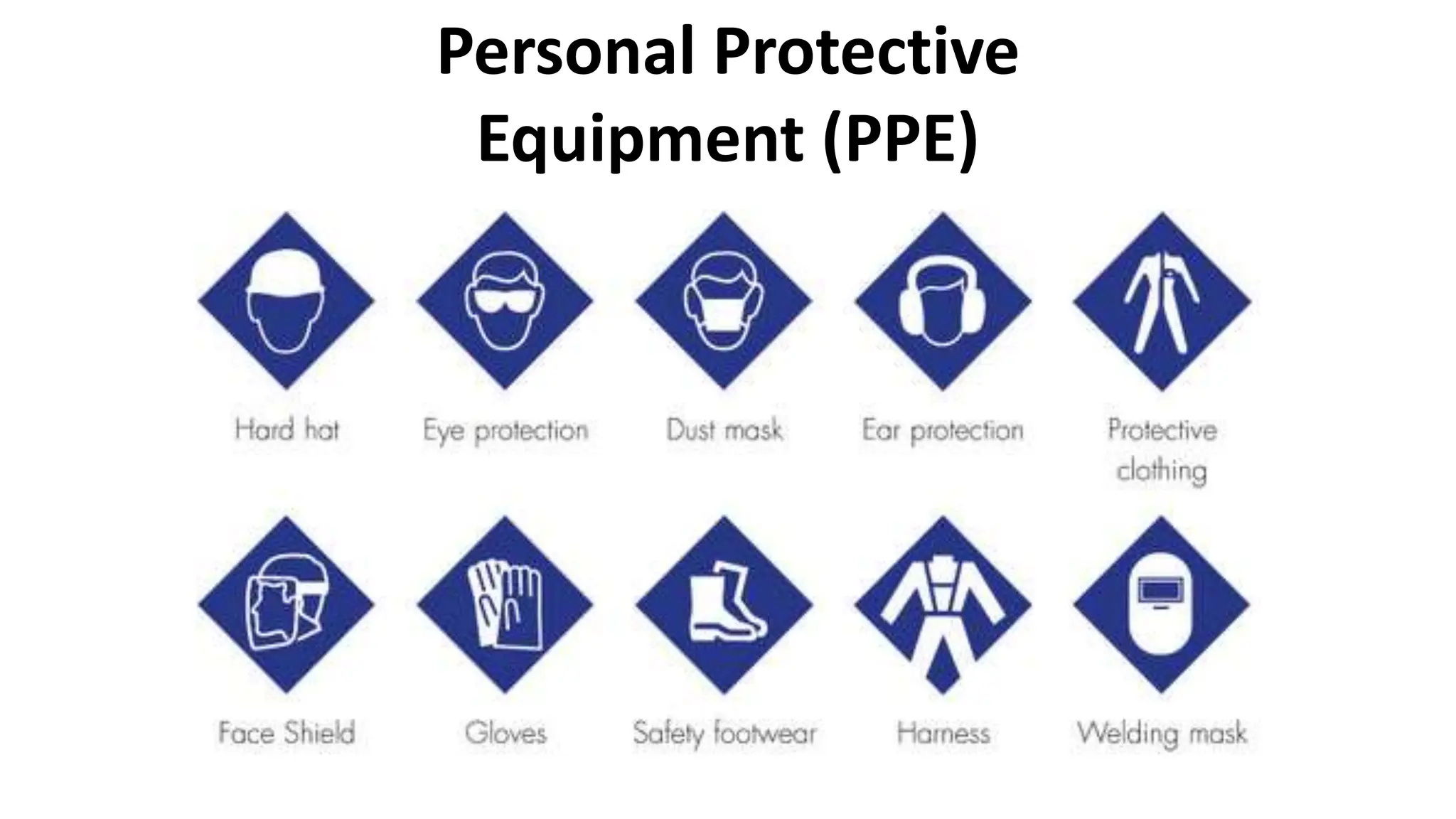
The document discusses occupational health and safety procedures, including identifying and evaluating hazards and risks in the workplace. The main objectives of the Occupational Safety and Health Center (OSHC) are to prevent work-related injuries, illnesses and deaths, effectively implement occupational health and safety programs to promote worker well-being, and establish training centers. Hazards are classified into dormant, armed, and active modes depending on whether the risk is potential or an incident has occurred. Common types of hazards include biological, chemical, mechanical, physical and ergonomic factors.