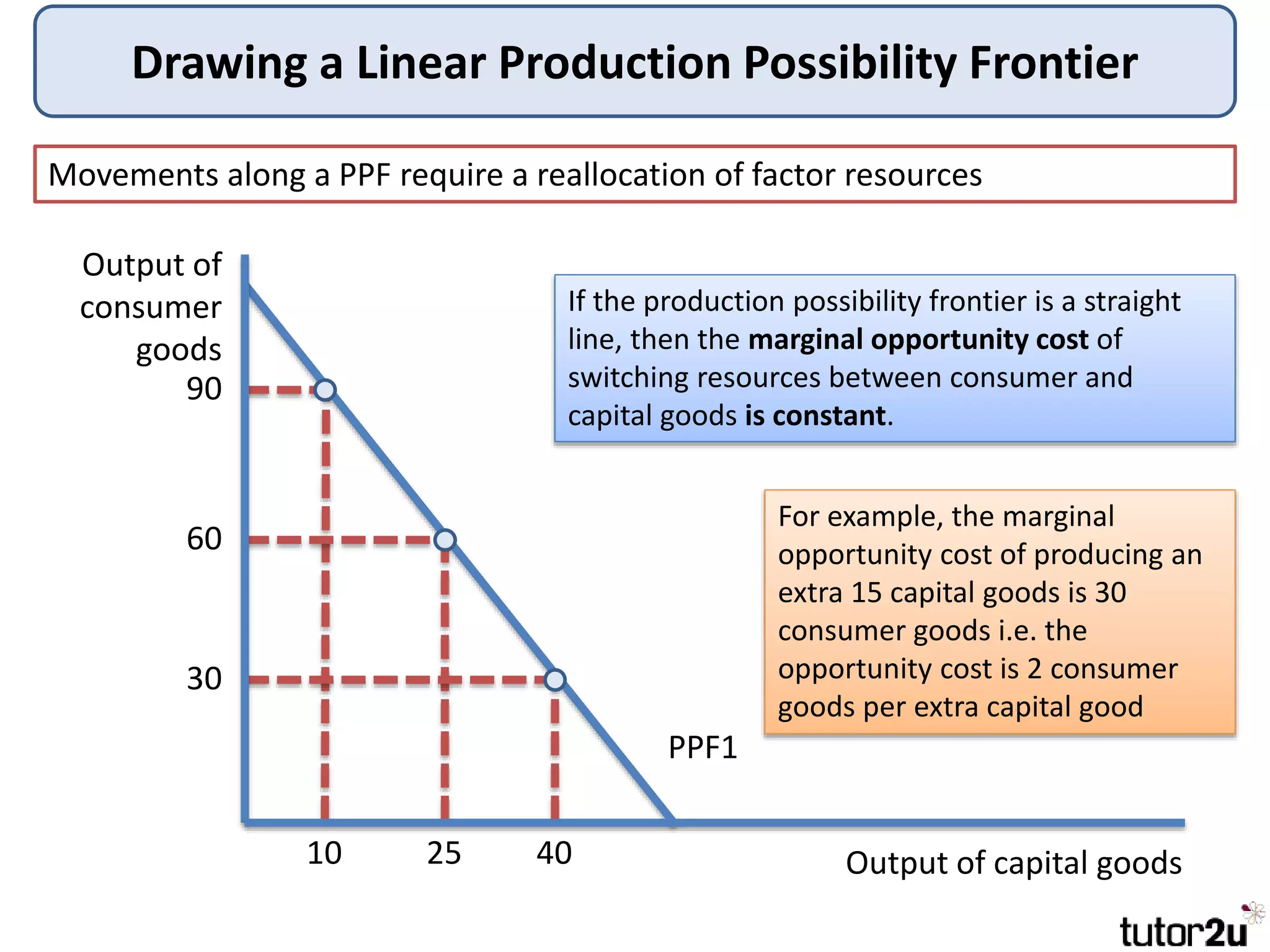
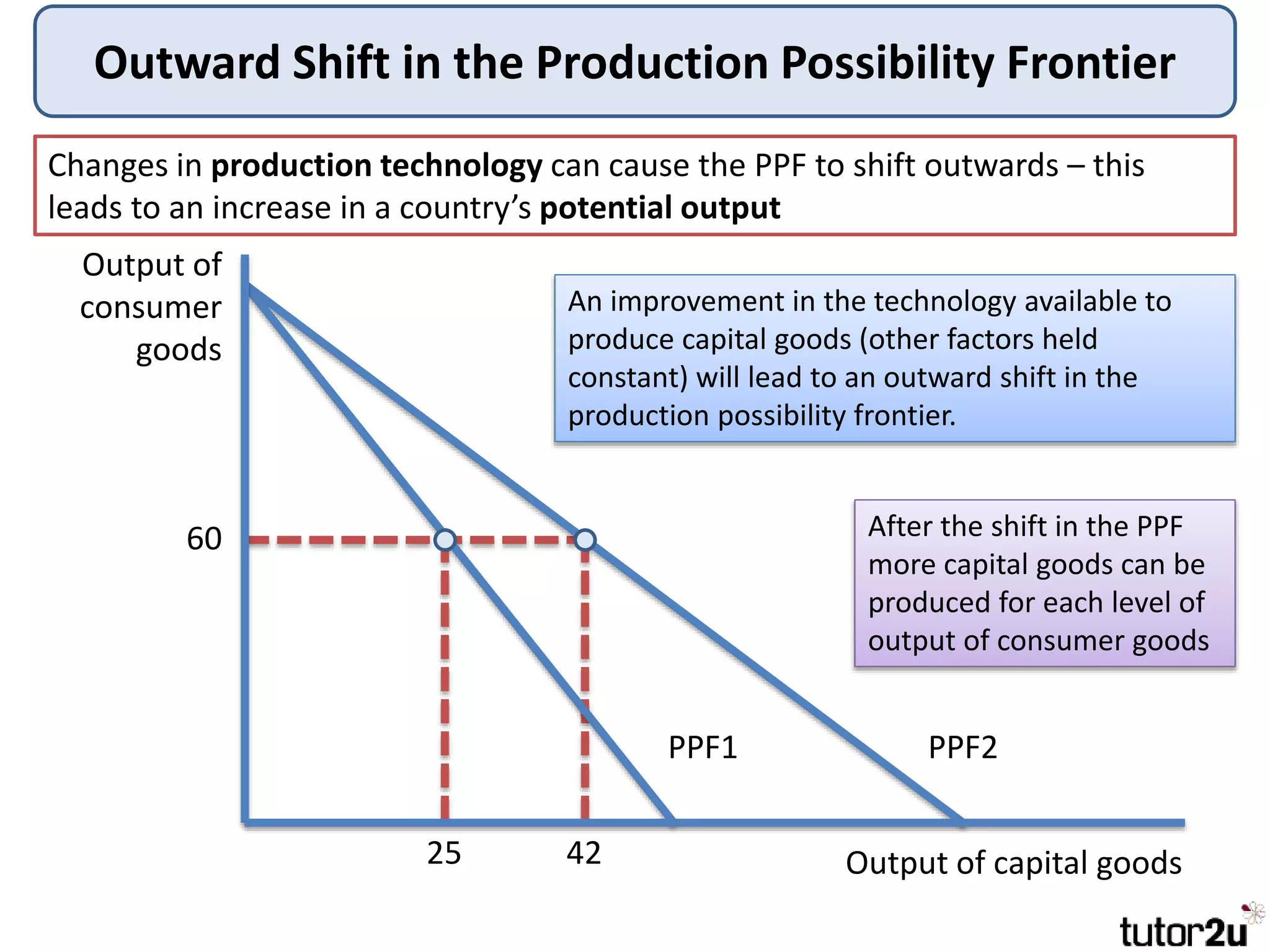
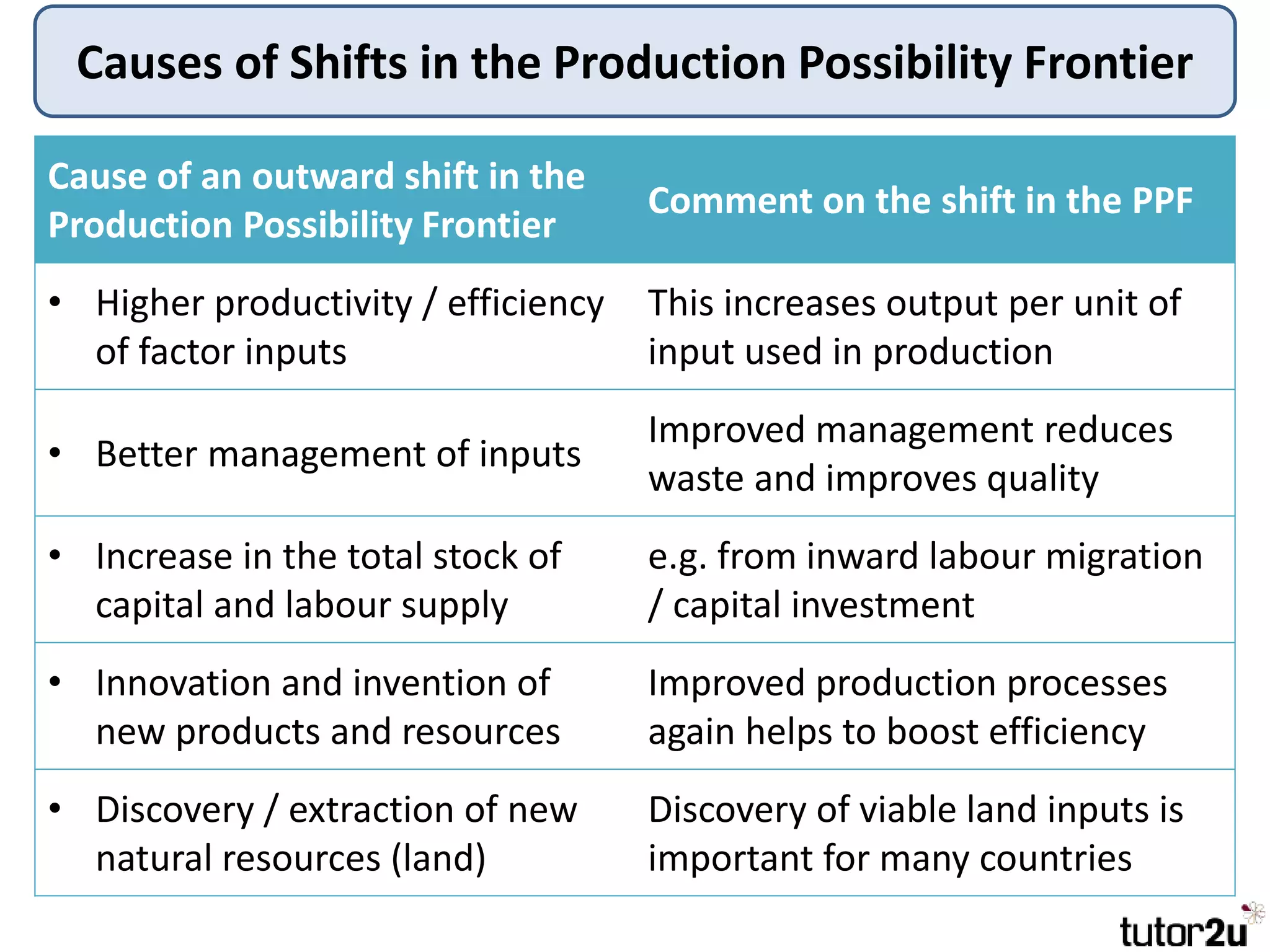
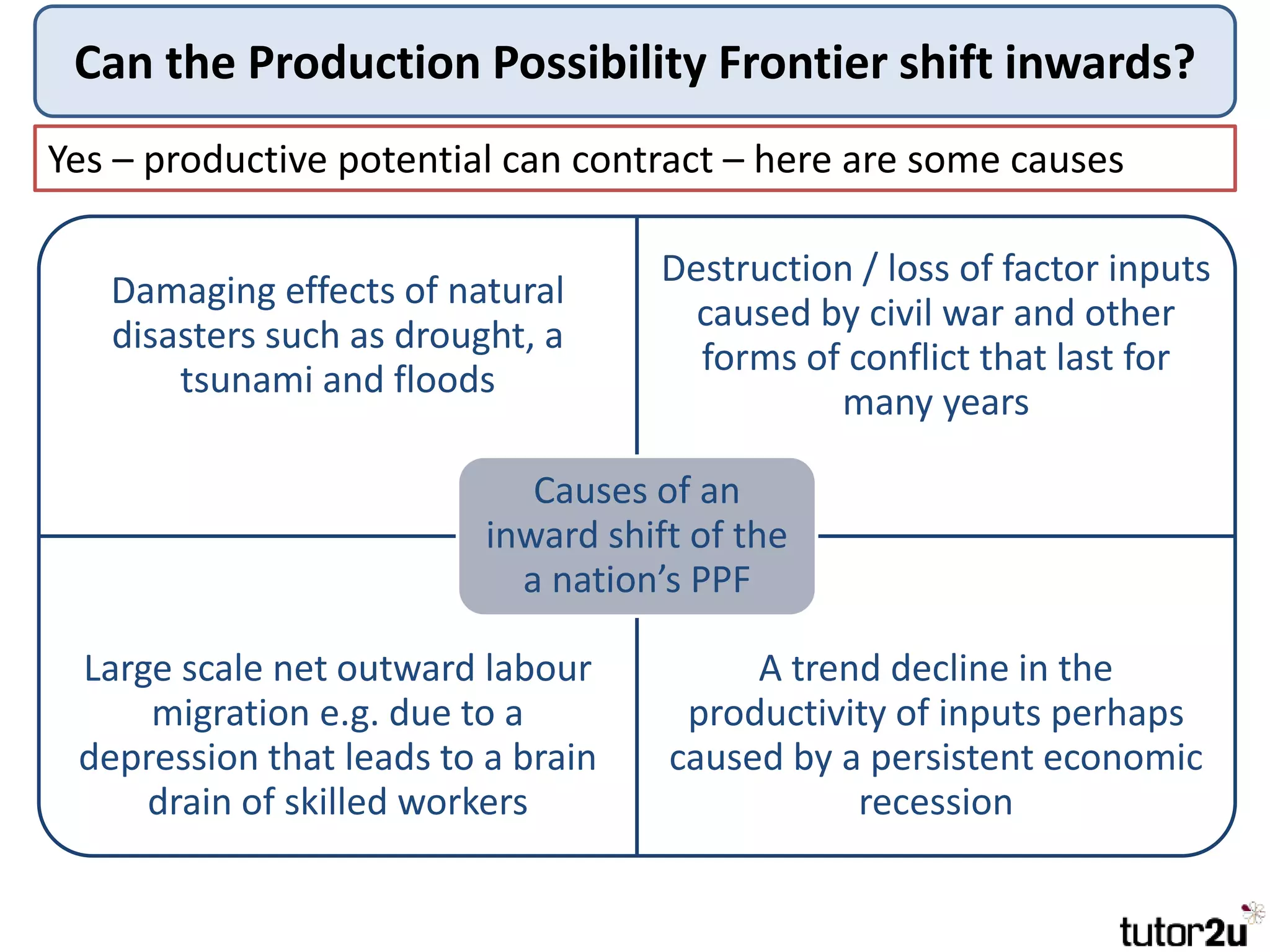
The document provides an overview of production possibility frontiers (PPF), highlighting how they illustrate efficient output combinations of two goods based on resource allocation. It explains concepts such as diminishing returns, opportunity cost, and factors that cause shifts in the PPF, including technological advancements and resource availability. Additionally, it discusses possible inward shifts in the PPF due to negative events like natural disasters or conflicts.