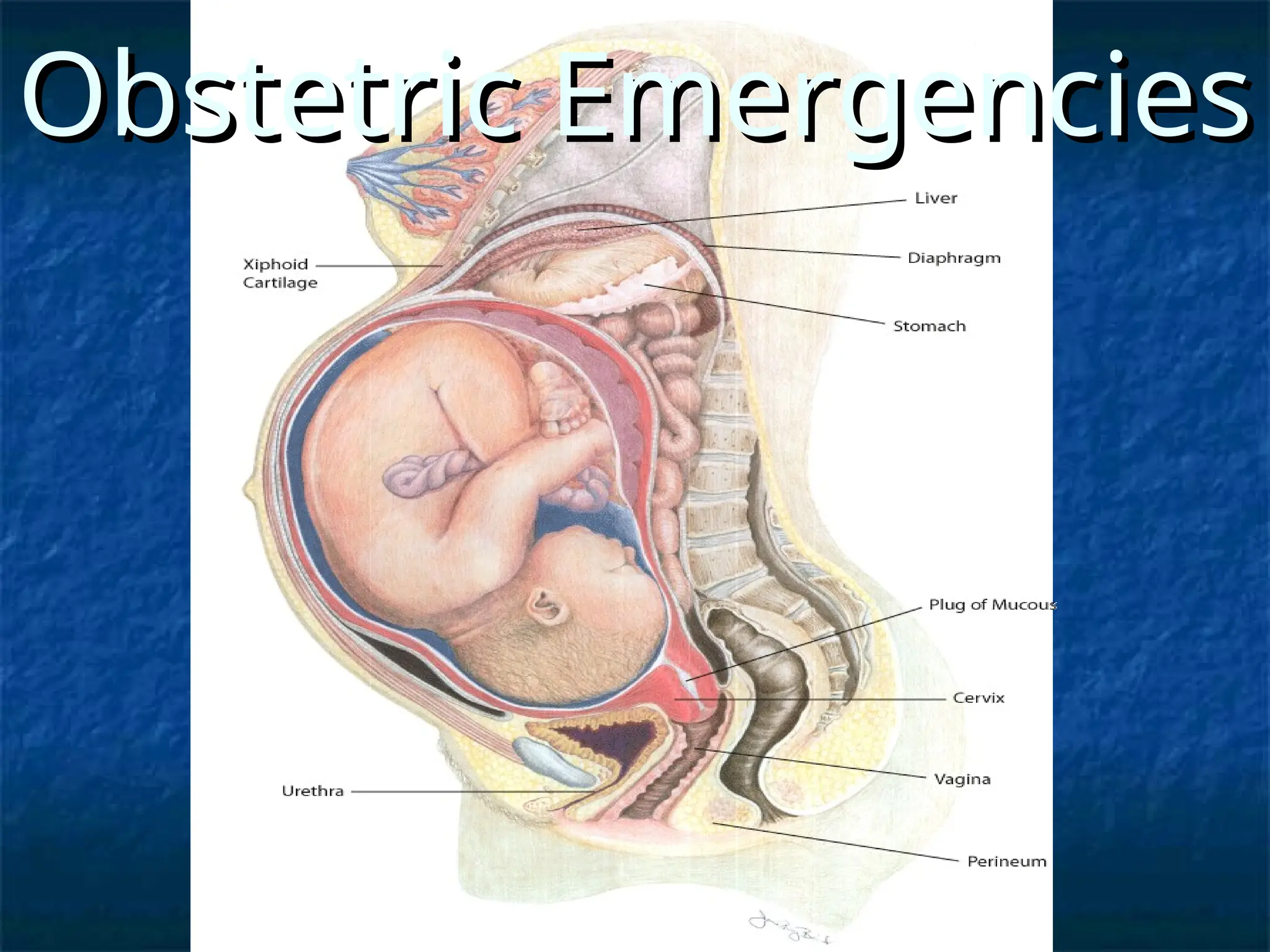
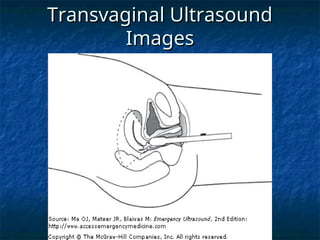
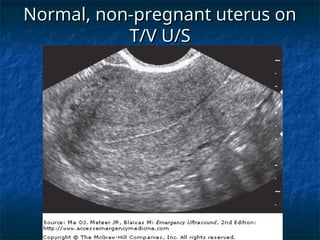
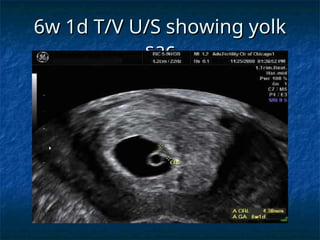
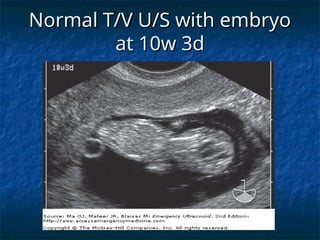
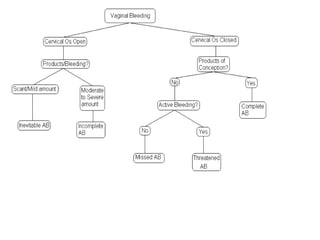
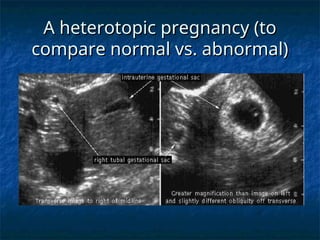
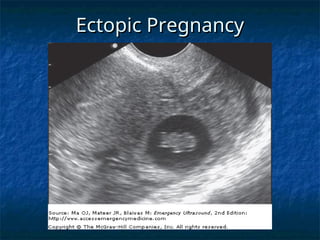
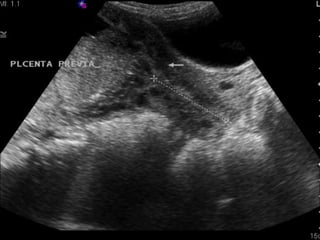
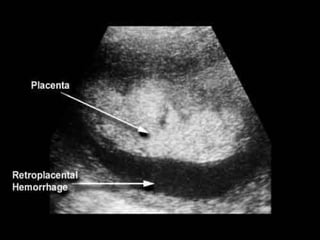
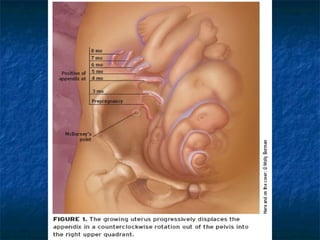
The document discusses obstetric emergencies, including normal pregnancy and common complications, such as ectopic pregnancies, bleeding during different trimesters, and hypertension. It outlines diagnostic tests, physiological changes during pregnancy, and management strategies for various scenarios, emphasizing the importance of timely intervention. Additionally, it covers drug safety in pregnancy and the implications of trauma, maintaining maternal health to ensure fetal survival.